The Law of Conservation of Energy is one of the cornerstones of physics, akin to a timeless axiom that governs the intricate dance of the universe. This principle asserts that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only transform from one form to another. Imagine a carefully orchestrated symphony, where each note may change in timbre or pitch, but the melody—the essence—remains unaltered. In the same vein, energy undergoes incessant transformations, tirelessly fueling the myriad processes that constitute our reality.
At its core, the Law of Conservation of Energy provides clarity to the chaotic facets of existence. From the flickering incandescent light bulb to the roaring engines of rockets, energy exists in multifaceted forms: kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, and nuclear, to name a few. When an object is in motion, it possesses kinetic energy, while potential energy is stored, waiting for a moment of release. The transformation between these states during everyday activities, whether it’s a child sliding down a hill or a car accelerating on the highway, exemplifies this principle in action.
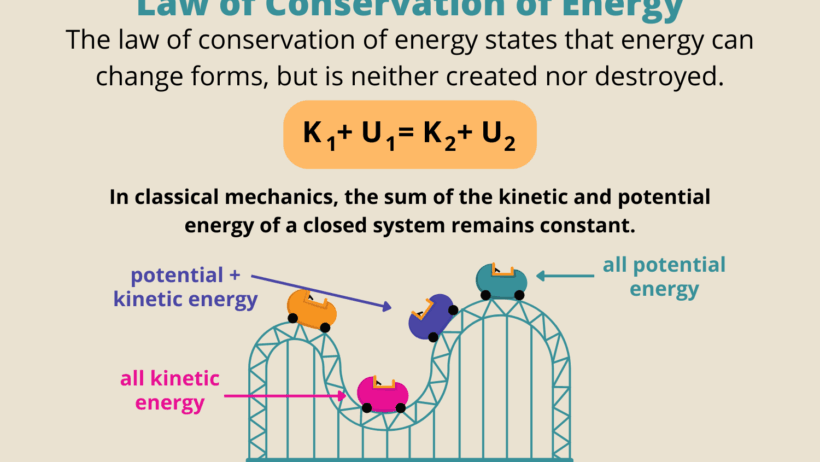
Consider a roller coaster, an exhilarating epitome of energy transformation. As the coaster climbs to its zenith, it gains potential energy; the higher the ascent, the more pronounced the accumulation. Upon its descent, this energy converts into kinetic energy, propelling the cars at dizzying speeds. This cyclical exchange is the Law of Conservation of Energy embodied. The energy that fuels enjoyment does not vanish; rather, it metamorphoses, a cyclical tale told through the language of forces and motion.
The implications of this law extend far beyond amusement parks. In nature, it forms the foundation of ecological systems. Photosynthesis serves as a compelling example, wherein sunlight is transformed into chemical energy by plants. Through this process, energy captured from the sun gets stored, facilitating not only the growth of flora but also feeding the intricate food webs that sustain wildlife and humanity alike. Energy is the vital ether, flowing through ecosystems, every organism partaking in this grand energy exchange.
Moving into the depths of chemical reactions, another layer of the law emerges. When you ignite a log in a fireplace, the potential energy stored in the wood undergoes a transformation into thermal energy and light. The warmth and illumination generated are merely transient states in the continuum of energy flow. This serves as a vivid metaphor for life’s impermanence; everything we possess, including energy, is in a constant state of flux.
In the realm of thermodynamics, the Law of Conservation of Energy operates hand-in-hand with the concept of energy efficiency. As we strive for sustainability, understanding this law becomes crucial. In modern technology, energy transformations are rarely 100% efficient. Take an internal combustion engine, a quintessential mechanism in vehicles. It converts chemical energy from fuel into kinetic energy; however, a significant portion of that energy dissipates as heat. Optimizing these processes not only conserves energy but also contributes markedly to environmental preservation, mitigating the adverse effects of our energy consumption.
This concept resonates profoundly within the sphere of renewable energy sources, an area of paramount importance in today’s world. Solar panels convert sunlight into electrical energy, while wind turbines transform kinetic energy from the wind into usable power. These forms of harnessing energy epitomize the existing law; they do not create new energy but rather tap into the abundant flows available from natural sources. As society shifts towards greener alternatives, recognizing the law equips us with the understanding necessary for innovation and sustainability.
Additionally, the implications of this law extend into the discussions surrounding climate change. As energy consumption burgeons, ecosystems and atmospheres are strained. Grasping the balance dictated by the Law of Conservation of Energy compels us to evaluate our habits and practices. Why maintain a lifestyle that disregards energy efficiency when the very essence of our environment is tied to these transformations? Each energy decision we make reverberates, illustrating our collective responsibility in protecting the planet.
A prominent metaphor of energy conservation is that of a bank account. Money, like energy, can be saved, spent, and transformed into various investments. When we use energy inefficiently, we are akin to squandered funds—depleting our reserves without accruing beneficial returns. Conversely, investing in energy efficiency is comparable to nurturing a savings account, leading to abundance over time. Embracing this understanding encourages individuals, businesses, and governments alike to act mindfully regarding energy consumption.
The Law of Conservation of Energy also finds significance in the field of astrophysics. Within the cosmos, it dictates the life cycle of celestial bodies. Stars spend billions of years transmuting hydrogen into helium, liberating energy that illuminates galaxies. Eventually, this energy depletes, leading to a star’s death, but not before instigating the birth of new elements and celestial phenomena. This perpetual cycle resonates with the rhythms of life and death on Earth, enhancing our understanding of existence at an astronomical level.
In summary, the Law of Conservation of Energy encapsulates a profound and intricate understanding of the universe. From commonplace activities to the vast expanse of the cosmos, energy is in a state of perpetual transformation. This principle can be likened to an everlasting river, flowing, adapting, and nourishing all within its reach. As custodians of the Earth, adhering to this law fosters an ethical relationship with our energy use, ensuring sustainability for future generations. Only by recognizing and embracing this truth can humanity navigate the road ahead, uniting science with stewardship to forge a more harmonious existence on this shared planet.