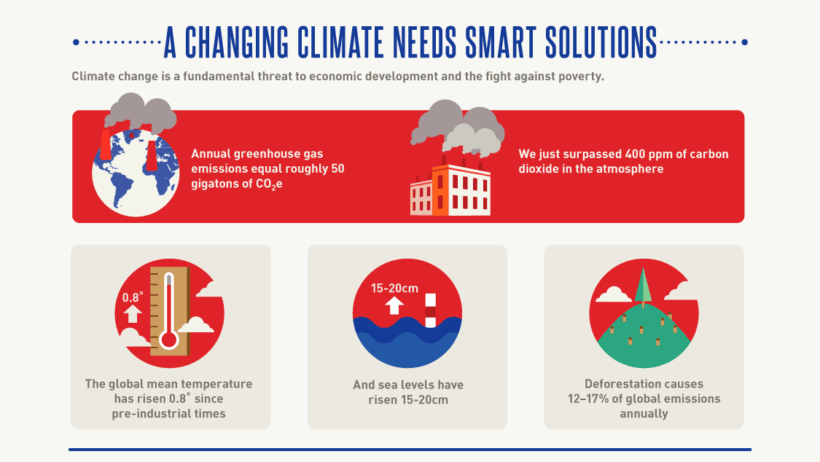
Climate change, an existential crisis of our era, demands urgent attention. The proliferation of scholarly discourse surrounding potential remedies warrants a closer examination of the most promising solutions. As the adverse impacts of global warming continue to manifest—arising in the form of extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and biodiversity loss—our preoccupation with viable innovations becomes a clarion call for action. While skeptics may argue about the feasibility of these solutions, it is imperative to explore their potential to engender transformative change.
One of the most compelling solutions advanced within contemporary environmental discourse centers around the concept of carbon capture and storage (CCS). This technology has emerged as a beacon of hope, enabling the extraction of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. By sequestering this greenhouse gas underground, CCS offers a dual advantage: it mitigates the effects of ongoing emissions while allowing existing fossil fuel infrastructure to remain operational, albeit in a more sustainable manner. Critics often cite high costs and technological limitations, yet advancements in engineering continue to demonstrate that the initial barriers to implementation are surmountable. Moreover, investing in CCS can catalyze job creation within the energy sector, thereby transforming economic landscapes while addressing climate concerns.
Equally worthy of consideration is the burgeoning field of renewable energy. Photovoltaic cells and wind turbines have started to dominate the discourse surrounding sustainable energy production. Transitioning from fossil fuels to these renewable resources is not merely a mere ecological endeavor; it represents a seismic shift in economic and social paradigms. The urgency inherent in such a transition lies in the reality that renewable energy sources are inexhaustible. Nations across the globe, from Germany to China, are embracing this evolution, which is propelled by technological advancements and decreasing costs. However, a comprehensive commitment to infrastructure development is paramount. Roadblocks, including policy inertia and institutional resistance, must be dismantled for the benefits of renewable energy to be fully realized.
Regenerative agriculture is another exhilarating prospect that warrants attention. Adopting agricultural techniques that prioritize soil health not only enhances food security but also acts as a formidable carbon sink. Practices such as agroforestry, cover cropping, and rotational grazing serve to enrich the earth while simultaneously sequestering atmospheric carbon. The burgeoning interest in organic farming is emblematic of wider societal shifts toward acknowledging stewardship of the land. This movement, while commendable, demands a concerted effort to educate farmers, incentivize sustainable practices, and reform agricultural policies that currently dismiss regenerative approaches. The marriage of ecology and agriculture is no longer an aspiration; it is a necessity.
The intersection of technology and biology introduces another promising strategy: biotechnology. Genetic engineering enables the development of crop varieties that are more resistant to climatic stressors. By enhancing drought tolerance and improving the efficiency of water usage, these innovations hold the potential to radically reshape agricultural yields in increasingly volatile climates. Nevertheless, ethical concerns surrounding genetic modification must be rigorously debated. The balance between innovation and safety should not obscure the promise of biotechnology to safeguard food supplies amid a changing climate.
Additionally, urban planning and sustainable cities present a multifaceted approach to addressing climate change. As the global population continues to surge and urbanization accelerates, cities must evolve into resilient ecosystems. Emphasizing public transportation, green spaces, and energy-efficient buildings can facilitate the reduction of urban carbon footprints. This transformation is underpinned by the necessity for progressive political will and community engagement. Local and national governments must prioritize urban policies that advocate for sustainable development while fostering inclusivity and equity.
Legislation, too, cannot be overlooked as a critical component in the climate action narrative. Global governance frameworks, such as the Paris Agreement, have facilitated international cooperation, yet their effectiveness hinges on national accountability. Policymakers must transcend partisan divides to enact robust climate legislation that encompasses regulations on emissions, subsidies for renewable technologies, and carbon pricing mechanisms. By galvanizing political will towards proactive legislation, society can leverage regulatory frameworks to catalyze broader behavioral shifts within industries.
Finally, the power of individual action and grassroots movements should not be underestimated. From local clean-up initiatives to global climate strikes, the collective voices of concerned citizens are reshaping societal norms regarding environmental responsibility. This grassroots momentum can influence policy changes and instigate corporate shifts toward greener practices. Each individual acting with purpose contributes to a larger tapestry of change, demonstrating that substantive action can originate from the ground up.
In conclusion, while climate change presents formidable challenges, the array of solutions available offers a myriad of possibilities. Carbon capture, renewable energy, regenerative agriculture, biotechnology, sustainable urban development, rigorous legislation, and grassroots activism together form a cohesive strategy to combat this pressing dilemma. Each solution, with its intricacies and logistical considerations, underscores the imperative for interdisciplinary collaboration. The pathway to a sustainable future is not linear; it is a dynamic interplay of technological advancements, cultural shifts, and policy formulations. As we navigate this complexity, the stakes are undeniably high—the health of our planet and the well-being of future generations hinge upon our ability to embrace and implement these critical solutions.