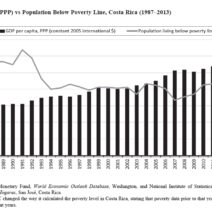
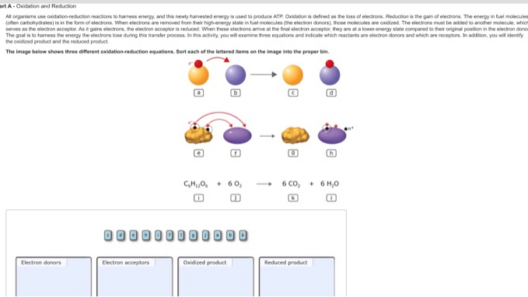
The Law of Conservation of Energy is a fundamental principle in physics that articulates a compelling understanding of how energy operates within our universe. It posits that energy cannot be created or destroyed; rather, it can only be transformed from one form to another. This premise underpins nearly all physical processes and has far-reaching implications not only in natural science but also in our everyday lives.
At its core, the Law of Conservation of Energy compels us to appreciate the intricate interconnections within energy systems. Whether it be a boiling kettle, a moving car, or the lighting of a city, every instance of energy interaction exemplifies this law at work. As energy is converted from one form to another—such as from chemical potential energy in gasoline to kinetic energy in an engine—this conservation principle assures us that the total energy in a closed system remains invariant. This notion evokes a sense of wonder for the methodologies nature employs to maintain equilibrium.
To grasp the law fully, it is crucial to delve into the various forms energy can take. They include kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, chemical energy, and electrical energy, among others. Kinetic energy relates to the motion of objects, while potential energy is associated with an object’s position in a gravitational field or its chemical structure. However, energy is seldom present in isolation. Energy transformations are commonplace; for example, a hydroelectric dam converts the potential energy of stored water into kinetic energy that generates electricity through turbines. Understanding these transformations aligns with fostering an appreciation for energy efficiency and conservation techniques.
Consider the role of this law in renewable energy practices. The transition from fossil fuels to sustainable energy sources is not merely an environmental necessity; it is rooted in a deeper understanding of energy conservation. By harnessing solar energy, wind energy, or biomass, we observe a shift in perspective regarding energy consumption. This paradigm shift encourages us to envision sustainability as not only beneficial but essential for future generations.
Education platforms like Quizlet and Brainly serve as pivotal resources for disseminating knowledge about the Law of Conservation of Energy. Quizlet, for instance, offers interactive diagrams and study guides that facilitate a comprehensive understanding of energy forms and transformations. Through visual aids, learners can grasp complex concepts more readily and retain information effectively. Such platforms promote an interactive learning experience, sparking curiosity among students who may have previously viewed science as an esoteric realm.
Additionally, Brainly provides a collaborative environment where learners can engage in discussions about energy conservation. The power of peer-to-peer learning harnesses diverse insights and sparks innovative ideas. Students sharing their interpretations of energy conservation enrich the learning landscape. This collaborative knowledge-building reflects the very essence of the Law of Conservation of Energy: that knowledge, like energy, is most potent when shared and transformed through interaction.
As we probe deeper into the implications of energy conservation beyond academia, a pressing question arises: How does this principle translate into our everyday decisions? Energy efficiency is a tangible manifestation of this law in contemporary society. Simple acts, such as switching to energy-efficient light bulbs or utilizing public transportation, embody the principle in practical applications. Each time we reduce energy consumption, we contribute to the maintenance of the energy balance, resonating with the broader global effort to mitigate climate change. Individual choices can collectively create ripples that influence environmental policies, corporate strategies, and community initiatives.
Moreover, the Law of Conservation of Energy paves the way for technological innovations. The quest for more efficient energy systems has inspired engineers and scientists to design solutions that capitalize on energy transfers and reconversions. For instance, advancements in battery technology aim to capture excess energy generated from renewable sources, enabling us to harness power for future use. Such innovations promise to revolutionize how we perceive and utilize energy, reflecting a growing commitment to sustainability.
As technology progresses, it also evokes ethical considerations. The conservation of energy is intricately woven with the socio-economic fabric of society. There exist disparities in energy access and consumption patterns globally. Recognizing that energy conservation is not merely an individualistic pursuit, but a collective obligation prompts a more profound examination of social justice issues. Engaging with this law demands a critical investigation of who is affected by energy production and what changes must be enshrined for equitable access.
In conclusion, the Law of Conservation of Energy serves as a cornerstone of physical science, influencing not only our understanding of matter and energy but also shaping our environmental ethos. The insights gathered from educational platforms such as Quizlet and Brainly highlight the importance of knowledge dissemination in empowering individuals to engage with this principle meaningfully. As we shift our perspective on energy consumption, we uncover a landscape rich with opportunity for innovation, collaboration, and ethical considerations. Every transformed light bulb, every sustainable technology design, and every conscious consumer choice encourages wider participation in the quest for a balanced energy future. As curiosity piques and knowledge proliferates, the impact of this law resonates across the globe, charting a course for a conscientious and sustainable future.