Nuclear energy plays a pivotal role in the global energy landscape. As the world grapples with climate change, the challenge before us is: how can nuclear energy be conserved safely? Understanding the intricacies of nuclear energy conservation is not merely an academic exercise; it’s an imperative for sustainable development. This exploration will delve into methodologies, policies, and technological innovations crucial for the responsible conservation of nuclear resources.
The term “conservation” typically conjures images of environmental preservation, yet in the context of nuclear energy, it implies optimizing the usage of extensive resources while minimizing waste and risk. To achieve this, several strategies come into play, encompassing operational efficiency, regulatory frameworks, and community engagement.
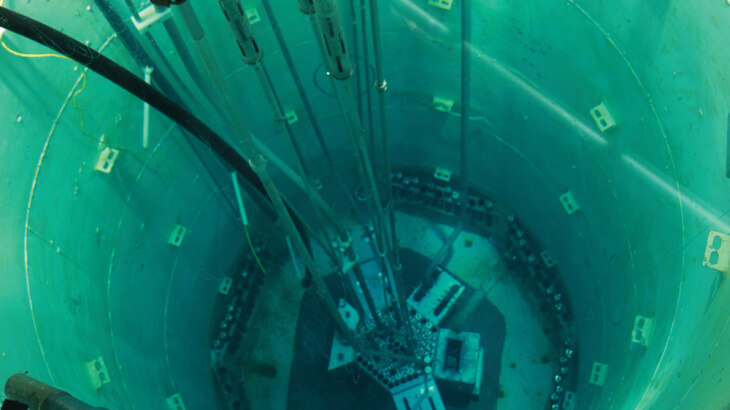
One foundational principle of nuclear energy conservation is optimizing reactor performance. Did you ever wonder how the materials and fuel used in reactors can be managed for maximum efficiency? Increasing the lifespan of reactor components through enhanced materials science can dramatically improve performance. Innovations such as advanced fuel designs allow for higher burn-up rates, resulting in less waste generation and more energy harnessed from the same quantity of uranium. Such methodologies not only reduce operational costs but also prolong the viability of nuclear power as a primary energy source.
Another captivating avenue lies within the realm of regulatory frameworks. What if a new set of guidelines could enhance nuclear safety while simultaneously fostering innovation? Effective regulation can encourage the adoption of best practices and new technologies that facilitate safe and sustainable operations. The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) plays a crucial role here, offering guidance on best practices that integrate safety, efficiency, and ecological responsibility. Their frameworks enable nations to collaborate in sharing knowledge, improving safety protocols, and developing incident-response strategies, thereby mitigating risks associated with nuclear energy production.
However, it is not enough to simply focus on operational and regulatory innovations. The social dimensions of nuclear energy conservation must be critically assessed. Community engagement is paramount. How can the public be involved in understanding the benefits and risks associated with nuclear energy? Educational initiatives aimed at demystifying nuclear technology can empower communities, creating a culture of safety and transparency. Public forums can serve as platforms for discourse, allowing stakeholders to voice concerns and suggestions, ensuring that nuclear energy is perceived as a communal resource rather than an abstract concept.
Waste management is a prominent concern entwined with nuclear energy conservation. The dilemma of what to do with spent nuclear fuel is not insurmountable, provided innovative solutions are pursued. Deep geological repositories have emerged as a preferred solution in many countries, where waste can be stored safely away from human activity. The challenge remains: how do you ensure public confidence in such sites? Research and development in waste transmutation—an advanced technique aimed at altering the isotopes in spent fuel—could also yield promising results by reducing the long-term radiotoxicity and heat generation of nuclear waste.
Continuing on the theme of innovation, let’s delve into the potential of small modular reactors (SMRs). Could SMRs revolutionize the nuclear industry? Unlike conventional nuclear power plants, which are large and complex, SMRs offer flexibility and scalability. These reactors can be built in factories and transported to sites, allowing for the provision of power in remote areas while simultaneously lowering capital costs. As these technologies proliferate, the conservation of nuclear energy could become multidimensional, with power derived effectively without the extensive infrastructure demands of traditional plants.
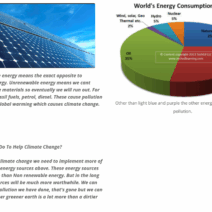
Additionally, symbiotic relationships can play a significant role in nuclear energy conservation. The integration of nuclear energy with renewable sources, such as solar and wind, presents a unique opportunity. Could a hybrid energy system provide a reliable base load while diminishing reliance on fossil fuels? This convergence could buffer the intermittent nature of renewables, facilitating a seamless transition to a more diversified energy portfolio. Collaborative projects between nuclear and renewable sectors can harness the strengths of each technology, ultimately leading to a greener, more sustainable energy future.
However, as we venture into this nuclear renaissance, interjecting public discourse remains critical. The acceptance of nuclear energy is heavily reliant on perceptions shaped by historical events and ongoing misunderstandings. What if we could bridge the knowledge gap through outreach programs? By actively engaging with communities, stakeholders can foster a better understanding of the benefits and safeguards of modern nuclear technologies. A well-informed public is more likely to support advancements in nuclear energy conservation.
In conclusion, the prospects for conserving nuclear energy safely are not only plausible; they are essential. Optimizing reactor performance, enhancing regulatory frameworks, engaging with communities, and pushing boundaries of technological innovation represent a holistic approach to ensuring the sustainability of nuclear resources. The challenge is multifaceted, but through collaboration, education, and forward-thinking policies, the potential of nuclear energy can be harnessed responsibly. By approaching nuclear energy conservation with vigor and mindfulness, we pave the way for a future that respects both energy needs and environmental imperatives.