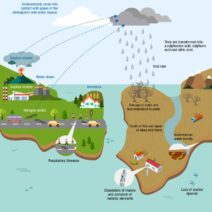
Water scarcity is becoming an alarming reality that engages environmental scientists, policymakers, and global citizens alike. The interplay between water scarcity and global warming is evolving, revealing a profound crisis that threatens ecosystems, economies, and human health. As the century progresses, it becomes imperative to understand the enormity of the challenge and engage with solutions that promise a more sustainable future.
The Current Landscape of Water Scarcity
Water scarcity affects more than 2 billion people worldwide; this deeply ingrained issue often arises from various factors including overconsumption, pollution, and inefficient agricultural practices. Ironically, while some regions grapple with a surplus of water, others face debilitating droughts. This disparity can be attributed to erratic weather patterns that are increasingly associated with climate change.
Global Warming: An Underlying Catalyst
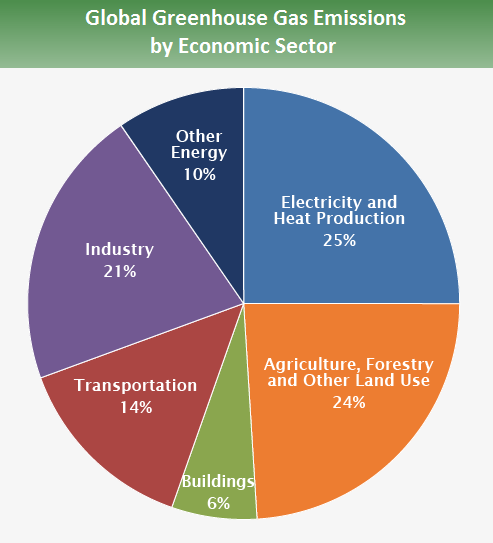
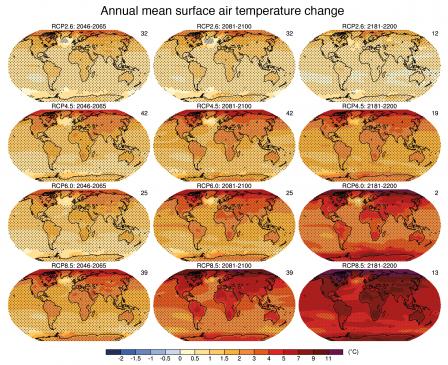
At the heart of this disparity lies global warming, a phenomenon primarily driven by human activities—namely, the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. As greenhouse gases accumulate in the atmosphere, they trap heat, leading to rising average global temperatures. The repercussions are multifold: glaciers are melting, sea levels are rising, and weather events are becoming more unpredictable and violent.
These changes translate into altered precipitation patterns. Some areas may experience torrential rainfall followed by prolonged periods of drought. This inconsistency profoundly impacts freshwater resources, making the management of these supplies progressively challenging. Freshwater is not merely a resource but a cornerstone of life, sustaining agriculture, industry, and personal well-being.
The Impacts of Water Scarcity
The ramifications of water scarcity extend well beyond the immediate inability to access clean drinking water. Agriculture, which employs a significant portion of the global workforce, is particularly vulnerable. Reduced water availability leads to crop failures, food shortages, and increased malnutrition rates. In developing countries, where agrarian economies dominate, the effects are often catastrophic, causing not just economic strain but also humanitarian crises.
Moreover, water scarcity has palpable social and geopolitical implications. Competition for dwindling water supplies may foster conflicts among communities, municipalities, and nations. The quest for water can lead to migratory patterns where individuals flee their native lands, magnifying the challenges related to displacement and urban overpopulation in refuge areas.
A Case Study: The Aral Sea
The distressing case of the Aral Sea, once one of the largest lakes in the world, serves as a stark reminder of the impacts of human activity on water resources. Political decisions in the Soviet era diverted rivers that fed the sea for agricultural purposes, leading to its near-total evaporation. The consequences were dire: local fisheries collapsed, regional climates altered, and communities crumbled. This ongoing environmental disaster emphasizes the peril of neglecting natural water systems.
Innovative Solutions to Water Scarcity
Despite the magnitude of the problem, innovative solutions are emerging. Technology plays a pivotal role in addressing water scarcity. Authorities and entrepreneurs are increasingly exploring advanced irrigation techniques that maximize water use efficiency in agriculture. Drones and satellite imagery can help monitor crop health and optimize water usage, ensuring that this precious resource is not squandered.
Additionally, the process of desalination—transforming seawater into potable water—offers a potential lifeline for arid regions. While currently energy-intensive and costly, technological advancements strive to make desalination a feasible solution for escalating freshwater demands.
The Importance of Water Conservation
Equally crucial is the mindset shift towards water conservation. Culture plays a significant role in how societies perceive and utilize water. Governments, corporations, and individuals need to foster a culture of mindfulness regarding water consumption. Educational campaigns can instill awareness of the value of water in everyday life, promoting behaviors that lead to its conservation.
The circular economy is another paradigm that holds promise for addressing water scarcity. By rethinking waste management and recycling water in industries and urban settings, communities can reduce the overall demand for freshwater. These strategies embrace sustainability, enhancing resilience against the threats posed by climate change.
Global Collaboration and Policy Frameworks
Addressing water scarcity in the context of global warming necessitates collaboration across borders. International treaties and agreements can establish frameworks for the fair distribution and management of shared water resources, mitigating potential conflicts. Organizations like the United Nations play an instrumental role in facilitating dialogues that bring together stakeholders from various sectors to combat water-related challenges globally.
By creating plum partnerships, governments, NGOs, and private sectors can pool resources and knowledge, allowing for the development of holistic approaches to water management. Collective action fosters shared responsibility, essential to ensuring that future generations possess the water resources they need.
Fostering a Resilient Future
The challenges posed by water scarcity and global warming are formidable but not insurmountable. Initiating a shift in perspective—viewing water not as an infinite resource but as a precious commodity—can catalyze transformative change. Engaging in dialogue, harnessing innovation, promoting conservation, and fostering collaboration are necessary steps toward achieving sustainable water management.
Ultimately, by addressing the intricate relationship between water scarcity and global warming, society can truly quench the thirst for a sustainable future, leaving behind a legacy of responsible stewardship that transcends generations. The urgency of the moment calls for a concerted effort; the future of billions hangs in the balance, awaiting action.