In the examination of the majestic tiger, one is inevitably drawn to the rich tapestry of climates that serve as its natural habitat. These apex predators, revered and feared, inhabit diverse environmental settings that range from humid rainforests to arid grasslands. Understanding the climates in which tigers thrive is paramount not just for their conservation, but also for the ecosystems they represent.
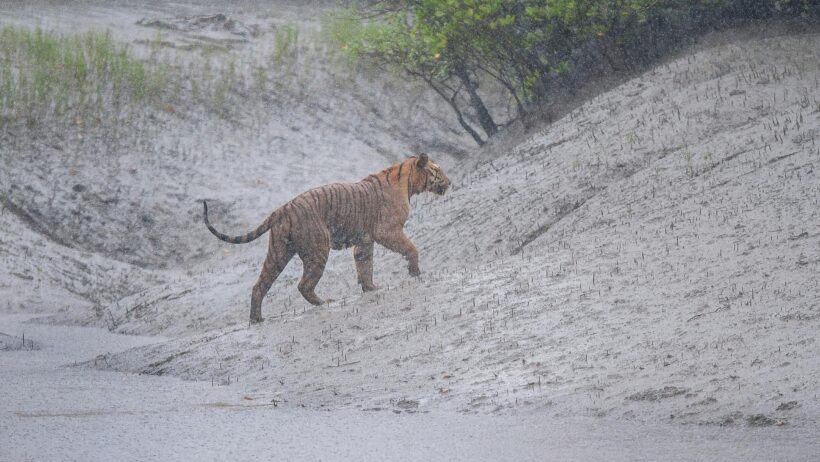
The primary range of the tiger extends across Asia, spanning countries like India, Indonesia, Russia, and Bangladesh. This vast geographical distribution reveals a multitude of climatic conditions and ecological features. The majority of tiger populations are concentrated in tropical forests and savannas, where warmth and moisture prevail. The Sundarbans, a vast mangrove forest, exemplifies the intricate relationship these felines have with their environment. The brackish waters and dense foliage of the Sundarbans not only provide a sanctuary for tigers but also shape their behaviors and hunting strategies.
In more temperate regions, such as the Russian Far East, tigers contend with a starkly different climate. Here, the Siberian tiger—largest of its kind—has adapted to survive the frigid winters. The extreme cold and substantial snowfall necessitate a different set of adaptations, including a thicker coat and a more solitary lifestyle to minimize energy expenditure. Such environmental pressures underscore the incredible resilience of tigers in the face of climatic diversity.
Across these varying climatic zones, tigers exhibit preferences for certain ecosystems that influence their distribution and behavior. Tropical forests provide ample cover and abundant prey, while grasslands and savannas offer expansive terrains for hunting. These ecosystems are not merely habitats; they embody the interconnectedness of species within the food web. The presence of tigers can regulate ungulate populations, ultimately leading to healthier vegetation and more balanced ecosystems.
Yet, the complexities of tiger habitats are increasingly threatened by anthropogenic factors. Deforestation, climate change, and poaching have disastrous impacts on their living conditions. A significant concern is the alteration of these climates due to global warming, which can lead to habitat fragmentation. Disturbances such as forest fires, which are becoming more prevalent due to rising temperatures, pose a serious threat to the delicate balance of these ecosystems. Alongside habitat destruction, illegal wildlife trade further exacerbates the decline in tiger populations, creating a scenario where about three subspecies of tigers have already vanished from existence.
An often-overlooked aspect of tiger habitats is the role of water bodies. Tigers are adept swimmers, often found near rivers and lakes. These aquatic environments not only provide hydration but also support diverse prey species such as deer and boar that venture into these waters. Therefore, the health of freshwater ecosystems directly correlates with the survival prospects of tiger populations. Protecting these habitats is crucial for maintaining the intricate web of life that sustains both tigers and their prey.
The seasonal shifts in climate also influence tiger behavior and availability of resources. In the tropics, monsoon seasons can drastically change the landscape, creating temporary floods that alter the dynamics of hunting. Conversely, during the dry season, competition for resources intensifies as water scarcity forces various species into a smaller area, leading to increased encounters between predators and prey. Such adaptations are central to the survival strategies exhibited by these formidable animals.
The conservation of tiger habitats begins with a deep understanding of their climate requirements. Organizations globally are racing against time to ensure these magnificent creatures continue to thrive. Initiatives focusing on preserving larger contiguous areas allow for greater genetic diversity and resilience against climate variability. Efforts to restore degraded ecosystems can play an essential role in paving the way for tigers to reclaim lost territories.
If we shift our perspective from viewing climate as a mere backdrop to understanding it as a critical component of the tiger’s survival, we recognize the urgency in preserving their habitats. Climate change is not merely a distant threat; it is an immediate challenge requiring collective action. The interconnectedness between tigers and their ecosystems should mobilize global efforts to mitigate climate impacts.
In an era marked by environmental uncertainty, fostering curiosity about the habitats of tigers can inspire innovative conservation strategies. Educating communities about the significance of these apex predators can help bridge the gap between local populations and biodiversity conservation. Engaging in policies that prioritize sustainable development offers a dual benefit: ensuring human welfare while protecting the rich biodiversity that underpins our planet’s health.
The climate in which tigers live is not simply an extension of where they hunt or roam. It shapes their existence and defines their ecological roles. Understanding the intricate balance of these ecosystems illuminates the pressing need for conservation efforts. By honoring the climate that nurtures these magnificent beings, we embark on a journey toward a more harmonious existence within the natural world.
As we delve deeper into the world of tigers, it becomes evident that preserving their habitats is inseparable from addressing broader climate change issues. The fate of the tiger is a stark reminder of the environmental crises we face today, inviting us to reconsider our actions and their repercussions on future generations. A future where tigers roam freely and thrive in diverse climates begins with us—our awareness, our advocacy, and our unwavering commitment to preserving their wild world.