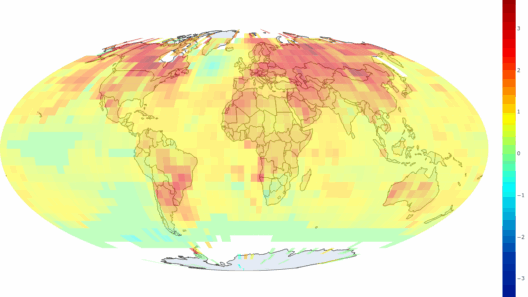
Climate is not merely the average of weather conditions but rather a complex interplay of various factors that collectively shape the environment we inhabit. Understanding the main factors that influence climate can lead to a profound shift in perspective, prompting a reevaluation of our relationship with the planet. By dissecting these elements, we can better appreciate their interconnections and the dire consequences of neglecting them.
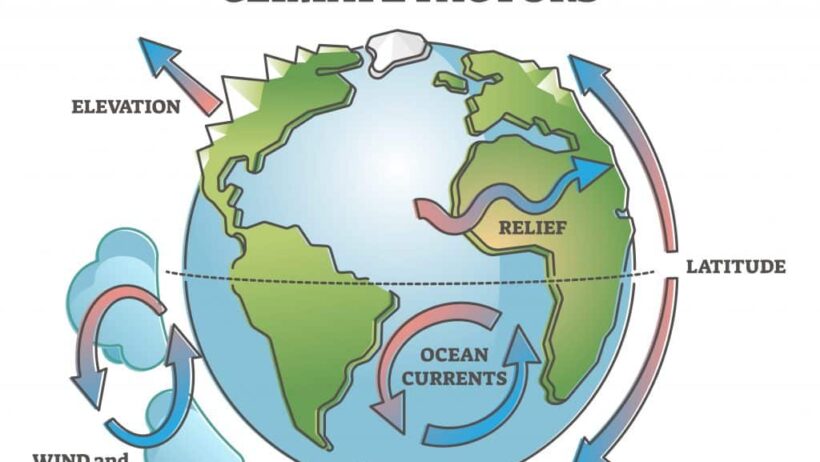
One of the most significant determinants of climate is the Earth’s geographical positioning. Latitudinal gradients play a pivotal role; areas near the equator typically experience warmer temperatures due to the direct angle of solar radiation throughout the year. In contrast, polar regions remain frigid as they receive sunlight at oblique angles. This fundamental aspect of climate provides an intriguing basis for understanding seasonal changes and regional variances.
Moving beyond latitude, we must consider the effects of altitude, or elevation above sea level. This vertical dimension significantly influences temperature and atmospheric pressure. As elevation increases, temperatures typically decrease, resulting in cooler climatic conditions in mountainous regions compared to surrounding lowlands. The famous adage, “the higher you go, the colder it gets,” succinctly encapsulates this phenomenon. Nevertheless, the environmental adaptations of flora and fauna in such regions showcase nature’s remarkable resilience and ability to thrive despite harsh conditions.
In addition to geographical factors, ocean currents serve as critical regulators of climate. The vast oceans, comprising over 70% of the Earth’s surface, assist in redistributing solar energy through currents that flow across global expanses. For instance, warm currents such as the Gulf Stream transport heat from the tropics to the North Atlantic, elevating temperatures in regions like Western Europe. Conversely, cold currents can lead to cooler climates in coastal areas. This dynamic interaction between oceanic and atmospheric systems holds profound implications for weather patterns and can even influence phenomena such as El Niño and La Niña, reinforcing the necessity of ocean currents in our climate comprehension.
Solar radiation itself, the source of warmth for our planet, is another inherent factor affecting climate. Variations in the sun’s output, influenced by solar cycles, can induce subtle changes in climate over prolonged periods. The Milankovitch cycles, which refer to the Earth’s orbital changes, also play a crucial role in determining climatic trends over millennia. These long-term fluctuations significantly influenced the Earth’s glacial and interglacial periods, showing that even minute variations can elicit transformative shifts in global climates.
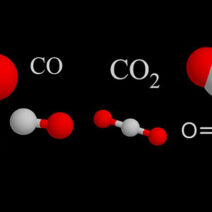
The atmosphere, as a protective blanket enveloping the Earth, is fundamental to climate regulation. Composed of various gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrogen, the atmospheric composition significantly impacts temperature and weather patterns. Greenhouse gases, in particular, are vital as they trap heat, allowing the planet to maintain its temperature. While this is essential for sustaining life, an excess of greenhouse gases due to anthropogenic activities has hastened global warming, leading us down a perilous path of climate change. The question arises: how can society mitigate these emissions to restore balance to our atmosphere?
Further complicating our climatic tapestry are biogeographic factors. Ecosystems, particularly forests, oceans, and wetlands, play a crucial role in regulating climate. They act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide and helping to stabilize atmospheric composition. Deforestation, urbanization, and land degradation release stored carbon, exacerbating the greenhouse effect. Additionally, biodiversity loss challenges resilience in the face of climatic shifts, raising urgent concerns about sustainability and the preservation of our planet’s ecological fabric. How do we promote ecological stewardship in our communities?
Human activities, undoubtably, have emerged as major players influencing climate. Urbanization, industrialization, and agriculture are significant sources of pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. The burning of fossil fuels for energy, coupled with unsustainable agricultural practices, have intensified climate change. As the global population continues to burgeon, the demand for resources grows, further straining our planet’s climate equilibrium. This reality forces us to confront a pressing moral imperative: can we transform our societal structures to foster sustainable living and mitigate climate impacts?
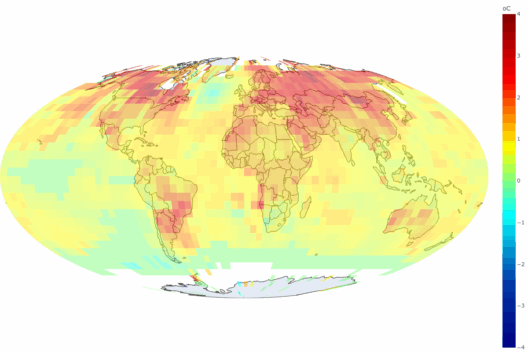
While natural factors set the stage for climate variability, human-induced alterations have curtailed the planet’s ability to adapt. The rising frequency of extreme weather events, prolonged droughts, and increasing sea levels disrupt ecosystems and pose existential threats to many communities. Climate change knows no borders; its ramifications are felt globally, serving as a solemn reminder that our actions have far-reaching consequences. The notion of climate justice emerges — one that advocates for equitable treatment of all communities, particularly those most affected by climate impacts and those least responsible for causing them.
As we ponder these myriad factors, it becomes clear that the intricate web of climate influencers cannot be untangled without realizing our interconnectedness with the environment. Each element, from geography to human actions, operates synergistically within the global climate system, demanding a concerted effort toward holistic understanding and action. This discourse invites society to reclaim stewardship over the planet, recognizing the profound responsibility we bear in shaping its fate.
The exploration of climate influences reveals a paradox: while we face colossal challenges, we also possess the power to effect change. Advocating for sustainable practices, embracing renewable energy, and fostering environmental awareness can forge pathways toward climate resilience. By rethinking our role within the natural world and prioritizing ecological preservation, we can redefine our future. It is time to transcend ignorance and embrace curiosity, for only by understanding the factors that influence climate can we actively contribute to a healthier, more sustainable planet.