Energy conservation is a pivotal element in the pursuit of sustainability, addressing the pressing challenges posed by climate change and environmental degradation. It involves the deliberate reduction of energy consumption through thoughtful practices, innovations, and policies, fostering a balanced relationship between human activities and the natural world. This essay will explore the various dimensions of energy conservation, elucidate its benefits, and provide a comprehensive outlook on how individuals and communities can engage in this vital endeavor.
The advent of modern industrialization has led to an exponential increase in energy demand. Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas, have been the primary sources of energy for various sectors, including transportation, residential, and industrial. However, the extensive reliance on these non-renewable resources has precipitated various environmental crises, including air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and habitat destruction. Consequently, energy conservation emerges as a crucial strategy for mitigating these adverse effects.
One of the primary methods of energy conservation is enhancing energy efficiency. This concept refers to using less energy to achieve the same level of output or service. For instance, transitioning from incandescent light bulbs to LED lighting can significantly reduce electricity consumption. LED bulbs use at least 75% less energy than traditional bulbs and last up to 25 times longer. By adopting energy-efficient technologies, households and businesses can drastically lower their energy expenditures while simultaneously reducing their carbon footprint.
In addition to substituting energy inefficient devices with energy-saving alternatives, optimizing energy use through behavioral changes is equally important. Simple habits such as turning off lights when not in use, unplugging electronic devices, and utilizing natural light can lead to significant energy savings. Moreover, the implementation of smart home technologies, which automate heating and cooling systems based on occupancy and need, exemplifies how behavioral shifts coupled with technology can result in substantial conservation.
Another key area of energy conservation involves the building sector. The construction of energy-efficient buildings through sustainable design principles can dramatically lower energy consumption. Techniques such as passive solar design, proper insulation, and the use of energy-efficient windows contribute to minimizing the energy required for heating and cooling. Additionally, green building certifications like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) encourage the use of sustainable materials and practices, promoting a holistic approach to energy conservation.
Furthermore, the transportation sector is a significant contributor to energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Transitioning to more sustainable modes of transport—such as walking, cycling, using public transit, or driving fuel-efficient or electric vehicles—can significantly curtail energy usage in this sector. Urban planning that prioritizes cycling and walking infrastructure, combined with effective public transportation systems, can foster a culture of sustainability while reducing reliance on personal vehicles.
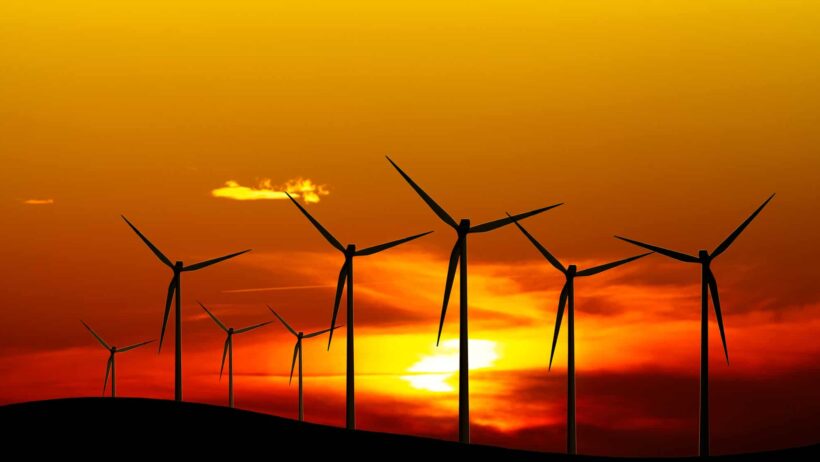
Renewable energy sources—such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal—play a quintessential role in energy conservation strategies. They provide a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels, allowing for the generation of clean energy. While the shift towards renewables is vital, integrating these technologies into existing energy systems requires significant advancements in energy storage solutions. This will ensure a reliable supply of energy even when renewable sources are not actively generating power.
At the community level, promoting energy conservation can be accomplished through educational programs and initiatives aimed at raising awareness about the importance of sustainable practices. Schools, local governments, and non-profit organizations can engage in outreach efforts to inform residents about energy-saving practices. Community challenges that incentivize reducing energy consumption—such as friendly competitions to see which neighborhood can conserve the most energy over a month—can also enhance participation and foster a collective spirit of stewardship.
Legislation and policy play an instrumental role in promoting energy conservation at broader levels. Governments worldwide are implementing policies to encourage sustainability through tax credits, grants, and rebates for energy-efficient appliances, building retrofits, and renewable energy installations. By establishing mandatory energy efficiency standards, governments can compel industries to invest in innovative technologies that reduce consumption while fostering a transition to a low-carbon economy.
The effects of energy conservation extend beyond the immediate advantages of reducing bills and emissions. They also encompass broader societal impacts. By prioritizing energy efficiency and sustainable practices, communities can experience improved air quality, enhanced public health, and economic benefits through job creation in green industries. Furthermore, an increased focus on sustainability fosters resilience against the fluctuating availability of fossil fuels and the economic uncertainties tied to them.
On an individual level, everyone can contribute to this global effort. Simple practices such as evaluating one’s energy consumption patterns, setting energy-saving goals, and participating in community initiatives can have profound ripple effects. Engaging in dialogues about sustainability, advocating for stronger environmental policies, and supporting businesses that prioritize energy conservation can galvanize collective action.
In conclusion, the multifaceted approach to energy conservation encapsulates a myriad of strategies and practices that can coalesce to create a sustainable future. By focusing on energy efficiency, optimizing consumption behaviors, advocating for policy changes, and utilizing renewable energy, a collective effort can be made to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, combat climate change, and safeguard our planet for future generations. Energy conservation is not merely an obligation; it is a necessity in the quest for sustainability, making it imperative for individuals, communities, and nations to champion this cause.