Solar panels, akin to modern-day alchemists, convert the sun’s radiant energy into a plethora of useful resources. Their ingenious design harnesses photons, transforming them into electricity, thereby providing an eco-friendly alternative to conventional energy sources. This method of converting light into usable energy not only curtails carbon emissions but also symbolizes a vital step toward a sustainable future.
Understanding how solar panels conserve energy first necessitates a closer look at their operational mechanics. At the heart of the solar panel lies the photovoltaic (PV) cell, which serves as a conduit for the sun’s energy. When sunlight strikes a PV cell, it excites electrons, causing them to move and generate an electric current. This phenomenon, known as the photovoltaic effect, is the cornerstone of solar energy conversion. In essence, these cells allow us to capture a slice of the sun’s immense energy bounty, transforming it into electrical energy. As if night had turned into day, this remarkable process presents an opportunity to illuminate our lives sustainably.
The capture of solar energy is not just a passive act; it embodies an active engagement with nature. When sunlight shines on a solar panel, it can be likened to a farmer receiving the rains necessary for a fruitful harvest. With each beam of sunlight collected, we gather the means to power our homes, schools, and industries without depleting our planet’s finite resources. This renewable energy source stands in stark contrast to fossil fuels, which exacerbate pollution and climate change, reminding us that nature provides us with abundant energy—if only we devise clever means of harnessing it.
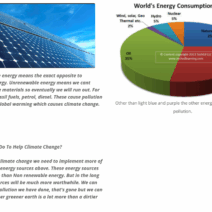
Solar panels significantly reduce dependency on non-renewable resources, thereby lessening energy wastage. Unlike traditional energy sources that require intensive extraction and transportation, solar energy is abundant and accessible. In a world where energy consumption often exceeds production—leading to shortages and environmental degradation—solar power stands as a beacon of hope. With the integration of solar panels, energy is not just consumed; it becomes a resource that can be retained and reused, similar to a farmer rotating crops to maintain soil health.
Moreover, solar panels promote energy conservation through net metering. This concept allows homeowners to generate electricity and, when they produce more than they consume, send the surplus back to the grid. It’s akin to a symbiotic relationship where energy flows back and forth—what one generates can bolster the community. This reciprocity diminishes reliance on traditional power sources and encourages a more sustainable energy ecosystem, ultimately transforming the way we perceive and utilize energy.
The aesthetic appeal of solar panels is undeniable. Their sleek, modern design can adorn rooftops and open spaces, harmonizing with their environment while simultaneously performing a crucial function. They serve as a statement of innovation, challenging the notion that energy production must be industrial and unsightly. As they gleam in the sunlight, solar panels exemplify the confluence of technology and nature, portraying an image of a brighter, greener future—one where sustainability and progress coexist.
In addition, solar panels offer economic advantages that further enhance their appeal. The initial investment might seem significant, yet the long-term savings on energy bills reveal a compelling narrative. The reduction in energy costs is akin to reaping profits from a well-tended garden. After the upfront expenditures, many homeowners find themselves in a position of financial advantage as their electricity costs diminish, and some even receive checks from their utility companies for surplus energy produced. This circular economy model encourages reinvestment in personal and community renewable energy projects, amplifying the overall impact of solar technology.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of solar panels cannot be overstated. By mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, they play a pivotal role in combating climate change. In a world grappling with the consequences of global warming—extreme weather, rising sea levels, and habitat loss—solar energy offers an alternative pathway. It provides a clear message: we need not succumb to environmental degradation; instead, we can turn toward solutions entrenched in nature. The solar revolution stands as testimony to human ingenuity at its finest, illuminating a path towards sustainable energy independence.
Nonetheless, certain challenges persist in the widespread adoption of solar technology. Infrastructure, initial costs, and technological accessibility remain hurdles that need addressing. Policymakers must strive to create a conducive environment for solar energy adoption, incentivizing individuals and businesses alike to invest in solar solutions. The transition to renewable energy sources requires collective commitment, emphasizing the importance of collaboration across government, industry, and society as a whole.
To sum up, solar panels serve as more than mere energy converters—they embody a philosophy of sustainability and innovation. Each panel captures the sun’s generosity, turning it into a resource that can underpin our energy future. By embracing this technology, we embark on a transformative journey towards energy conservation that ultimately benefits not just individuals, but the global community and the planet at large. As we continue to unveil the full potential of solar energy, we must remain steadfast in our pursuit of a sustainable world where energy is both abundant and environmentally responsible. The sun is rising on a new era of energy—let us seize the opportunity it presents.