The Mediterranean climate, characterized by its hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters, is lauded globally for its unique environmental features and its vital role in various ecosystems. This climatic zone is primarily situated along the Mediterranean Sea but extends to regions across five continents. Notably, its distinguishing characteristics sprawl across parts of California, central Chile, South Africa, and southwestern Australia. Understanding the intricacies of the Mediterranean climate requires an exploration of its defining features, ecological impact, socio-economic significance, and challenges in the face of climate change.
An emblematic characteristic of the Mediterranean climate is its temperature gradient. During the summer months, many areas experience temperatures that can soar above 30 degrees Celsius, making for long, sun-drenched days. Conversely, winters remain pleasantly mild, typically ranging from 5 to 15 degrees Celsius. This temperature variance creates a balance that supports a rich array of flora and fauna. The summers exhibit limited precipitation, often leading to arid conditions, whereas the cooler months incentivize precipitation, replenishing the region’s water reserves essential for both agriculture and natural ecosystems.
Flora adapted to this climate is notably diverse, with many species exhibiting unique adaptations to conserve water during the dry season. For instance, many plants display sclerophylly—thick, leathery leaves that minimize transpiration. Aromatic shrubs such as rosemary, thyme, and sage flourish, contributing to the region’s distinctive sensory landscape. Additionally, deciduous trees such as oaks and cork oaks are prevalent, imparting crucial carbon sequestration benefits. The flora, inextricably linked with the climate, creates habitats for diverse animal species, making the Mediterranean a biodiversity hotspot.
Alongside ecological value, the Mediterranean climate is a boon for agricultural endeavors. The region’s warm summers and wet winters provide optimal conditions for the cultivation of a myriad of crops, notably olives, grapes, and various fruits. Olive cultivation, for instance, is steeped in cultural heritage, with its oil being a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, recognized for its health benefits. Vineyards thrive under the robust conditions of this climate, yielding some of the most celebrated wines in the world, including those from regions like Tuscany in Italy and Bordeaux in France. The resilience of agriculture in Mediterranean climates supports local economies and sustains traditional practices, enhancing the socio-cultural fabric of these communities.
Tourism also thrives in Mediterranean climates, drawing visitors with their stunning landscapes, historical significance, and temperate conditions. Coastal regions feature beautiful beaches that attract tourists seeking respite during the hot summer months. Meanwhile, cultural sites steeped in history beckon those interested in the rich narratives of human civilization that flourished along the Mediterranean. The allure of the Mediterranean homes, vibrant markets, and culinary delights further elevate its status as a premier tourist destination. The economic implications of tourism cannot be overstated; it is a vital industry, creating jobs and providing income to local residents.
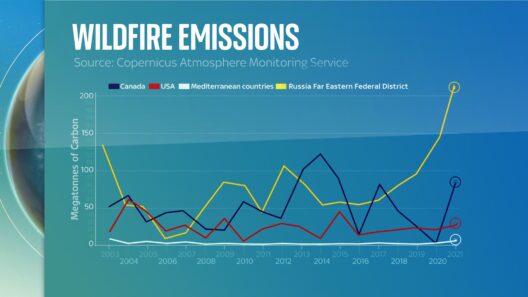
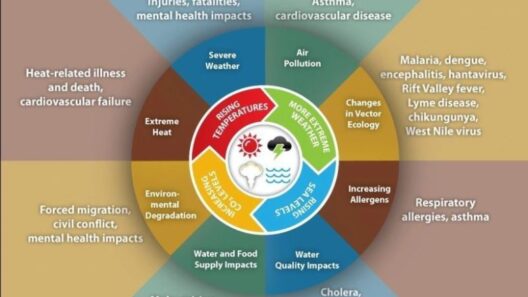
However, the benefits of the Mediterranean climate are not without challenges. Climate change looms as a significant threat, altering precipitation patterns and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events. Growing temperatures can exacerbate drought conditions, endangering water supplies and potential agricultural yields. Wildfires, too, have become a more prevalent threat during drier seasons, often devastating vast swathes of land and ecosystems. This volatility compels a need for adaptation and strategic action to mitigate adverse effects. Sustainable practices such as water conservation, reforestation, and responsible land management are paramount in preserving the integrity of the Mediterranean ecosystem.
As urbanization continues to proliferate in Mediterranean regions, the interplay between human activity and natural ecosystems mandates meticulous attention. Urban expansion can disrupt delicate ecological balances, displacing native flora and fauna, and leading to habitat degradation. Nonetheless, integrating green spaces within urban planning can not only enhance aesthetic value but also promote biodiversity. Furthermore, community-driven conservation initiatives encourage the preservation of natural areas amidst urban pressures, underscoring the critical role of public engagement in environmental stewardship.
The Mediterranean diet, which encapsulates the culinary traditions stemming from this climate, has garnered global recognition for its health benefits, fostering a holistic appreciation for the region. Rich in vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, it promotes longevity and well-being. The connection between the Mediterranean diet and the landscape from which it originates highlights a symbiotic relationship, one that encourages conscious consumption and sustainability practices. This diet not only emphasizes the importance of local sourcing but also champions the utilization of seasonal produce, further amplifying a sense of community and environmental responsibility.
In conclusion, the Mediterranean climate is a global favorite for myriad reasons, encompassing its distinctive climatic conditions, ecological richness, and cultural significance. From the thriving biodiversity supported by its unique flora and fauna to the agricultural prowess and cultural heritage visible in the Mediterranean diet, this climatic zone offers a multifaceted perspective on nature’s wonders. Nevertheless, as challenges mount in the form of climate change and urbanization, proactive measures are essential to safeguard this cherished environment. Adopting sustainable practices and fostering community involvement are vital steps in preserving the Mediterranean climate’s legacy for generations to come. Understanding its complexities ensures a more profound appreciation of this irreplaceable environment, enhancing the global dialogue on climate adaptability and ecological conservation.