Solar energy, an inexhaustible and renewable resource, has emerged as a crucial ally in the quest to combat climate change and conserve energy. The sun, an abundant powerhouse, showers the Earth with electro-magnetic radiation that can be harnessed through solar panels. Understanding how to effectively utilize this stellar resource not only mitigates carbon emissions but also promotes sustainability in our everyday lives. This discourse elucidates various strategies for optimizing solar panel usage, emphasizing the myriad benefits of solar energy.
Understanding Solar Panels
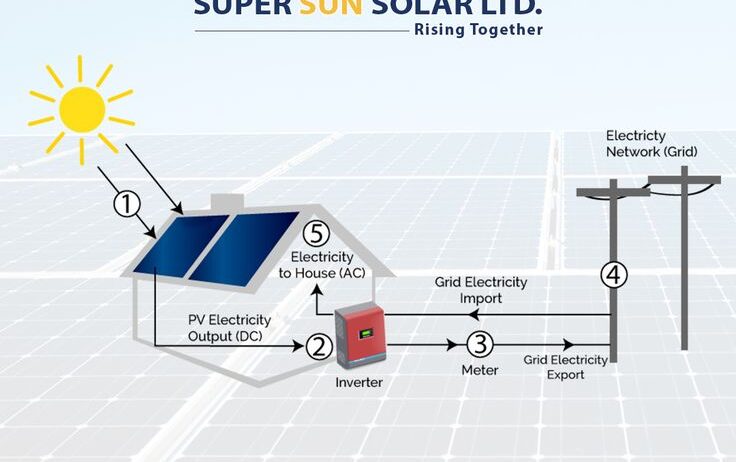
At the core of harnessing solar energy are photovoltaic (PV) panels, which convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This process involves the excitation of electrons within semiconductor materials, typically silicon-based, when exposed to sunlight. As electrons are mobilized, they generate an electric current that can be used to power homes, businesses, and even electric vehicles. Beyond their functionality, solar panels often signify a commitment to environmental stewardship and a demand for sustainable practices.
Optimal Placement and Orientation
The efficacy of solar panels hinges substantially on their location and orientation. To maximize energy absorption, panels should ideally be installed in locations with minimal shading from trees, buildings, or other obstructions. Furthermore, the orientation of the panels plays a pivotal role; south-facing installations generally capture the most sunlight in the northern hemisphere. The angle of tilt is equally significant and can be adjusted according to seasonal sun paths to further improve efficiency. Regular adjustments may seem cumbersome but can yield substantial gains in energy collection.
Energy Storage Solutions
While direct solar energy use is laudable, the intermittency of sunlight compels consideration of energy storage solutions. Incorporating battery systems, like lithium-ion or lead-acid batteries, allows homeowners to store excess energy generated during sunny days for consumption during evening hours or overcast conditions. By utilizing battery storage, individuals can enhance their energy independence and diminish reliance on fossil fuel-based energy sources. The cost-benefit analysis of installing such systems reveals potential savings on energy bills over the long term.
Embracing Smart Technology
In an age of digital innovation, the integration of smart technologies can significantly enhance the efficiency of solar energy systems. Smart inverters and monitoring systems facilitate real-time tracking of energy production and consumption. This data can identify patterns and inefficiencies, enabling users to make informed decisions about energy usage. Such technologies can automate energy consumption, redirecting power usage to off-peak hours or when solar generation peaks, further optimizing the benefits garnered from solar panels.
Solar Energy for Heating
Beyond electricity generation, solar energy can be adeptly employed for heating purposes, particularly through solar thermal systems. These systems utilize solar collectors to absorb direct sunlight, transferring heat to water or air for domestic hot water needs or space heating. The integration of solar thermal technology with existing heating systems can markedly reduce reliance on conventional heating fuels, leading to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and overall energy consumption.
Government Incentives and Financial Considerations
Transitioning to solar energy installation encompasses not only technical considerations but also economic implications. Various governments and local jurisdictions offer incentives—such as tax credits, rebates, and grants—to encourage solar adoption. These financial mechanisms significantly reduce the upfront costs associated with purchasing and installing solar panels, allowing individuals to recoup their investments more swiftly. Additionally, as the technology matures, the prices of solar panels have plummeted over the past decade, making this an increasingly viable financial investment.
Community Solar Initiatives
For those unable to install solar panels on their property due to financial constraints or structural limitations, community solar initiatives provide a pragmatic alternative. These programs allow individuals to invest in or subscribe to a larger solar energy project, sharing the benefits and savings associated with collective solar generation. Community solar not only democratizes access to renewable energy but also fosters a sense of camaraderie and shared responsibility in the fight against climate change.
Sustainability Beyond Solar
While solar energy adoption is a monumental step towards reducing carbon footprints, it is but one piece of the sustainability puzzle. Complementing solar energy with other renewable sources, such as wind and hydro, can create a more resilient and diversified energy portfolio. Furthermore, the embrace of energy-efficient practices—like utilizing LED lighting, insulating homes, and optimizing appliances—further amplifies the benefits of solar energy by minimizing overall consumption.
Conclusion
Harnessing solar energy presents a compelling opportunity to not only conserve energy but also contribute positively to the planet’s ecological balance. The fusion of technology, economics, and community engagement in promoting solar energy reflects a paradigm shift towards sustainable living. As individuals become increasingly aware of their carbon footprints and the pressing urgency of climate action, solar panels emerge not merely as functional devices, but as symbols of hope and commitment to a sustainable future. Though challenges remain, the synthesis of ingenuity, cooperation, and environmental consciousness heralds a brighter path forward—one where energy conservation becomes a shared venture, empowered by the sun itself.