The temperate forest is often considered Earth’s seasonal middle ground, an ecological sanctuary where varying climates converge and create distinctive environmental characteristics. But what exactly is the climate in temperate forests, and how does it influence the life forms that inhabit this unique biome? This question invites us to delve deeper into the intricate relationships between climate, flora, and fauna in one of the most diverse ecosystems found on our planet.
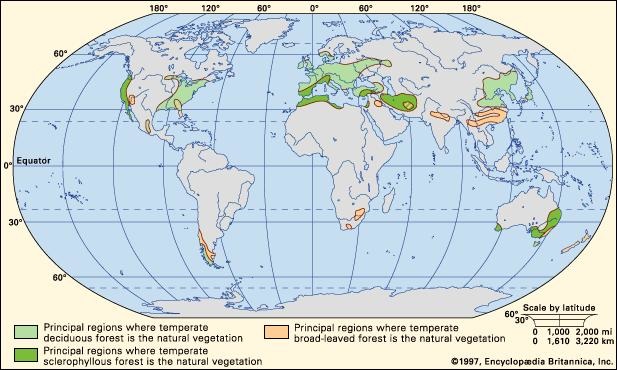
To begin with, temperate forests are primarily located between the polar regions and the tropics, predominantly in areas with moderate climates. What sets them apart is their distinct four-season cycle, which includes spring, summer, autumn, and winter. Each season brings with it a range of climatic conditions, contributing to the dynamic and vibrant ecosystems that flourish in these regions. How do these seasonal changes affect the life cycles of the trees and animals? This poses an intriguing challenge for any ecological observer.
The climate in temperate forests is characterized by moderate temperatures and rainfall, which varies significantly throughout the year. Typically, annual precipitation ranges from 30 to 60 inches, distributed relatively evenly across the seasons. This consistency allows lush vegetation to thrive, supporting a plethora of biodiversity. However, the temperature can oscillate dramatically. Winters can be harsh, with temperatures plummeting below freezing, while summers tend to be warm, sometimes soaring into the high 80s or even 90s Fahrenheit (approximately 30 to 35 degrees Celsius). These climatic fluctuations shape a unique habitat where specific species have adapted to endure the changes.
One of the most fascinating aspects of temperate forests is their deciduous trees, which shed their leaves in the autumn. The rich, kaleidoscopic display of colors during this season captivates onlookers. But beyond their beauty, these cyclical transformations play an essential role in nutrient cycling and soil health. As leaves fall, they decompose, enriching the forest floor with organic matter. This process not only fosters robust soil but also sustains diverse life forms from fungi to insects, each playing a vital role in the ecosystem.
Interestingly, the temperate forest is not solely limited to deciduous trees. Coniferous species, such as pines and spruces, can also be found, particularly in regions where the climate is slightly cooler. These trees have adapted remarkably well to their environment. Their needle-like leaves are designed to minimize water loss and withstand cold temperatures. This adaptation emphasizes the resilience of life in temperate forests, showcasing how species can thrive amidst climatic challenges.
Moreover, the rich variety of climate conditions found in temperate forests supports a diverse array of wildlife. From the nimble deer and playful raccoons to stealthy bobcats and soaring hawks, each species has adapted uniquely to their specific habitat. The presence of multiple trophic levels—producers, consumers, and decomposers—creates a balanced ecosystem, where each organism plays a significant role in maintaining the health of the forest. As seasonal changes occur, the interdependencies among these species become even more pronounced, revealing a complex web of life that relies heavily on the climate’s mercy.
However, the delicate equilibrium of these ecosystems is increasingly being threatened by climate change. Background shifts in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt the synchrony between plant blooming and animal breeding seasons, leading to mismatches in food availability. This challenge forces numerous species to adapt swiftly or face extinction. Can life in temperate forests endure these rapid climate shifts? The answer lies in the resilience of the species, their ability to adapt, and the ongoing efforts to protect and rehabilitate their habitats.
As we witness the changing climate, understanding the specific climate characteristics of temperate forests becomes paramount. Efforts to mitigate climate change, such as reducing carbon emissions and preserving natural habitats, are crucial for maintaining the health and viability of these ecosystems. Conscientious actions at an individual level, such as advocating for sustainable practices and supporting conservation initiatives, can collectively make a significant impact on the climate of these forests.
Additionally, the importance of temperate forests extends beyond ecological implications. They also contribute to global carbon storage, helping to mitigate the effects of climate change. The trees in these forests store vast amounts of carbon dioxide, acting as natural ‘carbon sinks’. This feature highlights the intrinsic value of conservation—protecting these areas is not just about preserving the beauty of the landscape or the diversity of species; it is about safeguarding our planet’s climate for future generations.
In conclusion, the climate in temperate forests serves as a critical driver for biodiversity, ecological balance, and global health. As we grapple with climate-related challenges, recognizing the nuances of temperate ecosystems becomes essential. They remind us of the interconnectedness of life and the pressing responsibility we hold to protect these vital natural resources. Can we rise to the challenge? The answer lies in our ability to adapt, innovate, and commit to making meaningful changes that foster resilience, not just for ourselves, but for the myriad forms of life that call temperate forests home.