In the contemporary age, where climate change looms large, understanding how to conserve energy through electricity has become paramount. Utilizing electrical resources judiciously not only reduces carbon footprints but also results in financial savings and promotes a more sustainable future. This discourse examines various strategies and methods for smart electricity usage, facilitating cleaner energy consumption without compromising on comfort or convenience.
To begin with, it is essential to comprehend the significance of energy conservation. Electricity is intricately linked to fossil fuels, the burning of which contributes to atmospheric pollution and the greenhouse effect. By conserving energy, we mitigate the demand for electricity generation, consequently reducing harmful emissions. This conservational ethos engenders a ripple effect; as more individuals engage in energy-efficient practices, the cumulative impact on the environment becomes markedly less detrimental.
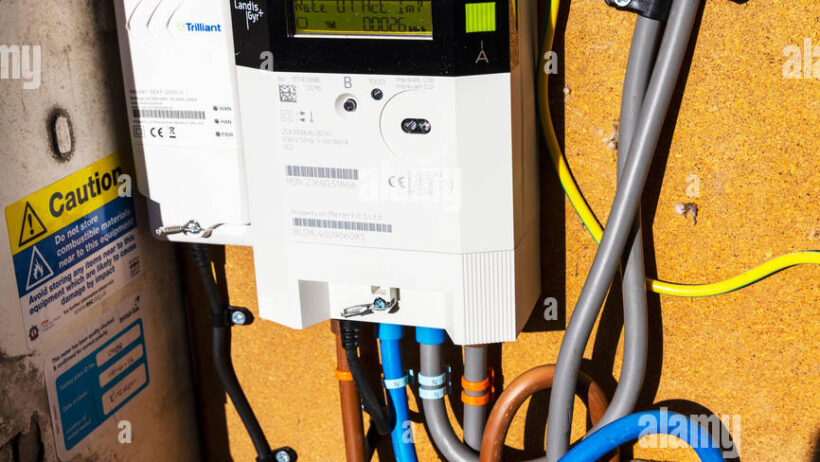
One of the most efficacious strategies in energy conservation is the employment of smart technology, particularly smart meters. These devices facilitate real-time monitoring of energy consumption, empowering consumers to make informed decisions about their usage. By providing granular insights into energy habits, smart meters encourage users to adjust their consumption patterns—turning off appliances during peak demand hours or acknowledging the inefficiency of certain devices. The increase in awareness that comes from monitoring consumption patterns leads to a conscientious approach to energy usage.
In conjunction with smart meters, the implementation of energy-efficient appliances stands as a cornerstone of energy conservation. The market is replete with appliances boasting high energy-efficiency ratings—such as ENERGY STAR certified products—that utilize less electricity while maintaining, or even enhancing, performance. These appliances are designed with cutting-edge technologies that reduce waste and optimize functionality. For instance, modern refrigerators operate efficiently at lower temperatures, while LED lighting uses a fraction of the energy compared to incandescent bulbs. Replacing outdated appliances may require an initial investment; however, the long-term savings on utility bills and the corresponding positive environmental impact warrants serious consideration.
Moreover, home insulation plays an instrumental role in energy conservation. Properly insulating a residence minimizes the need for heating and cooling, two major contributors to electricity consumption. By mitigating heat loss in the winter and keeping interiors cool in the summer, households can significantly decrease their reliance on HVAC systems. Techniques for enhancing insulation encompass the use of weather stripping, thermal curtains, and adequate attic insulation. More comprehensive measures, such as retrofit insulation for walls and floors, can yield substantial energy savings over time.
In addition to insulation, the strategic management of heating and cooling systems contributes to optimal energy usage. Programmable thermostats enable households to regulate temperatures based on occupancy patterns. By lowering temperatures during unoccupied hours or overnight, energy consumption reduces drastically. A setback of just a few degrees can lead to remarkable reductions in energy usage, demonstrating how small alterations can result in significant conservation. Furthermore, incorporating ceiling fans can enhance air circulation and comfort, allowing for higher thermostat settings without sacrificing comfort.
Equally important is the mindful use of lighting. Traditional practices such as relying predominantly on artificial lighting not only escalate energy usage but also contribute to light pollution, which can adversely impact nocturnal ecosystems. By harnessing natural daylight whenever possible, individuals can reduce dependence on electric lighting. When artificial lighting is necessary, utilizing dimmers and motion sensors can further optimize energy consumption. Additionally, to promote longevity and efficient usage of light fixtures, regular maintenance—like cleaning bulbs and fixtures—ensures maximum illumination efficacy.
The role of renewable energy sources cannot be overstated when discussing sustainable electricity usage. Solar panels, for instance, have garnered attention for their ability to convert sunlight into usable electricity, thereby dramatically reducing reliance on grid power. For homeowners, the adoption of solar energy systems can initially prove costly; yet, tax incentives and decreasing installation costs have made this an increasingly viable option. Once installed, solar panels diminish monthly electricity bills and, as technology advances, often result in surplus energy that can be sold back to the grid.
An integral component of energy conservation is community engagement and education. Promoting awareness within neighborhoods and communities fosters collaborative efforts toward sustainable practices. Community initiatives, like local clean energy cooperatives or group purchasing programs for solar panel installations, create an atmosphere of shared responsibility. Schools, local organizations, and workplaces can also serve as platforms for energy conservation education, spreading knowledge about sustainable habits that can be adopted on both micro and macro levels.
In summary, conserving energy through smart electricity usage is not only beneficial but imperative. By embracing advanced technologies such as smart meters, investing in energy-efficient appliances, enhancing home insulation, and managing heating and cooling systems wisely, individuals can significantly alter their energy consumption footprint. Furthermore, promoting renewable energy sources alongside community engagement cultivates a collective movement toward a more sustainable future. Ultimately, every small action contributes to the larger goal of mitigating climate change, and it is the responsibility of each individual to partake in this crucial endeavor.