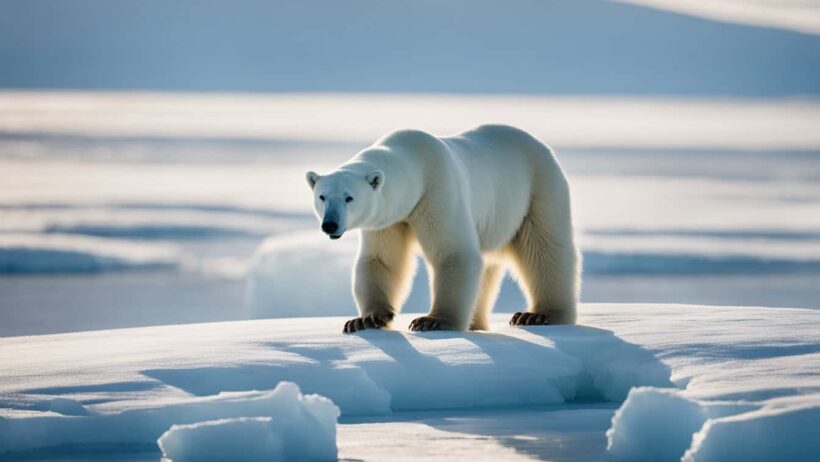
Polar bears, the majestic denizens of the Arctic, have captivated the imagination of many due to their formidable presence and fascinating adaptations to one of the planet’s most extreme environments. To truly appreciate their survival strategies, one must delve into the mechanisms by which these magnificent creatures conserve energy while thriving in the relentless Arctic chill. Understanding this intricate dance of survival not only evokes wonder but also enlightens discussions on climate change and its impact on these iconic animals.
One of the primary strategies employed by polar bears to conserve energy is their remarkable physiological adaptation to extreme cold. The polar bear’s thick layer of blubber, sometimes exceeding four inches in thickness, acts as an exceptional insulator. In conjunction with their dense, water-repellent fur, this evolutionary trait minimizes heat loss, allowing bears to maintain their core body temperature despite frigid surroundings. This insulated design enables the bears to reduce their metabolic rate when temperatures plummet, conserving precious energy that is paramount for survival.
In addition to anatomical adaptations, behavioral strategies play a vital role in energy conservation within the polar bear population. These bears are keenly aware of the advantages of remaining inactive during severe cold spells. By limiting movement during extreme weather conditions, polar bears significantly reduce energy expenditure. They frequently engage in a behavior known as “resting,” where they will sit or lie still for prolonged periods. This not only conserves energy but also minimizes the risk of hypothermia, another critical consideration in their harsh habitat.
Moreover, during periods when food is not readily available, polar bears enter a state of “walking hibernation.” Unlike true hibernation, this semi-torpid state allows them to lower their metabolic rate even further. This biological quirk enables them to survive on their fat reserves while minimizing their movement. For a species wholly reliant on sea ice and the seals that inhabit it, the capacity to endure long stretches without feeding is invaluable. Thus, during food scarcity, a polar bear’s ability to conserve energy ensures it can weather periods of deprivation without succumbing to starvation.
Social behavior also plays a role in energy conservation. When the weather worsens, polar bears may choose to aggregate, allowing them to share body heat. Though generally solitary creatures, these magnificent animals can benefit from proximity during severe cold spells. This behavior might seem counterintuitive in the context of the hunt. However, by clustering together, they can reduce individual energy expenditures, which becomes crucial during prolonged periods of adverse weather.
The polar bear’s hunting strategy also reflects their sophisticated understanding of energy conservation. Seal hunting, their primary source of sustenance, requires an immense expenditure of energy. To balance this, polar bears demonstrate remarkable patience and strategic prowess. They often utilize the “still-hunting” technique—remaining completely still for prolonged periods while waiting to ambush a seal. This method minimizes unnecessary movement and reserves energy, maximizing the chances of a successful hunt when the opportunity arises.
Furthermore, the seasonal changes in the Arctic environment dictate the polar bear’s energy conservation strategies. During the summer months, when the ice melts and food becomes scarce, polar bears must exhibit a high level of adaptability. Some may retreat to land to scavenge for food, relying on an omnivorous diet. This dietary flexibility is crucial as it diverts energy use toward finding alternative sources of sustenance rather than fruitless seal hunts. The ability to switch up their diet depending on the season showcases a cunning awareness of their ecological surroundings.
Environmental challenges, primarily attributed to climate change, are imposing unprecedented threats to polar bear populations and the mechanisms of energy conservation they have honed over eons. The melting ice caps mean diminished hunting grounds and longer fasting periods for these bears. As sea ice recedes, the distance to hunting grounds increases, necessitating additional energy expenditure that could compromise their survival. The delicate balance they maintain teeters as climate change disrupts their habitat, forcing a re-evaluation of their energy conservation strategies.
In conclusion, polar bears epitomize the resilience of life in extreme conditions through a combination of anatomical, behavioral, and ecological strategies for energy conservation. From their blubber insulation to hunting techniques, these magnificent animals exhibit a well orchestrated adaptation to survive in the icy domains of the Arctic. However, as climate change looms, the very essence of polar bear survival is challenged. The shifting landscape and its far-reaching effects on energy conservation warrants urgent attention. By rethinking our relationship with the environment and addressing the fundamental issues of climate change, we can foster a future where polar bears continue to roam the Arctic with the resilience and grace they have embodied for generations.