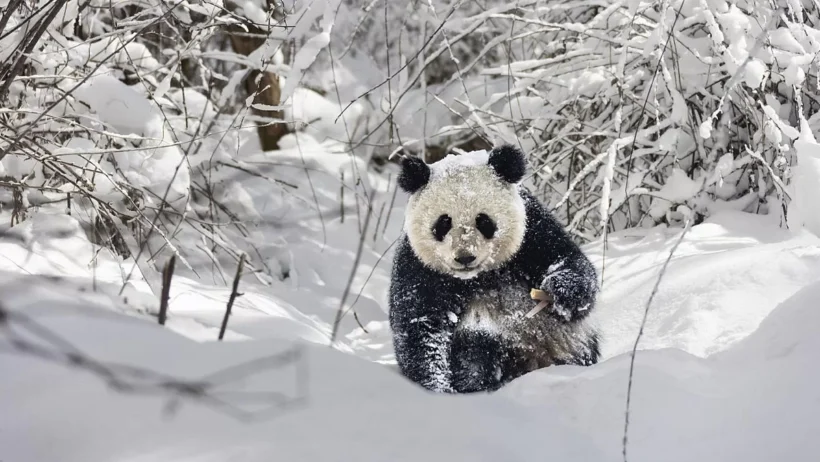
What if I told you that the giant panda, an iconic symbol of conservation, thrives in a blend of luxurious flora and temperate climates? Indeed, the climate in which pandas reside is both intricate and essential to their survival. Pandas predominantly inhabit the mountainous regions of southwestern China, particularly in Sichuan, Tibet, and Shaanxi provinces. This unique habitat poses a compelling question—what makes the climate in these mountainous forests so pivotal for the survival of this beloved species?
The atmosphere in these areas is predominantly cool and moist, promoting a rich biodiversity. Giant pandas are typically found at elevations ranging from about 5,000 to 10,000 feet. The temperature ranges drastically but generally hovers between 40°F (4°C) to 60°F (15°C). This climate creates a favorable environment for the growth of bamboo, their primary food source, which represents about 99% of their diet.
Bamboo, a crucial resource, thrives in the altitude and temperature of these mountainous regions. The nutrient composition of bamboo keeps the pandas nourished, despite its low calorie count. Interestingly, there are around 40 different species of bamboo in their habitat, ensuring a steady food supply throughout the year. However, the ecological challenges that come with climate change threaten these bamboo forests, and ultimately, the pandas themselves.
As the climate warms, the range of suitable bamboo growth habitats is shifting. If temperatures increase significantly, what will happen to the panda’s food source? These magnificent creatures require a lot of bamboo to sustain their energy levels—around 20 to 40 pounds daily. If bamboo growth becomes limited or erratic due to rising temperatures, what avenues will remain for a panda’s survival?
Moreover, the climate within these regions is subject to seasonal variations, with distinct wet and dry seasons. The wet season, from June to September, provides crucial moisture, enabling bamboo to flourish. The dry season also plays a role, as it allows for the growth of diverse vegetation that pandas can consume during periods when bamboo is less available. However, as climate patterns grow increasingly erratic, these historical cycles could become disrupted, exacerbating the existing challenges pandas face.
In addition to temperature fluctuations, other climatic factors, such as precipitation and humidity, are essential for sustaining panda habitats. These factors contribute to the health of the forest ecosystem, which includes not just bamboo but also other plant species. The intricate web of interdependence among various flora and fauna underscores the importance of stable climatic conditions. An environment that becomes too dry or too wet could spell calamity for not just giant pandas, but countless other species that cohabitate in these forests.
To further understand the impact of climate on panda habitats, one must consider the geography of their mountainous environment. The steep terrain provides natural barriers, restricting the movement of pandas and limiting their ability to migrate to other regions that may offer more favorable conditions. In light of climate change, these physical boundaries can hinder their adaptation to shifting climatic conditions, thus raising significant conservation concerns.
The recent increase in extreme weather events, attributed to climate change, adds another layer of complexity. Flooding, landslides, and increased frequency of droughts directly threaten the delicate balance of the ecosystems that support pandas. These events can decimate bamboo forests in a matter of moments, leading to loss of habitat and acute food shortages. Imagine a panda, accustomed to a specific range of bamboo, faced with an untenable situation due to an unexpected flood. Where will it find sustenance?
The plight of the giant panda acts as a clarion call for humanity. The environment in which they flourish is increasingly fragile, a fact that demands our immediate attention. If we fail to mitigate climate change, we risk not only the survival of the panda but also the integrity of the entire ecosystems that depend on the stability of these mountainous climates. Though they may seem resilient, the intricate interplay of species and climate is not easily disentangled.
Conservation strategies focused on habitat preservation have proven essential for maintaining panda populations. Establishing protected areas that encompass critical bamboo forests is crucial. However, these efforts must be accompanied by a broader recognition of climate change’s far-reaching consequences. Communicating the urgent need for global cooperation on climate action, preserving not only pandas but the myriad of species reliant on these environments, is imperative.
Efforts like reforestation, sustainable agriculture, and community education about climate change can also help bolster panda populations by addressing the root causes of habitat degradation. Furthermore, sustainable tourism can be encouraged as a means of engaging local communities in conservation, providing them with incentives to protect their natural heritage while contributing to global awareness and action against climate change.
As we ponder the climatic conditions in which pandas thrive, we must accept the responsibility that comes with this knowledge. The challenge is formidable, yet the potential for meaningful change lies within our reach. How will you contribute to preserving the habitats of these extraordinary creatures? Whether through advocacy, awareness, or action, each of us has the power to make a significant difference in the fight against climate change and ensure that pandas continue to thrive amidst the lush, mountainous forests they call home.