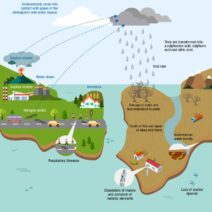
Climate change is a multifaceted phenomenon that encapsulates an array of alterations in global or regional climate patterns, predominantly stemming from human activities. This alteration typically manifests through deviations in temperature, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather anomalies. While climate change is a natural phenomenon that has occurred throughout the Earth’s history, the contemporary context is marked by unprecedented rates of change, primarily induced by anthropogenic actions. Understanding climate change extends beyond scientific explanations; it also necessitates an exploration of its implications, consequences, and the urgent call for action.
At its core, climate change is primarily driven by the accumulation of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in the Earth’s atmosphere. Carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) are the foremost contributors to this phenomenon. These gases trap heat from the sun, consequently leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect. The consequence is a gradual rise in average global temperatures, often referred to as global warming. This rise in temperatures is not just a headline statistic; it has profound implications on ecosystems, human health, and global economies.
One of the most pressing indicators of climate change is the increase in average sea levels, attributable primarily to the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, alongside the thermal expansion of seawater as it warms. Coastal regions, which house significant populations and economic activities, are at heightened risk. Cities like New Orleans, Miami, and Jakarta face perilously rising tides that threaten their very existence. The exigency of such risks requires immediate and concerted efforts to devise adaptive strategies, including the construction of resilient infrastructure and effective zoning regulations.
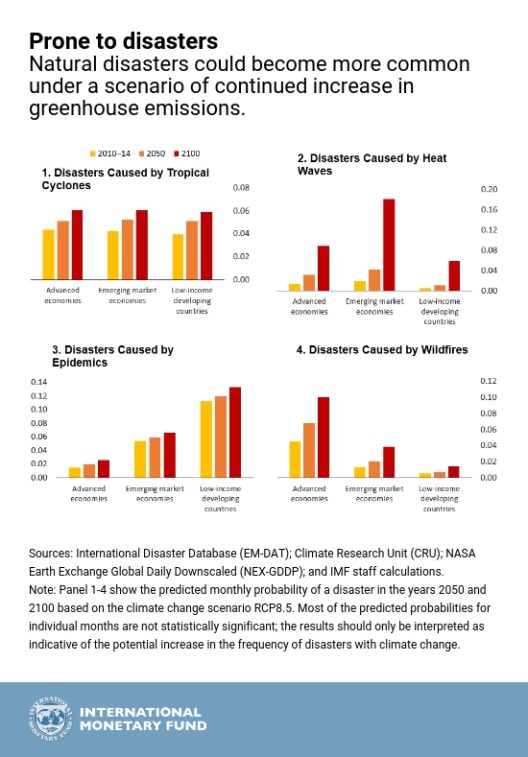
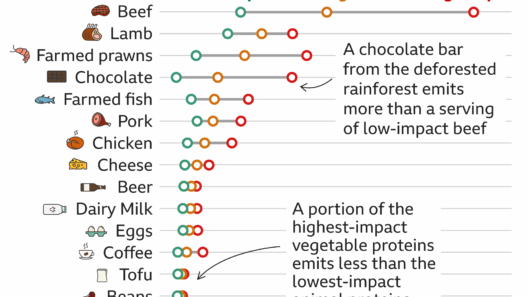
Furthermore, changing climatic conditions engender a cascade of extreme weather events. Hurricanes are becoming more formidable, droughts more protracted, and wildfires more frequent. The increasing intensity of these events not only poses a direct threat to human life but also wreaks havoc on agriculture, forestry, and water resources. The agricultural sector, which is intricately linked to climatic patterns, witnesses crop yields decline due to erratic weather, pest proliferation, and altered growing seasons. Consequently, food security is jeopardized, leading to socioeconomic ramifications that exacerbate existing inequalities.
In addition to immediate physical impacts, climate change also catalyzes sweeping changes in biodiversity. Many species, unable to adapt swiftly to the rapid shifts in climate, face extinction. Changes in temperature and habitat disrupt ecosystems, prompting alterations in the distribution of plants and animals. These ecological repercussions are alarming; they threaten not only individual species but also the intricate interdependencies that sustain entire ecosystems. Biodiversity loss can diminish resilience against environmental changes, thus perpetuating a vicious cycle of ecological decline.
The nexus between climate change and health cannot be overstated. The proliferation of vector-borne diseases, exacerbated by climate fluctuations, poses new challenges for public health systems. Regions formerly deemed inhospitable to diseases such as malaria and dengue fever are now experiencing outbreaks due to rising temperatures and shifting rainfall patterns. Additionally, extreme heat events can lead to heat-related illnesses, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions. Access to clean water and nutritious food is further compromised, presenting challenges that must be addressed at both local and global scales.
While the impacts of climate change are daunting, it is important to recognize the potential pathways towards mitigation and adaptation. The paradigm shift towards renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydropower, is paramount in reducing dependence on fossil fuels. Transitioning to a low-carbon economy is essential to curtail the influx of GHGs into the atmosphere. Policy frameworks aimed at incentivizing clean technologies and promoting energy efficiency can facilitate a smoother transition while simultaneously bolstering economic growth.
International cooperation is vital in addressing what is, fundamentally, a global issue. Agreements such as the Paris Accord aim to unite nations in the collective pursuit of lowering carbon emissions and fostering sustainable practices. The principle of common but differentiated responsibilities underscores that while all nations must contribute to the fight against climate change, those that have historically contributed the most to GHG emissions, typically developed nations, should lead the way in providing resources and technology to developing nations. This collaborative endeavor seeks to ensure that vulnerable populations are not left to bear the brunt of climate change.
Community engagement in climate action is equally essential. Grassroots movements and local organizations play a pivotal role in raising awareness and advocating for environmentally sustainable practices. Education and outreach can empower individuals to make informed choices, fostering a culture of sustainability that transcends geographical and socio-economic boundaries. Initiatives focused on urban greening, waste reduction, and conservation have shown that collective local actions can indeed contribute significantly to the overarching goal of climate mitigation.
In conclusion, climate change signifies not merely an environmental crisis but a profound moral challenge. The implications of inaction are dire. By comprehensively understanding what climate change entails, its causes, and its expansive impact, we can better appreciate the urgency of our collective responsibility. Fueled by scientific understanding and imbued with ethical rationale, the fight against climate change must be an inclusive and sustained global endeavor, for the well-being of our planet and future generations hinges on it.