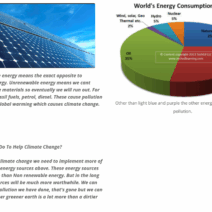
In an era where the implications of climate change loom larger than ever, the quest for conserving electrical energy has taken center stage. The urgency of reducing power consumption is not merely a fleeting trend; it is an essential endeavor that underpins our collective responsibility to foster a sustainable future. Understanding the simple yet effective methods by which we can curtail our energy use is imperative. Here, we explore actionable strategies that can be seamlessly integrated into daily life, allowing individuals and households to significantly diminish their power utilization while fostering environmental stewardship.
Understanding Energy Consumption
Before delving into conservation strategies, it is vital to comprehend where energy consumption predominantly occurs within the household. According to various studies, HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems account for a substantial portion of electricity usage, often exceeding 40%. Water heating, lighting, and appliances follow suit. By identifying these energy hogs, we can prioritize our conservation efforts effectively.
1. Optimize Heating and Cooling Efficiency
Heating and cooling systems are not only critical for comfort but are also significant contributors to energy bills. One effective approach to enhance their efficiency involves regular maintenance, such as cleaning or replacing filters and ensuring ductwork is sealed properly. Additionally, consider embracing programmable thermostats, which automatically adjust settings based on occupancy patterns, thus preventing unnecessary energy expenditure.
Moreover, employing natural ventilation techniques during temperate months can diminish reliance on air conditioning. Opening windows and utilizing ceiling fans can promote airflow, making indoor environments more comfortable without extra energy costs.
2. Embrace Energy-Efficient Appliances
The appliances in our homes play a pivotal role in determining energy consumption. Transitioning to energy-efficient models, denoted by the ENERGY STAR label, can significantly reduce power usage. Although the initial financial outlay may be higher, the long-term savings on energy bills can render these appliances economically advantageous. Examples of efficient appliances include refrigerators, washers, and dryers that utilize advanced technology to minimize consumption.
Furthermore, adopting habits such as using dishwashers and washing machines only with full loads, and air-drying clothes whenever feasible, can further conserve energy without sacrificing functionality.
3. Revamp Lighting Practices
Lighting occupies a considerable fraction of electrical energy use, particularly in households with outdated incandescent bulbs. Transitioning to compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) can yield dramatic reductions in energy consumption due to their efficiency and long lifespan. LED lights, for instance, consume up to 75% less energy than traditional bulbs and can last up to 25 times longer.
Besides upgrading bulbs, employing strategies such as maximizing natural light during the day through strategic window placement and minimizing the use of artificial lighting can further trim energy use. Installing dimmers or motion sensors can also enhance energy efficiency, ensuring that lights operate solely when needed.
4. Elevate Insulation and Seal Drafts
Insulation plays a crucial role in maintaining thermal comfort within the household. Enhancing insulation in attics, walls, and floors can lead to a remarkable decrease in heating and cooling demands. Additionally, sealing gaps around windows, doors, and electrical outlets prevents air leakage, which can exacerbate energy usage due to the HVAC system working overtime to maintain desired temperatures. Investing in weatherstripping or caulking materials can be a cost-effective solution to this ubiquitous issue.
5. Utilize Smart Home Technology
The advent of smart home technology has revolutionized the way we consume energy. Devices such as smart thermostats, energy monitors, and smart plugs allow homeowners to monitor and adjust their energy usage remotely. These technologies not only facilitate real-time adjustments but also provide insights into energy consumption patterns, empowering users to make informed decisions and identify opportunities for further savings.
Moreover, establishing routines with automation—such as turning off lights and devices at specific times—can enhance the overall efficacy of energy conservation efforts.
6. Generate Your Own Renewable Energy
While conservation is vital, generating your own energy can significantly augment efforts. Installing solar panels on rooftops enables households to harness renewable energy, effectively reducing reliance on grid power. Although the initial investment may be substantial, government incentives and decreasing technology costs have made solar energy more accessible. This shift not only lowers electricity bills but also diminishes one’s carbon footprint.
7. Cultivate Awareness and Community Involvement
Individual actions can have a multiplicative effect when communities come together to promote energy conservation. Engaging in local initiatives, such as energy audits organized by utility companies or community workshops on sustainability practices, fosters a culture of conservation. Educating friends and family about the importance of conserving energy can spur collective action, amplifying the impact of personal efforts.
Conclusion
Conserving electrical energy is not just an individual nicety; it is a necessity driven by the reality of climate change and environmental degradation. By adopting sustainable practices, such as optimizing heating and cooling, upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, improving insulation, and leveraging smart technology, we can significantly reduce our power usage. As more individuals become cognizant of their energy consumption and take actionable steps to conserve, the cumulative effect can lead to a substantial positive impact on our planet’s health. The journey toward sustainability is not a sprint but a marathon—each effort we make steers us closer to a greener, more sustainable future for generations to come.