The Law of Conservation of Energy is a fundamental principle in physics that states energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another. Understanding this principle is crucial for students, as it lays the groundwork for various scientific concepts and helps instigate an appreciation for the environment. Teaching this law effectively requires a strategically diverse approach that caters to varied learning styles. Here are several classroom strategies and techniques to facilitate the comprehension of the Law of Conservation of Energy.
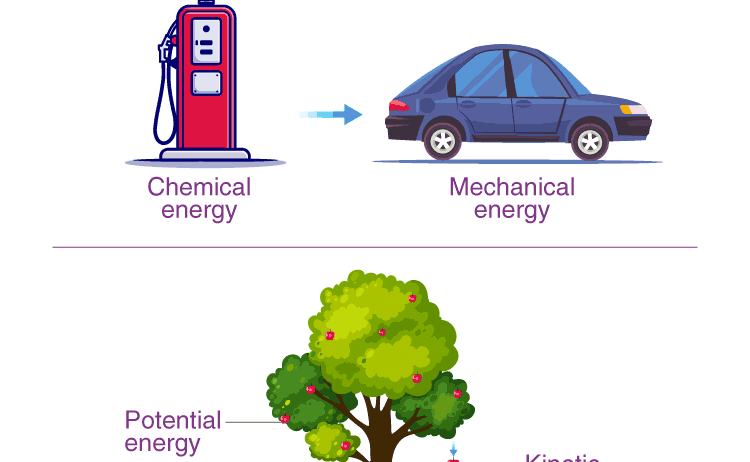
Firstly, it is paramount to establish a solid theoretical foundation. Begin with a clear and concise explanation of the law. Use straightforward language to articulate that energy exists in many forms, such as kinetic, potential, thermal, and chemical energy. Illustrate these concepts with tangible real-world examples—like a roller coaster’s kinetic energy transforming to potential energy at the peak, or the transformation of electrical energy in a toaster to thermal energy.
Next, employ visual aids to supplement explanations. Visual representations can be particularly effective for grasping abstract concepts. Diagrams, charts, or videos illustrating energy transformations can cement understanding. For instance, showing a roller coaster ride can effectively visualize the interchange of potential and kinetic energy. Consider using multimedia resources, such as animations and simulations, to depict dynamic interactions of energy in various systems.
To cater to kinesthetic learners, hands-on activities are invaluable. Facilitate experiments that allow students to observe energy transformations in action. A simple choice could be a pendulum swing to demonstrate kinetic and potential energy shifts. Another engaging experiment involves using a wind-up toy. As the toy operates, students can experience energy transformation first-hand, from stored elastic potential energy in the spring to kinetic energy in motion.
Furthermore, scavenger hunts can captivate students while imparting learnings about energy in their surroundings. Create a checklist of different forms of energy observable around the school or at home, such as solar panels (solar energy), electrical outlets (electrical energy), and even food items (chemical energy). This activity fosters observational skills and encourages students to think critically about energy sources in their daily lives.
Another technique to enhance retention of knowledge is to incorporate collaborative learning. Group discussions and collaborative projects enable students to engage with peers, fostering deeper understanding through dialogue. Consider assigning small groups to explore specific types of energy, such as mechanical, thermal, or chemical, and present their findings to the class. This group work cultivates a sense of accountability and encourages teamwork, while allowing students to share unique perspectives and interpretations of energy concepts.
Moreover, encourage critical thinking by integrating problem-solving exercises related to the Law of Conservation of Energy. Present hypothetical scenarios where energy is transformed in various contexts. For example, calculate the total energy at different points in a simple system, such as a roller coaster or a swinging pendulum, to demonstrate that energy remains constant, despite its changing forms. These activities challenge students to apply their knowledge, enhancing their understanding of energy conservation laws.
In addition, utilize technology to create interactive and immersive learning experiences. Educational software and online simulations can provide students with the opportunity to manipulate variables and observe the outcomes instantly. Programs like PhET Interactive Simulations offer experiments that visually depict energy transformations in a controlled environment, allowing students to gain mastery over complex processes in a safe and engaging way.
To further pique interest, introduce interdisciplinary connections. Discuss energy conservation in the context of environmental science. Highlight the significance of sustainable energy practices and the environmental impacts associated with energy consumption. This not only enforces the concept of energy conservation but also instills a sense of responsibility among students to advocate for sustainable practices in their communities.
Moreover, storytelling can serve as a powerful tool in education. Narratives that revolve around energy can help contextualize the principles at play. Create stories that illustrate the life cycle of energy in household systems or natural ecosystems, emphasizing how energy moves through different forms and the importance of energy efficiency. This method not only captures interest but also facilitates memory retention through relatable contexts.
In conclusion, teaching the Law of Conservation of Energy necessitates a multifaceted approach that acknowledges the diverse learning styles of students. By blending theoretical instruction with hands-on experiments, collaborative projects, and technology, educators can effectively convey this essential principle. Encourage critical thinking through problem-solving exercises and foster awareness of energy’s relevance in daily life through interdisciplinary applications. By implementing these diverse classroom strategies, educators can cultivate a meaningful understanding of the Law of Conservation of Energy, essential for nurturing informed, environmentally conscious citizens.