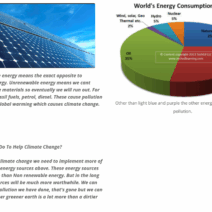
In the era of climate urgency, the focus on energy conservation is more paramount than ever, especially within educational institutions. Schools, as focal points of community engagement and development, present an opportunity for profound shifts in energy consumption practices. This guide will outline multifaceted strategies students can adopt to facilitate energy conservation in their schools, fostering both environmental stewardship and heightened awareness.
Understanding the necessity to conserve energy begins with recognizing the impact that schools have on the environment. Collectively, educational institutions consume vast amounts of electricity and produce significant carbon emissions. By proactively engaging in sustainable practices, students can not only reduce their school’s ecological footprint but also set a precedent for future generations.
1. Awaken Awareness: Educate and Engage
The first step in energy conservation is cultivating awareness within the school community. Organizing workshops or discussions can illuminate the importance of energy-efficient practices. Engage peers in conversations about energy consumption—what it is, how it impacts the planet, and how their actions can contribute to a solution. Awareness campaigns can be as simple as classroom posters or as elaborate as school-wide assemblies dedicated to sustainability.
In addition, students can initiate a “Green Club” to centralize efforts for promoting sustainable practices. This club can lead various projects, such as energy audits of the school’s current usage, identifying areas where efficiency can be enhanced.
2. Implement Practical Energy-Saving Habits
Small changes in daily habits can yield substantial energy savings. Students should be encouraged to turn off lights when leaving a room, utilize natural light whenever possible, and power down electronic devices at the end of the day. Additionally, placing reminders near light switches and electronic equipment can serve as cognitive nudges, reinforcing these energy-saving behaviors.
Moreover, utilizing energy-efficient appliances and lights, such as LED bulbs instead of incandescent ones, can drastically decrease energy consumption. Advocating for the adoption of these technologies in schools can also provide a platform for students to demonstrate leadership in sustainability practices.
3. Optimize Heating and Cooling Systems
Heating and cooling systems are notorious energy guzzlers in educational facilities. Encouraging the maintenance of these systems can help to maintain their efficiency. Students can raise awareness regarding proper thermostat settings—keeping it lower in winter and higher in summer—and emphasize the importance of closing windows and doors when systems are in operation.
Participating in or initiating a campaign to promote energy-efficient building designs can also be beneficial.
Students might advocate for retrofitting older buildings to include better insulation, ENERGY STAR-rated appliances, and programmable thermostats, all of which can drastically reduce energy use over time.
4. Champion Renewable Energy Sources
The transition to renewable energy sources is imperative for sustainable energy consumption. Bringing in experts to discuss solar panels or wind energy can spark interest among students to consider these alternatives. If feasible, students can propose to school administrations the installation of solar panels, which not only reduce reliance on traditional electricity but also serve as a hands-on educational tool for science classes.
Beyond implementation, developing projects around these renewable sources can deepen students’ understanding of their functionality and application. Conducting research on successful case studies from other schools that utilize solar or wind energy can also provide a compelling argument for adopting such practices locally.
5. Promote Water Conservation
Energy and water conservation are intricately linked. The energy used in water heating and treatment is a significant part of school energy consumption. Simple actions, such as fixing leaks and using water-efficient fixtures, are vital in mitigating water waste. Students can initiate campaigns to inform their peers about the importance of water conservation, such as reducing shower times or reporting leaks immediately.
Furthermore, schools can introduce rainwater harvesting systems for irrigation, thereby reducing the reliance on treated water for outdoor purposes. Educating students on the water cycle and its relation to energy consumption can also create a robust understanding of the interconnectedness of our resources.
6. Incorporate Energy Efficiency into Projects
Students should be encouraged to incorporate energy efficiency in their academic projects and presentations. Whether in science fairs, economics projects, or art displays, promoting themes of sustainability can foster creativity while reinforcing the principles of energy conservation. For instance, designing a model of an eco-friendly building or conducting research on energy-efficient technologies can provide invaluable experiential learning opportunities.
Additionally, students can collaborate on social media campaigns highlighting energy conservation tips, engaging their wider community and fostering a culture of sustainability beyond school boundaries.
7. Collaborate with Local Energy Organizations
Building connections with local energy organizations can offer students access to additional resources and expertise. These organizations often have programs aimed at fostering energy education and may provide grants or materials for sustainability projects. Students can invite guest speakers from these organizations, facilitating a broader understanding of energy conservation and creating opportunities for hands-on engagement in community initiatives.
Conclusion: A Collective Shift in Perspective
Energy conservation in schools is a collective endeavor that demands imagination, commitment, and action from every student. By taking responsibility and implementing energy-saving practices, students can pioneer a significant movement within their educational landscapes. This guide serves as not just a collection of strategies but a launchpad for a profound movement toward sustainability—one that invites curiosity, ignites passion, and cultivates leadership in the realm of environmental stewardship. With awareness as the catalyst, students will not only change their schools but also inspire their communities to reimagine their relationship with energy and the environment.