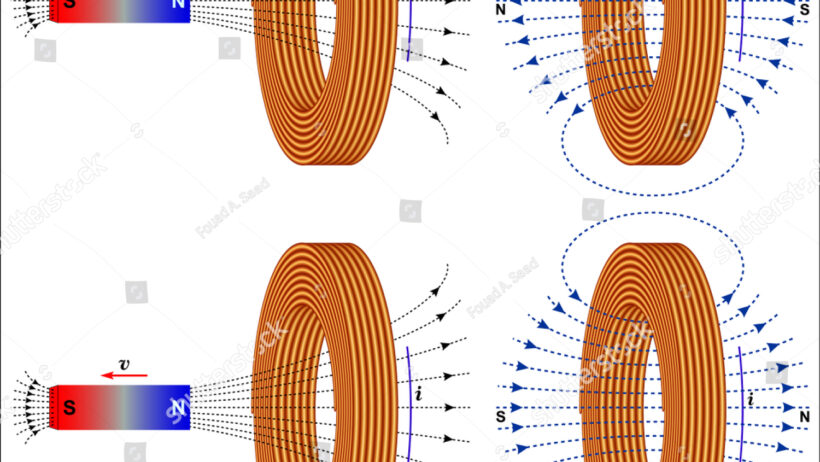
The realm of electromagnetism unveils a fascinating interplay between energy, motion, and forces that govern our universe. Among the pivotal principles that underlie this intricate dance is Lenz’s Law, which eloquently embodies the conservation of energy. Lenz’s Law asserts that the direction of induced electromotive force (EMF) always opposes the change in magnetic flux that produces it. This profound relationship not only serves as a fundamental characteristic of electromagnetic induction but resonates with the broader principle of energy conservation, creating an elegant harmony within natural processes.
In essence, Lenz’s Law is an empirical observation that arises from the continuous efforts of nature to maintain equilibrium. One might observe this law in action when moving a magnet toward a coil of wire. As the magnet approaches, it influences the magnetic field around the coil, inducing a current. However, this induced current—according to Lenz’s Law—flows in such a direction that it generates a magnetic field opposing the incoming magnet’s field. This resistance epitomizes one of the most astounding observations in physics; nature inherently salvages and tends to preserve energy.
To appreciate the depth of this phenomenon, one must explore the relationship between induction and conservation. Conservation of energy, often lauded as one of the foundational principles of physics, posits that the total energy within a closed system remains constant, although energy may transform from one form to another. Lenz’s Law acts as a manifestation of this premise. When a current is induced, it does not create energy from thin air; rather, it transfigures the energy involved in varying magnetic fields into electrical energy. The magnetic field, originating from the moving magnet, diminishes as it induces a current, ensuring that energy is neither generated nor lost, but conserved in its various forms.
This intricate relationship fosters a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of physical laws. The antagonistic nature of the induced current, as defined by Lenz’s Law, illustrates the inherent struggle within electromagnetic systems to abide by the conservation of energy. A magnet’s approach incites a diligent response from the coil, preserving the system’s stability by effectively countering changes in its magnetic environment. This empirical reality elicited puzzlement and curiosity among early scientists, laying the groundwork for future explorations in electromagnetic theory.
Furthermore, the implications of Lenz’s Law extend beyond theoretical physics into practical applications. Consider the technologies harnessing electromagnetic induction, such as electric generators and transformers. In electric generators, mechanical energy—often derived from renewable sources like wind or hydro—is employed to rotate coils within magnetic fields. The induced currents generated by this movement satisfy both Lenz’s Law and conservation principles. The energy from the mechanical input is intricately transformed into electrical energy, paving the way for ubiquitous applications in modern society.
Moreover, in transformers—essential devices for voltage conversion—the role of Lenz’s Law is equally paramount. When an alternating current passes through one coil, it induces a varying magnetic field. The second coil, strategically situated within this field, experiences changes in magnetic flux. Consequently, Lenz’s Law dictates that the induced current generated in the secondary coil flows in a direction opposing the changes produced by the primary coil. This opposition is crucial in effectively converting voltage levels while adhering to the conservation of energy, allowing electricity to traverse vast distances with minimal loss.
The elegance of Lenz’s Law also fosters a broader understanding of energy efficacy in our daily lives. In an era increasingly mindful of environmental impacts, recognizing the principles of energy conservation becomes imperative. Embracing renewable energy systems, which actively rely on electromagnetic induction, underscores our collective responsibility to foster energy sustainability. The transition to technologies like solar panels and wind turbines, inherently grounded in electromagnetic phenomena, aligns seamlessly with the conservation of energy, forming a resilient framework that underpins developmental strategies for reducing carbon footprints and combating climate change.
Yet, despite the extensive pedagogical discourse surrounding Lenz’s Law, intriguing inquiries persist. Why does nature exhibit such steadfastness in conserving energy? The mechanisms of electromagnetism provoke admiration but also lead to philosophical ruminations about the fundamental laws of the universe. Nature’s proclivity towards equilibrium suggests that systems inherently evolve to avert imbalance, thus perpetuating stability within their realms. This behavioral consequence sparks curiosity, inviting inquisitive minds to delve deeper into the exquisite fabric of reality woven by physical laws.
In conclusion, Lenz’s Law epitomizes the intricate relationship between electromagnetic phenomena and the conservation of energy. Through its opposition to changes in magnetic flux, the law manifests nature’s commitment to perseverance and equilibrium. As we decipher the complexities of electromagnetism, we unveil fundamental truths that resonate deeply with contemporary challenges. By fostering a comprehensive understanding of energy conservation through the lens of Lenz’s Law, we equip ourselves with the intellectual sustenance necessary to navigate the shifting tides of modernity and environmental responsibility. Engaging with these principles not only illuminates fascinating intersections within physics but also propels collective human endeavors toward a sustainable and harmonious future aligned with the laws of nature.