The harnessing of wind energy represents a monumental shift in the global energy paradigm. As climate change poses an increasing threat to our ecosystems and way of life, the need for sustainable energy sources has never been more pressing. Wind energy, a cornerstone of renewable power, offers immense potential when conserved and utilized effectively. Understanding how to conserve wind energy—while simultaneously appreciating its vast capabilities—could lead to a more sustainable future.
The Essence of Wind Energy
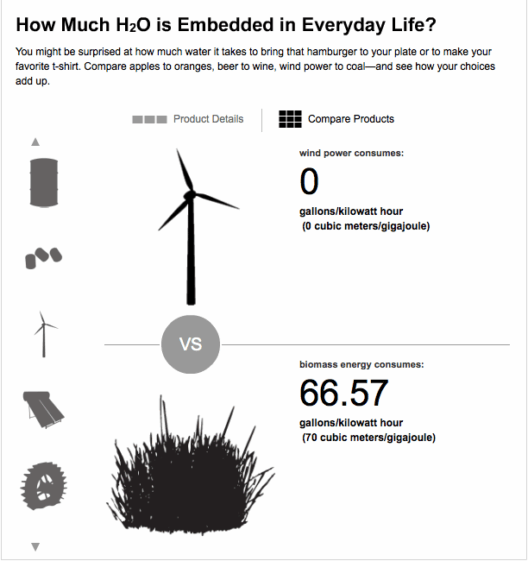
Wind energy derives its force from the movement of air, generated by the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface by the sun. This natural phenomenon can be converted into mechanical power via wind turbines, primarily designed to generate electricity. The advantages of wind energy are manifold: it is abundant, inexhaustible, and emits no greenhouse gases during operation. Nevertheless, the conservation of wind energy is paramount in optimizing its benefits without compromising other ecological systems.
Strategic Implementation of Wind Turbines
Effective conservation begins at the site selection phase for wind turbines. Placing turbines in areas with consistent and strong winds maximizes energy production and minimizes the need for excessive infrastructure. These locations—often found on hilltops, ridgelines, and open plains—foster optimal wind flow, reducing turbulence and ensuring a steadier power output. Careful consideration should also be given to local wildlife, as poorly planned wind farms may disrupt migratory paths and habitats.
Utilizing Advanced Technology
The advent of sophisticated technologies enhances the conservation of wind energy. Innovative turbine designs, incorporating larger blades and improved aerodynamics, enable the capture of more wind energy at lower wind speeds. Furthermore, the implementation of smart grid technologies allows for real-time monitoring and optimization of wind power generation. Energy storage systems, such as battery storage, can collect excess energy generated during peak wind periods, thereby providing a consistent energy supply during calmer times.
Environmental Integration
The integration of wind energy within existing ecosystems is crucial for conservation. Erecting wind farms in synergy with agricultural practices can yield a dual benefit; farmland can coexist with energy production. This approach, often termed dual-use or agrivoltaics, allows farmers to harness wind energy while simultaneously cultivating crops. Not only does this conserve space, but it also stimulates local economies and bolsters food security, addressing multiple sustainability challenges in one cohesive strategy.
Community Engagement and Education
Community involvement plays an indispensable role in the successful conservation of wind energy. Public awareness campaigns can elucidate the benefits and functionalities of wind power, dispelling myths and fostering broader acceptance. Engaging local communities in energy production initiatives—such as community wind projects—can further enhance conservation efforts. When individuals stake a claim in the energy they consume, a shift toward mindful energy practices is cultivated.
Policy and Legislation
The importance of robust policy frameworks cannot be overstated in the quest for effective wind energy conservation. Governments must implement and enforce regulations that support research, development, and deployment of wind technology. Incentives such as tax credits, grants, or subsidies for wind energy projects can encourage investment and innovation. By creating a conducive environment for growth, policies can facilitate the transition towards a renewable future while preserving existing ecosystems and communities.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the promises of wind energy, challenges persist that must be surmounted for effective conservation. One such challenge is the intermittent nature of wind; energy output can fluctuate significantly based on weather conditions. This unpredictability necessitates advancements in energy storage solutions and diversification of energy sources to maintain grid stability. Moreover, aesthetic concerns and potential noise disruptions from turbines can lead to public opposition. Balancing environmental benefits with local interests remains an ongoing dialogue.
The Future of Wind Conservation
The momentum for wind energy adoption is accelerating globally. As technology evolves, the efficiency of wind power generation will likely improve. Cutting-edge innovations, such as floating wind turbines, expand the potential to harness wind energy offshore, where winds are typically stronger and more consistent. These advancements promise not only to amplify energy capture but also to enable countries with limited land resources to tap into this renewable source effectively.
Conclusion: A Paradigm Shift
Conserving wind energy necessitates a paradigm shift in how we perceive and utilize our natural resources. By synergizing technology, community engagement, and policy advocacy, the potential for wind energy to play a pivotal role in mitigating climate change can be realized. This endeavor to conserve wind energy is not merely a quest for energy efficiency; it embodies a commitment to protecting our planet for generations to come. As we embark on this journey, we must remain inquisitive, continually seeking innovative solutions that respect both human needs and the environment. The future hinges on our capacity to embrace these possibilities, ensuring that we not only tap into the winds of change but do so wisely and sustainably.