Have you ever wondered how a simple pulley system can teach us profound lessons about the conservation of energy? Imagine a world where mechanical advantage can be harnessed to elevate heavy objects with minimal effort. This brings forth a playful challenge: if a pulley makes work easier, does it really save energy? Or is it simply redistributing the input required? In a world grappling with energy consumption and environmental degradation, understanding these concepts holds far-reaching implications.
To delve into this, we must first elucidate the fundamental principles of a pulley system and the laws of physics that govern energy. In its essence, a pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft designed to support movement and change the direction of force. By redirecting force, a pulley system provides mechanical advantage, allowing a smaller input force to lift larger weights over a distance. This principle is enshrined in the law of conservation of energy, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
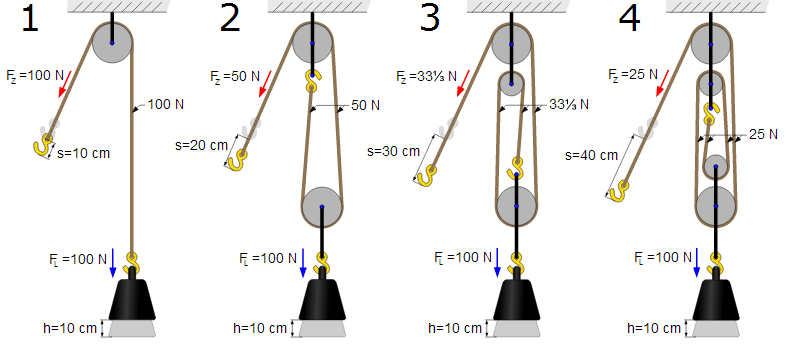
The working mechanism of a pulley illustrates the intricate interplay between force, distance, and energy. The work done on an object is defined as the product of force and distance (W = F × d). Consider a scenario where an individual attempts to lift a weight directly. The effort exerted corresponds directly to the weight lifted, and hence the energy expended is substantial. In contrast, employing a single fixed pulley allows the individual to pull down with force, redistributing the effort over a longer distance. Thus, while the force required diminishes, the distance through which the force is applied increases, preserving the total amount of work done.
Let’s consider a practical example: lifting a load that weighs 100 kilograms. If one were to lift this load vertically using only human strength, the physical exertion required would be immense. However, by incorporating a pulley, the force required may be halved if the pulley is fixed. The operator pulls downwards, causing the load to ascend with grounded mechanical efficiency. Herein lies the crux of the discussion: energy conservation prevails as the work input equals the work output. However, it is vital to remember that energy is not conserved in the form of ‘reduction of effort’; rather, it is maintained through the conversion of movement and direction.
A more complex system can involve multiple pulleys, also known as a block and tackle. This configuration further amplifies mechanical advantage; as the number of pulleys increases, the force required decreases. This setup raises an intriguing viewpoint concerning energy conservation. While the load becomes easier to lift, the distance moved increases suitably. Thus, the total energy input remains constant. This rhythmic balance of forces lends itself to broader applications beyond simple mechanical tasks. For instance, industries utilize such systems for efficient transportation of raw materials, minimizing energy wastage and reducing fossil fuel consumption.
Despite the profound advantages, it is critical to recognize the inefficiencies that accompany any mechanical system. Friction, for instance, generates heat and represents an energy loss. In the case of pulley systems, the materials used, pulley quality, and installation affect the overall efficiency. The challenge lies in optimizing these systems to minimize energy losses while maximizing mechanical advantage. Such enhancements can contribute to sustainable practices in engineering and energy management.
Now, let us explore the implications of pulley mechanisms in broader environmental contexts. By leveraging pulley systems effectively, industries can reduce their energy footprint. The advancement of technology has led to the production of lightweight and durable materials, improving system efficiency. Thus, not only do pulleys illustrate conservation principles, but they can also serve as integral components in green technology initiatives. This not only promotes energy conservation but also fosters a culture of resource stewardship.
Educationally, pulley systems serve as an engaging entry point into discussions about force dynamics and energy principles. In classrooms, educators can utilize hands-on experiments to demonstrate these concepts, fortifying students’ comprehension of physics and environmental responsibility. By engaging young minds in such explorations, the next generation can be inspired to innovate and employ sustainable systems in their future endeavors.
As we look ahead, the potential for pulley systems extends far beyond academic understanding. They may enable us to rethink traditional methodologies across various sectors. From construction to logistics, harnessing the power of simple machines can lead to significant reductions in energy use. Ultimately, this elucidates a pressing paradigm shift: achieving energy efficiency and sustainability requires reimagining even the simplest of tools.
Addressing the challenge of climate change necessitates comprehensive understanding and innovative thinking in all aspects of society. By appreciating the role of pulleys in the context of energy conservation, we begin to unlock new pathways to sustainability. Just as these mechanical devices affect our physical environment, they can inspire a philosophical shift in how we regard energy consumption. In embracing these principles, we move closer to a world where efficiency and environmental stewardship become synonymous, ultimately contributing to a healthier planet.
In conclusion, how do pulley systems illustrate the conservation of energy? They serve as a physical representation of energy transformation through mechanical advantage, embodying the delicate balance between force, distance, and work. The journey towards sustainability is replete with opportunities, and understanding the potential of seemingly simplistic systems can lead us toward a more energy-conscious era. The playful question about the efficiency of pulleys beckons for deeper exploration—a pursuit that may ultimately drive actionable change in our ongoing battle against climate change.