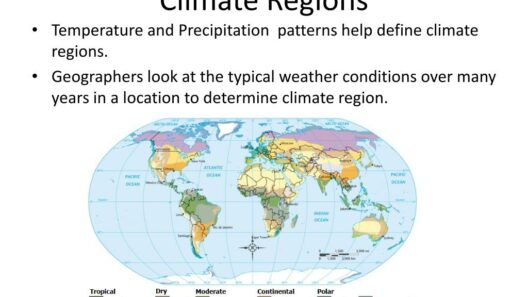
The climate of Virginia is an intricate tapestry woven from the contrasting threads of mountain and coastal air. This unique blend creates a diverse meteorological landscape that captivates both the ecologist and the casual observer alike. Understanding Virginia’s climate zones offers a glimpse into the various ecosystems that flourish across its expanse, revealing how geography orchestrates the dance of the seasons.
Situated in the southeastern region of the United States, Virginia encompasses a variety of geographical features—from the intimidating peaks of the Blue Ridge Mountains to the gentle undulations of the Piedmont, and finally to the sprawling coastal plains that meet the Atlantic Ocean. This diversity gives rise to pronounced variations in climate across the state, categorizing it primarily into two distinct climate zones: humid subtropical and humid continental. Each of these zones contributes uniquely to the state’s environmental palette.
The humid subtropical climate predominates in eastern Virginia, particularly in Tidewater and the northern neck area. Characterized by hot, humid summers and mild winters, this climate is a nurturing cradle for a wide array of flora and fauna. The warmth wraps around the region like a cozy blanket, promoting the luxuriance of growth. Here, lush gardens and vibrant landscapes flourish, blossoming with azaleas and dogwoods during spring, and yielding an abundance of crops in summer. The colors paint an impressionistic landscape that transforms with the seasons, embodying the rhythmic beats of nature’s cycle.
The transition into the humid continental climate occurs as one ventures westward into the mountainous regions. The Blue Ridge Mountains serve as the dividing line, a natural barrier that influences weather patterns and temperature variations. This zone is characterized by more pronounced temperature swings, with colder winters and cooler summers compared to its eastern counterpart. The elevation changes introduce altitudinal variations, leading to a dramatic shift in biodiversity. Ecologists have come to appreciate the rich habitats supported by this climate, from the rich oak-hickory forests to the breathtaking display of foliage in the autumn, where leaves turn into a fiery palette of reds, oranges, and yellows.
As one traverses from the coastal plain to the heights of the mountains, it becomes evident how the interplay of air masses shapes the overall climate. The estuaries and bay areas receive moist maritime air blowing off the Atlantic, while the mountains’ elevation ushers in drier and cooler air from the west. Invariably, these contrasting air masses collide, resulting in dynamic weather patterns. Storm systems frequently meander over Virginia, nourished by the moisture-laden winds of the coast, yielding generous rainfall that replenishes the verdant landscapes.
This climactic interplay does not simply create scenic vistas; it also poses significant challenges. Rising global temperatures, the consequence of climate change, affect the delicate balance of Virginia’s ecosystems. The humid subtropical zone, once a haven of agricultural abundance, faces threats from unpredictable weather patterns, including severe storms, prolonged droughts, and irregular growing seasons. Farmers and conservationists find themselves vying against time, striving to adapt to the climatic shifts that threaten both crop yields and biodiversity.
The coastal regions, too, are not impervious to the consequences of climate change. Rising sea levels encroach upon Virginia’s shoreline, threatening not only ecosystems but also the local economies reliant on tourism, fishing, and maritime industries. The unique ecosystems of the Chesapeake Bay, a nexus for wildlife and human activity, face the grim prospect of degradation under the weight of coastal erosion and pollution.
In the face of these formidable challenges, Virginians are increasingly taking steps to cultivate resilience. Restoration projects aimed at revitalizing the marshlands and restoring oyster populations serve to bolster the natural defenses against rising waters. Community engagement in sustainable practices is on the rise, reflecting a society that acknowledges its responsibility to steward the land. The winds of change are blowing, and with them, a burgeoning awareness about the importance of sustainable development and climate adaptation fuses with Virginia’s rich heritage.
Moreover, Virginia’s diverse climate fosters a fertile ground for innovation and renewable energy initiatives. Solar farms rise like sunflowers in the rural expanses, embodying the hopeful surge towards a sustainable future. With a history steeped in agriculture, the concept of regenerative farming practices is gaining traction. Farmers are integrating techniques that enhance soil health and promote biodiversity, echoing a desire for a harmonious coexistence with the environment.
In summary, Virginia’s unique climate zones are a microcosm of the larger narrative surrounding climate change and adaptation. From the bustling cities of the coastal plains to the serene mounts of the Blue Ridge, the state’s environmental condition weaves a story of resilience, innovation, and hope. Virginia exemplifies the delicate balance between enjoying nature’s bounteous offerings and confronting the undeniable truths of a changing climate. The blending of mountain and coastal air is as much an invitation to explore as it is a call to action—a reminder that the stewardship of this land rests in the hands of its inhabitants. The future, shaped by informed choices and proactive measures, holds profound promise for Virginia’s diverse landscapes.