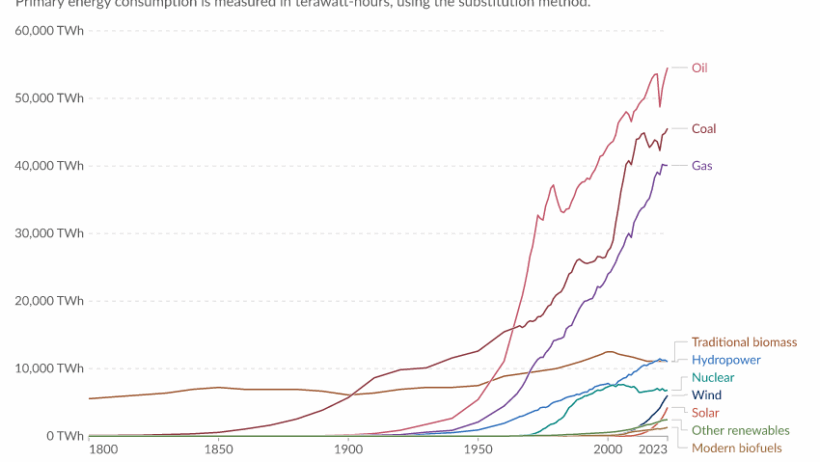
As the globe grapples with the implications of climate change, the significance of energy conservation becomes increasingly evident. This multifaceted endeavor not only aims to reduce energy consumption but also to foster sustainable practices that can alleviate the environmental burden caused by excessive energy use. An examination of global energy consumption reveals intriguing patterns in energy conservation efforts, highlighting the diverse strategies employed across various regions. In this discourse, we will elucidate how many people engage in energy conservation worldwide, the global initiatives that propel these efforts, and the impact of such practices on a sustainable future.
Energy conservation represents a conscious effort by individuals, communities, and nations to reduce their energy footprints. The degree to which energy conservation is practiced varies significantly across different demographic segments and geographic locales. In developed nations, a higher proportion of the population engages in energy-efficient practices, driven by technological advancements and heightened awareness of environmental stewardship. Conversely, in many developing countries, energy consumption levels may be lower overall, but the potential for energy conservation remains largely untapped.
Understanding the scale of energy conservation requires an assessment of its proponents. Sustainable living enthusiasts, environmental organizations, and policymakers are at the forefront of advocating for energy conservation. However, the majority of the global population—over 7 billion people—must be considered when analyzing collective efforts. Estimates suggest that billions partake in at least some form of energy conservation, whether through small daily habits or larger lifestyle changes.
The efficacy of energy conservation hinges on the cultural and socio-economic contexts within which it is implemented. For instance, communities in Scandinavia are often cited as examples of progressive energy conservation practices. With robust policies promoting renewable energy and sustainable living, these nations report high levels of energy efficiency. The energy awareness propagated through governmental campaigns, educational programs, and incentivized green initiatives encourages widespread participation, resulting in a populace eager to minimize their energy consumption.
Regions like these illustrate what can be achieved through cohesive governmental strategies coupled with active citizen participation. In contrast, in many regions of Africa and parts of Asia, the energy conservation narrative is often shaped by necessity rather than choice. Here, limited access to energy resources compels individuals to adopt practices that align closely with the principles of conservation. While the tools may differ—ranging from solar-powered devices to energy-efficient cooking methods—the end goal remains the same: minimizing energy waste while meeting essential needs.
Governmental policies play an indispensable role in facilitating energy conservation on a grand scale. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, serve as frameworks that compel nations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These accords delineate specific targets that encourage countries to invest in renewable energy production, foster energy efficiency technologies, and promote sustainable practices among the citizenry. Countries that take bold steps towards compliance with these agreements not only contribute to the fight against climate change but also cultivate environments that are amenable to energy conservation.
In recent years, grassroots movements have emerged, demonstrating the power of community-based initiatives. Local campaigns often inspire large segments of the population to adopt energy conservation habits. In regions plagued by energy scarcity, community-led programs can offer innovative solutions, ranging from cooperative solar farms to shared electric vehicle systems. These collective efforts serve as vital learning opportunities, showcasing effective energy conservation practices that can be replicated elsewhere.
The role of education cannot be overstated when discussing energy conservation and its adoption on a global scale. Educational institutions are increasingly incorporating environmental sustainability into their curricula. Initiatives that inform students and local communities about the benefits of energy conservation can engender an ethos of responsibility towards the planet. When young people are equipped with knowledge and practical skills, they are more likely to carry these values into adulthood, influencing future generations and reinforcing a culture of sustainability.
Technological innovation also holds a pivotal position in the energy conservation dialogue. Advancements in energy efficiency technologies, such as smart home systems, LED lighting, and energy-efficient appliances, have made it easier for individuals to monitor and reduce their energy usage. The proliferation of these technologies offers not only convenience but also tangible benefits in terms of energy savings. The appeal of lower utility bills often acts as a powerful incentive for consumers to embrace energy conservation practices.
Moreover, social media platforms have emerged as potent tools for disseminating information about energy conservation. Awareness campaigns can reach millions, encouraging individuals to share their experiences and strategies for reducing energy consumption. By cultivating a sense of community online, advocates can inspire action and create a ripple effect that fosters collective change. The shared narratives and practical tips showcased across these platforms can ignite interest and emphasize the importance of energy conservation in everyday life.
Ultimately, while strides have been made globally to champion energy conservation, challenges remain. The disparity in energy resources and consumption levels presents a significant obstacle to achieving universal adoption of conservation practices. Furthermore, entrenched economic models reliant on fossil fuel consumption can complicate efforts toward sustainability. The transition to a greener future mandates cooperation across borders, sectors, and communities. Only through collaborative action can the world strive towards a sustainable energy future.
In conclusion, the engagement of individuals in energy conservation is a mosaic, characterized by diverse practices, cultural influences, and technological advancements. Global efforts to enhance energy efficiency stand at the intersection of personal responsibility and systemic change. By fostering a multi-dimensional understanding of energy conservation, the world can pursue pathways that lead to a sustainable future. Collective action, ambitions, and education are paramount to overcoming the myriad barriers that obstruct energy conservation efforts. The future necessitates a harmonious balance between energy consumption and conservation, as humanity charts its course in the face of climate change.