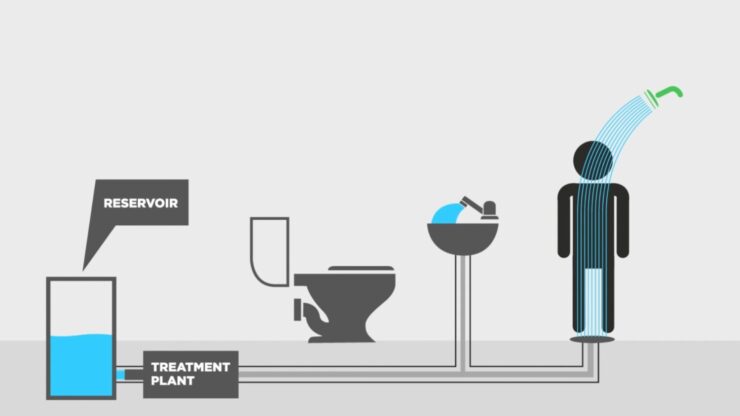
In an era dominated by climate crises, understanding innovative solutions to conserve resources is paramount. One such solution that is gaining traction is greywater recycling. Greywater, the relatively clean wastewater generated from household activities such as washing dishes, laundry, and bathing, offers an unprecedented opportunity to conserve water and, consequently, energy. The process of reclaiming this resource is not just beneficial for water conservation; it also presents substantial energy-saving potential, thereby promising a paradigm shift in how we perceive and utilize our water resources.
The first facet to consider is how traditional water usage involves a substantial energy input. Water must be sourced, treated, and transported, which requires electricity and fossil fuels. Greywater recycling mitigates this by reusing water within its original context, drastically reducing the demand for freshly treated potable water. When households treat and recycle greywater, they lessen the strain on municipal water treatment facilities, which in turn reduces the energy expended in processing and delivering clean water. The energy embedded in the production of this primary water supply dissipates significantly when one opts for greywater solutions.
When analyzing water conservation through greywater recycling, it is crucial to examine the energy costs associated with heating water. Heating water for showers, baths, or dishwashing is one of the most energy-intensive household activities. Greywater recycling systems, particularly when integrated with advanced technologies, allow for the collection of warm water from showers or sinks. This warm greywater can then be reused for irrigation or toilet flushing without the need for additional heating. The energy saved in this process can be transformative. Rather than continuously heating fresh water, households can decrease energy consumption, contributing to lower utility bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
Moreover, let’s delve into the environmental implications. Conventional water systems are often fraught with inefficiency. Water must be extensively treated to meet potable standards, incurring high energy costs. In stark contrast, greywater, typically free of harmful pathogens and chemicals when sourced from certain activities, can bypass a substantial portion of this treatment. By repurposing greywater, municipalities can alleviate the energy-demanding processes associated with water purification. This not only decreases operational energy costs but also reduces the overall consumption of fossil fuels associated with water treatment plants.
In further exploring the interconnectivity of water conservation and energy savings, it’s essential to recognize the impact of drought and water scarcity on energy production. Hydroelectric power, a significant renewable energy source, relies heavily on accessible water resources. As climate change exacerbates drought conditions, the efficiency of hydroelectric plants diminishes, leading to greater reliance on fossil fuels and higher overall energy consumption. By promoting greywater recycling, more water is conserved, ensuring more consistent water levels for renewable energy production. This cyclical relationship highlights the integrated nature of energy and water resources, emphasizing the pressing need to adopt practices like greywater recycling.
Integration of greywater systems into existing infrastructure poses an additional consideration. Adopting greywater recycling on a larger scale requires shifts in regulatory frameworks, investments in technology, and public awareness. Innovative greywater systems, such as those that filter and treat greywater through natural processes like wetlands or advanced filtration methods, must be embraced. Planting a seed of curiosity about these technologies can enrich discussions surrounding sustainable practices within communities. Such integration not only reflects an ecological commitment but also serves as a tangible, empowering mechanism for common individuals to engage in energy conservation efforts.
Furthermore, educating individuals about the practicalities of greywater systems can reshape societal perceptions of water use. Informed individuals can advocate for the implementation of these systems in local governance, influencing policies that prioritize environmental sustainability. As awareness grows, so too does the potential for widespread adoption of greywater recycling, ultimately leading to substantial contributions toward energy conservation. It is vital to underscore that these systems are not just feasible but also accessible, often requiring minimal alterations to existing plumbing infrastructure.
To entice curiosity about the tangible benefits of greywater recycling, one can examine case studies from cities where such systems have been implemented. For instance, in areas facing persistent droughts, local governments incentivize greywater recycling systems, yielding palpable reductions in water consumption and energy use. These initiatives foster an environment where individuals recognize that they can be active participants in combating climate change simply by rethinking their water management practices. By showcasing success stories, a narrative begins to unfold – one that weaves together community engagement and environmental stewardship.
In conclusion, greywater recycling emerges as a linchpin in the broader conversation surrounding energy conservation and climate responsibility. Through the lens of water security, one can appreciate the intricate interconnections between water use and energy demand. By embracing innovative recycling systems, we not only address critical water scarcity but also significantly minimize the energy embedded in traditional water systems. As society stands at a pivotal juncture, characterized by increasing environmental challenges, it is imperative to regard greywater recycling as an essential practice. Envision a future where individuals, empowered by knowledge and capability, transform their water use behaviors to engender both ecological balance and energy conservation—a true testament to human ingenuity in the face of climate change.