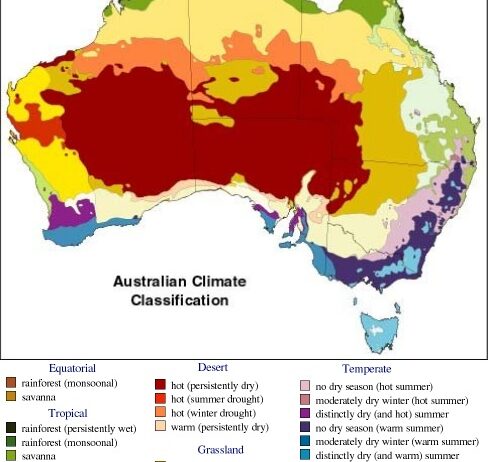
Australia, a continent brimming with biodiversity and stark contrasts, presents an array of climatic zones that is intriguing to explore. The climatic conditions range drastically—spanning from parched desert regions to the lush, tropical wetlands. This complexity reveals not just the geographic diversity of Australia but also the intricate interplay between the environment and climate. Understanding this climatic tapestry helps provoke curiosity about the ecological systems at play and underscores the urgency of recognizing climate change’s impact on such delicate balances.
To begin with, Australia is characterized by having several distinct climate zones: tropical, dry, temperate, and alpine. Each zone is steeped in unique vegetation, animal life, and seasonal variations. The vast interior of the continent, known as the Outback, is dominated by arid and semi-arid climates, wherein relentless heat can reach soaring temperatures. This region’s climate is classified as desert-like, with sporadic rainfall and extreme temperature variations between night and day.
The arid interior contrasts sharply with Australia’s coastal regions, where the climate often emerges as humid and temperate. Major cities like Sydney and Brisbane enjoy a more moderate climate with four distinct seasons. Summer temperatures in these areas can escalate, yet coastal breezes and proximity to water bodies mitigate the extreme heat experienced inland. With average summer highs recorded around 30°C (86°F), residents often relish in the balmy evenings that accompany this urban setting.
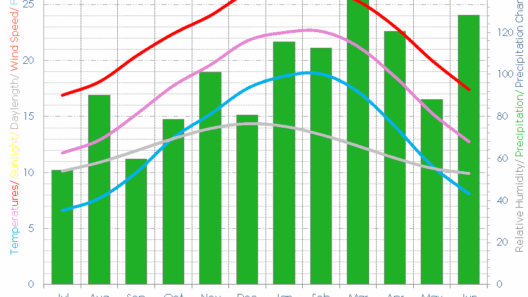
Heading further north, we encounter the tropical climates of Queensland and the Northern Territory. These regions experience dramatic seasonal changes, categorized into wet and dry seasons. The wet season, occurring between November and April, brings intense monsoonal downpours. This influx of moisture transforms the landscape into verdant expanses, nourishing robust ecosystems in both rainforests and savannahs. Indeed, the tropical wetland regions play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, underscoring their importance in combating the impacts of climate change.
Moving from the tropics to the temperate zones delineates the journey across Australia’s geographical breadth. In southeastern Australia, cities like Melbourne and Hobart reflect a convergence of oceanic climate effects, where precipitation is relatively evenly distributed throughout the year. The presence of the Southern Ocean significantly influences temperatures, preventing extremes and allowing for a myriad of agricultural endeavors. The flourishing wine regions in this area attest to the climatic suitability for such industries, yet underscore the climatic fragility susceptible to shifts instigated by global warming.
The alpine regions residing in the Australian Alps present a different narrative. This area experiences a distinct colder climate, where winter can blanket the peaks in snow. The ecosystem here is uniquely adapted, hosting flora and fauna that withstand the chilling temperatures and variable snow conditions, making it a haven for winter sports. Climate change poses a significant threat to these alpine ecosystems, as rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns lead to diminished snowfall and consequent habitat loss. Surveys indicate that many species are struggling to adapt, thus exemplifying the broader risks posed across Australia.
The diverse Australian climatic zones contribute extensively to its plethora of ecological systems, each interlinked and influenced by overarching climate trends. However, such rich biodiversity faces unprecedented challenges in the face of climate change. For instance, the frequency of heatwaves has risen, with notable records observed in recent years. These events jeopardize not only human health and agricultural viability but also the intrinsic ecological balance that maintains wildlife populations.
Moreover, the intensifying climate patterns result in extreme weather phenomena, manifested as devastating bushfires in the eastern states or severe flooding during tropical storms. Such occurrences are more than mere aberrations; they illustrate a pattern that demands serious scrutiny. They force us to reckon with harsh realities and the interconnectedness of climate events—what happens in one region invariably influences another, amplifying the call for a comprehensive understanding of climatic interconnectedness.
The relevance of climate change, especially in Australia, is intrinsically tied to global narratives. Examples of biodiversity loss, water scarcity, and altered weather patterns echo within the broader discussions on sustainability and environmental stewardship. It becomes paramount to foster an understanding that transcends geographical borders, as the implications of climate change are universal.
In navigating through the intricacies of Australia’s climate, there lies a profound opportunity for enrichment in perspective. The stark contrasts—from the blistering heat of the Outback to the salubrious coasts and verdant tropics—encourage a deeper questioning of how climate encompasses both beauty and vulnerability. By immersing oneself in this diverse climatic environment, one cannot help but become an advocate for change, engaging others in conversations surrounding ecological conservation and climate action.
Notably, the potential for a sustainable future hinges on humanity’s capacity to adapt in the face of climate realities. The juxtaposition of Australia’s deserts and wetlands serves as a poignant reminder of nature’s resilience and fragility. Bridging curiosity with facts can ignite a more profound commitment to environmental activism, laying the groundwork for strategies that combat climate change. As climatic conditions continue to evolve, so too must our understanding and engagement with the world around us.
Australia’s climatic diversity invigorates our desire to learn; it pushes the boundaries of curiosity and compels us to reflect on our environmental responsibilities. All inhabitants of this planet share the same air, the same sky, and consequently, the same duty to steward this shared ecosystem wisely. In the face of climate variability, the onus is upon us to act with conviction and sustain the myriad forms of life that call this remarkable continent home.