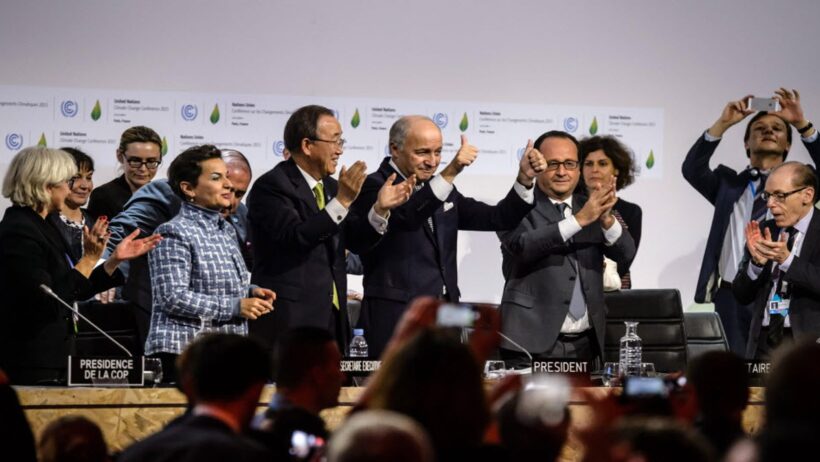
The Paris Climate Treaty, an unprecedented international accord, symbolizes humanity’s unified aspiration to combat the exigent threat of climate change. Officially known as the Paris Agreement, it was forged in December 2015 during the 21st Conference of the Parties (COP21) in Paris, France. The treaty emerged from a potent recognition: climate change does not respect borders. The world must join together in concerted action to foster a sustainable future.
At its core, the Paris Agreement encapsulates the collective promise of nations to limit global temperature rise to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels, while ideally aiming for a ceiling of 1.5 degrees Celsius. This ambitious target is predicated on the understanding that exceeding these thresholds significantly exacerbates the consequences of climate change, including extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and loss of biodiversity. The magnitude of these threats necessitates a transformative shift in both policy and perspective.
One of the treaty’s most innovative aspects is its framework of nationally determined contributions (NDCs). Unlike previous agreements that mandated uniform standards applicable to all parties, the Paris Agreement respects the sovereignty of individual nations by allowing them to set their own emission reduction targets. Each country is encouraged to formulate its action plans based on its national context, capabilities, and circumstances. This decentralized approach fosters a spirit of ownership and accountability, compelling countries to act in alignment with their articulated goals.
The mechanism of NDCs is significant not only for its flexibility but for its iterative nature. Nations are required to update their commitments every five years, progressively intensifying the ambition of their climate actions. As more countries participate, the cumulative effect of these improvements could yield substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, a critical step toward decelerating global warming.
Moreover, the treaty emphasizes the importance of transparency and accountability. Signatory countries are obliged to provide regular updates on their emissions and progress towards their respective goals. Such transparency is paramount in maintaining trust among nations and ensuring that pledges are not merely symbolic gestures. The provision for a robust review mechanism instills a sense of urgency and underscores the necessity for tangible results over time.
The foundations of the Paris Agreement also extend to financial commitments. Recognizing that climate action necessitates substantial investment, the treaty calls for developed nations to provide financial resources to assist developing countries in their efforts to mitigate and adapt to climate change. This financial support is crucial for fostering resilience in vulnerable populations, who often bear the brunt of climate impacts despite contributing the least to the problem. It embodies the principle of climate justice, emphasizing equity in the realm of global environmental governance.
Despite its laudable objectives, the Paris Agreement is not without its critiques. Some commentators argue that the voluntary nature of NDCs may lead to insufficient ambition, as countries may be reluctant to commit to aggressive targets without legally binding accountability. Others highlight the challenges of political will, especially in nations where climate activism encounters fierce opposition or apathy. These tensions serve as reminders that climate diplomacy requires not just governmental action, but also societal engagement.
Furthermore, the implications of climate change transcend mere environmental concerns; they permeate economic, social, and geopolitical spheres. Addressing climate change entails reimagining economic paradigms. Transitioning to renewable energy, enhancing energy efficiency, and fostering sustainable agriculture are not only fundamental for curtailing emissions but also present immense opportunities for innovation and job creation. A green economy holds the potential to stimulate growth while ensuring the health of our planet.
The role of technology in this transformation is instrumental. Breakthroughs in clean energy technology, carbon capture and storage, and sustainable supply chain management can substantially mitigate emissions. The Paris Agreement encourages technological cooperation, recognizing that innovation plays a pivotal role in overcoming the barriers to implementing climate solutions.
In light of these dynamics, the Paris Agreement can be seen as a catalyst for a broader cultural shift towards sustainability. As awareness of climate change grows, so too does the imperative for individuals and communities to adopt sustainable practices. The treaty serves as a foundation upon which individuals can build local initiatives that align with global goals. From reducing plastic waste to endorsing sustainable transport, every action contributes to the collective effort envisioned by the Paris Agreement.
The path forward, however, is fraught with challenges. Scientists warn of the urgency to act, as the window for limiting global warming is rapidly closing. While the Paris Agreement represents a beacon of hope, it is essential that nations move beyond mere rhetoric and translate commitments into actionable policies. The intersection of environmental science, political will, and public awareness must coalesce to catalyze meaningful change.
In conclusion, the Paris Climate Treaty stands as a pivotal moment in global history, embodying a shared resolve to confront the existential crisis of climate change. Its mechanisms, rooted in cooperation, transparency, and equity, create a framework for nations to collaborate and innovate in tackling this profound challenge. Embracing the principles of the Paris Agreement is not merely an obligation; it is a profound opportunity to redefine our relationship with the planet. The future is contingent upon the choices made today—choices that, if taken collectively and resolutely, can secure a sustainable legacy for generations to come.