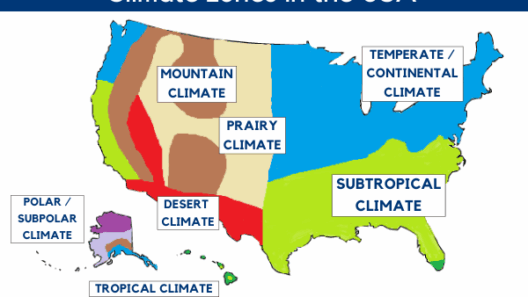
In the grand tapestry of our planet’s climate, the concept of “moderate climate” weaves a narrative that speaks to both balance and harmony. It beckons us to explore the symbiotic relationship between human activity and the Earth’s natural systems. Amidst a backdrop of climate extremes—where scorching summers and frigid winters vie for dominion—a moderate climate emerges as a sanctuary for biodiversity, agriculture, and human settlements. This climate, often characterized by mild temperatures, seasonal rainfall, and a delicate equilibrium, plays a pivotal role in sustaining life as we know it.
Understanding what constitutes a moderate climate involves delving into the intricate interplay of various climatic elements, including temperature, precipitation, and geographical features. Think of climate as a finely tuned orchestra; each instrument—the winds, the waters, the land—must harmonize to produce a pleasing symphony. When one section becomes too loud, or an instrument falls out of tune, dissonance ensues, resulting in climatic extremes that can disrupt ecosystems and human societies alike.
Moderate climates are often defined by their temperate nature. Regions with this climate type typically experience four distinct seasons, each offering a sense of renewal and transition. Spring’s gentle blooms give way to summer’s lush growth, followed by the bountiful harvests of autumn, and finally, the quiet dormancy of winter. This rhythmic cycle enables a flourishing of life; ecosystems thrive, and agricultural pursuits flourish, illustrating how moderation can yield abundant rewards.
One of the most defining characteristics of a moderate climate is its propensity for moderate temperatures. This “Goldilocks zone” is neither too hot nor too cold, creating an environment conducive to a wide array of flora and fauna. For instance, regions such as the Mediterranean climates found along coasts and some continental areas exemplify this phenomenon. Here, the convergence of oceanic currents and land formations crafts an oasis where citrus trees, olives, and diverse wildlife find their niche. It is a delicate balance that sustains life and maintains the integrity of natural systems.
Moreover, rainfall patterns in moderate climates are generally characterized by sufficient precipitation to support plant life while avoiding the torrential downpours or extended droughts seen in more extreme climates. The precipitation in these regions often follows a predictable seasonal rhythm, enhancing biodiversity and agriculture. Think of rainfall as an artist’s brushstroke upon a canvas, painting landscapes with vibrant greens and bountiful harvests.
The benefits of a moderate climate extend beyond natural ecosystems. Human civilizations throughout history have gravitated toward regions that embody this climatic ideal. The temperate zones of the world have become cradles of civilization, fostering innovation, trade, and cultural exchange. These regions often serve as the nexus for agriculture and industry, allowing societies to cultivate their lands without the fear of catastrophic weather events. Here, the delicate equilibrium fuels economic prosperity while providing an enviable quality of life.
However, this idyllic scenario is increasingly threatened by climate change. The planet’s warming temperatures and erratic weather patterns put pressure on the delicate balance inherent in moderate climates. As intense droughts, unpredictable storms, and rising sea levels become the new normal, the repercussions are profound. The very fabric of agriculture, which has thrived for millennia in moderate climates, faces the existential threats of shifting growing seasons and diminished yields.
To safeguard the future of moderate climates, a multi-faceted approach is essential. First and foremost, it is imperative to prioritize sustainable land management practices. Transitioning to regenerative agricultural practices, such as crop rotation and permaculture, can improve soil health and enhance biodiversity. By harnessing nature’s wisdom, we can cultivate resilience against the looming threats of climate change.
Furthermore, promoting urban development that respects natural landscapes can help maintain the integrity of these regions. Thoughtful planning that integrates green spaces, community gardens, and ecosystems into urban environments fosters resilience. Cities can mitigate heat waves and improve air quality, all while supporting biodiversity. This approach is akin to reintroducing lost melodies into a symphonic score—each note essential in preserving the harmony of a vibrant environment.
Education and community engagement are also essential components in the quest to maintain moderate climates. Raising awareness about the impacts of climate change and the importance of moderation in all aspects of life enables individuals and communities to take action. From reducing carbon footprints to advocating for local policies that protect natural habitats, every effort counts. When individuals unite for a common cause, they create a formidable force for change—resembling a mighty river that carves valleys and shapes landscapes.
In summary, the quest for understanding what constitutes a moderate climate reveals a world of intricate connections and relationships. It is a realm where temperatures are balanced, seasons are distinct, and the interplay of life thrives. As we forge ahead in the face of climate challenges, the need to protect and preserve these climates becomes paramount. The pursuit of moderation transcends mere temperature—it invites us to cultivate a sustainable world that values balance, resilience, and the rich tapestry of life that flourishes within these environments. Together, we can strive for a future where moderate climates remain not a fleeting ideal, but a lasting reality for generations to come.