Energy conservation is an essential pillar in the fight against climate change, interwoven intricately with science and technology. Understanding the methodologies and innovations that underpin energy conservation not only elevates our grasp of environmental issues but also empowers individuals and organizations to enact meaningful change. The following sections explore various facets of energy conservation, highlighting scientific principles, technological applications, and the potential for future developments.
Understanding Energy Conservation
At its core, energy conservation refers to the practice of reducing energy consumption by employing various strategies and technologies. This principle is grounded in the law of conservation of energy, which asserts that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another. Thus, conserving energy effectively means minimizing waste and optimizing the use of existing energy resources.
Scientific Principles of Energy Conservation
Several fundamental scientific principles govern the practices surrounding energy conservation. The first is thermodynamics, which examines the relationship between heat, energy, and work. The second law of thermodynamics posits that energy transfers occur in ways that increase entropy, which implies that energy systems can never be perfectly efficient. Understanding these concepts helps inform strategies to reduce overall energy use and enhance efficiency.
Another critical scientific finding is the impact of Joule’s heating, which illustrates how electrical energy can be transformed into heat energy, often leading to unwanted energy loss in appliances and systems. Engineers and scientists work collaboratively to create energy-efficient devices that mitigate this loss, utilizing advanced materials that boast higher thermal conductivities or insulation properties.
Technological Innovations in Energy Efficiency
Technological advancements have spurred a wave of innovations in energy conservation. One of the most prominent fields contributing to energy efficiency is the development of smart technology. Smart meters and smart grids enhance monitoring capabilities, allowing consumers and organizations to track and manage their energy usage in real time. This data-driven approach supports informed decision-making, ultimately reducing unnecessary consumption.
Moreover, energy-efficient appliances have emerged as a significant countermeasure against wasteful energy use. The incorporation of LED lighting, Energy Star-rated devices, and smart thermostats are notable examples where technology plays a crucial role in minimizing energy expenditure. LEDs, for instance, consume approximately 75% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs while lasting significantly longer, showcasing both resource efficiency and long-term savings.
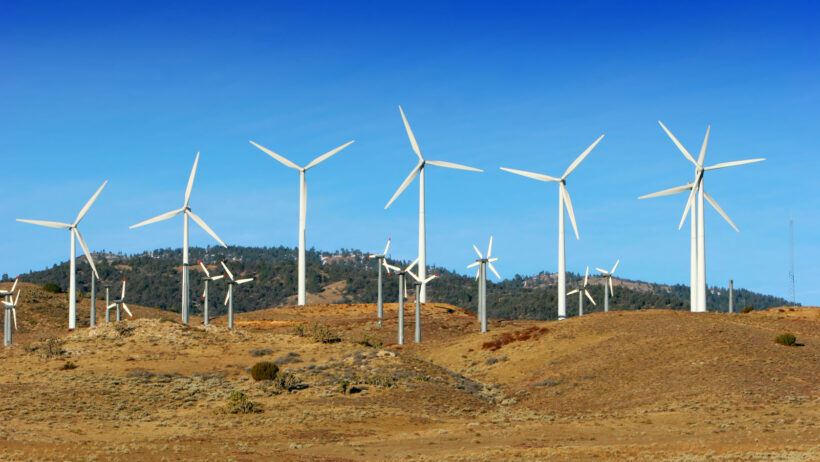
Renewable energy technologies also stand at the forefront of energy conservation. Solar panels, wind turbines, and bioenergy are alternative energy sources that contribute to sustainable practices. As these technologies evolve, efficiency improves; for instance, advancements in solar photovoltaics allow for higher energy conversion rates, leading to diminished reliance on fossil fuels. This progress reflects a paradigm shift toward sustainable energy systems.
Sustainable Practices and Behavioral Changes
While technological innovations are critical, behavioral change is equally significant in the quest for energy conservation. Encouraging individuals to adopt sustainable practices—such as reducing water heater temperatures, unplugging devices when not in use, and utilizing public transport—can yield substantial reductions in energy consumption. Educational initiatives and awareness campaigns play a vital role in fostering a culture of energy conservation within communities.
Incorporating energy conservation into daily life can be simple. For instance, families can create energy-efficient routines by being mindful of power usage during peak hours. Such habits, when adopted broadly, can reduce energy demand dramatically. Schools and workplaces can also contribute by implementing energy-saving policies and initiatives, demonstrating leadership in the ongoing effort to mitigate climate change.
The Role of Policy and Regulation
Effective energy conservation is not solely a grassroots movement; it requires robust policy frameworks designed to promote efficiency and sustainability. Governments and regulatory agencies play a formidable role in shaping the landscape of energy use through legislation and incentives. Implementing energy standards for appliances, setting renewable energy targets, and providing tax credits for energy-efficient home improvements are examples of how policies can influence user behavior and industry practices.
International agreements, such as the Paris Accord, further underline the global commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, with energy conservation being a critical component of these efforts. Policymakers must continue to work collaboratively to establish binding commitments that prioritize energy efficiency and conservation on a global scale.
Future Trends in Energy Conservation
Looking ahead, the future of energy conservation seems promising, with emerging technologies poised to revolutionize the field. Innovations such as artificial intelligence can enhance energy management systems, enabling predictive analytics that optimize consumption patterns. Building automation systems can further streamline organizational energy strategies, making operations more efficient.
Additionally, advancements in energy storage technologies—such as high-capacity batteries—present tremendous potential. By efficiently storing excess energy, particularly from renewable sources, societies can mitigate the intermittency challenges often faced by solar and wind systems. This capability will undoubtedly facilitate a more extensive integration of renewable energy in our daily lives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fusion of science and technology has set the stage for a comprehensive approach to energy conservation. Understanding the scientific underpinnings, embracing technological advancements, promoting sustainable practices, creating supportive policies, and anticipating future innovations are all indispensable components in the fight against climate change. By embedding energy conservation into the fabric of daily life, individuals and societies can collectively contribute to a more sustainable future, significantly mitigating the impacts of climate change while simultaneously preserving the planet for generations to come.