The concept of conservation of matter and energy is fundamental in the world of science. At its core, it posits that matter and energy cannot be created or destroyed; they can only be transformed from one form to another. This principle is essential for understanding natural phenomena and is a cornerstone of physics and chemistry. But let’s pause for a moment. What if everything we know about conservation was turned on its head? Imagine a world where matter and energy could spontaneously appear or vanish. What chaos would that entail? This hypothetical situation poses challenges that can be intriguing to explore.
The laws of conservation can be traced back to the Enlightenment, where thinkers began to question the nature of the universe. The rigorous studies of scientists like Antoine Lavoisier, who formulated the law of conservation of mass, laid the groundwork. According to this law, during a chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products. If, for instance, you burn wood, its mass does not disappear. Instead, it transforms into gases, ash, and heat energy. This transformation exemplifies the interdependence of matter and energy.
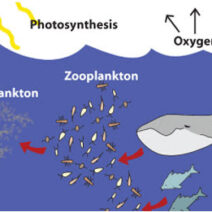
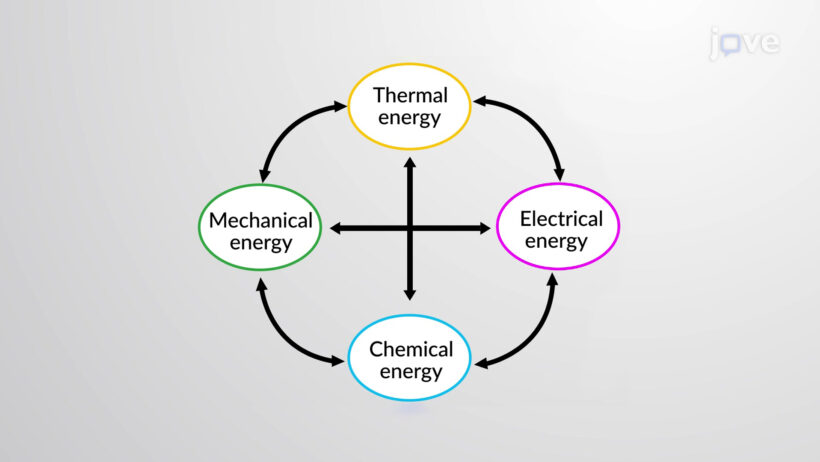
Energy itself exists in various forms, including kinetic, potential, thermal, electromagnetic, and chemical energy, among others. The conservation of energy law asserts that the total energy within an isolated system remains constant. It can change forms—for example, potential energy stored in a compressed spring converts to kinetic energy when released. This transformation is observable in everyday life, from the simple act of a ball rolling down a hill to the more complex mechanisms powering engines and electrical devices.
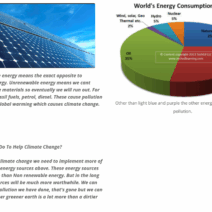
Delving deeper into these concepts reveals an astonishing interconnectedness between matter and energy, which invites further reflection. Can we harness energy without depleting our natural resources? This question finds its answer in the emerging field of renewable energy sources. Solar panels, wind turbines, and hydroelectric systems exemplify modern innovations that utilize the law of conservation of energy to generate power sustainably. They exploit the principles of energy transformation, converting natural resources into usable electricity, thereby adhering to the conservation laws while minimizing environmental impact.
The ramifications of these conservation laws extend beyond mere academic exercises. Consider the implications of ignoring them. An environment devoid of understanding conservation principles could lead to disastrous consequences. Wasteful energy consumption, pollution, and habitat destruction are frequently the outcomes of humanity’s disregard for these basic tenets. By recognizing the principle of conservation of matter and energy, individuals can champion sustainability, advocating for practices that reduce energy consumption and promote ecological balance.
Another important aspect is thermodynamics, the study of energy transfer and transformation. The first law of thermodynamics aligns closely with the conservation principle, stating that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only transferred or changed in form. In contrast, the second law introduces the concept of entropy, describing how energy transformations inevitably lead to increases in disorder within a system. This reality highlights the importance of efficiency in energy use and the necessity of developing technologies that reduce energy waste.
In practical terms, conservation practices can significantly alleviate our planet’s environmental challenges. Actions like insulating homes, using energy-efficient appliances, and maximizing public transportation contribute to energy conservation. Each decision reflects the conservation laws, reaffirming humanity’s role as stewards of the Earth. By engaging in these practices, individuals actively contribute to a larger movement towards sustainability and ecological responsibility.
Moreover, conservation isn’t merely a personal endeavor but a collective responsibility. Governments and organizations play pivotal roles in shaping policies that promote energy efficiency and sustainable practices. Legislative measures can incentivize the adoption of renewable energy technologies, enforce stricter regulations on emissions, and fund research focused on enhancing energy technologies. By joining forces and pooling resources, society can tackle the multifaceted issues posed by energy conservation.
Educational initiatives also serve as a vital conduit for spreading awareness about the conservation of matter and energy. Schools and community programs that emphasize science education equip individuals with knowledge about these principles, empowering them to effect positive change. Through interactive experiences, such as science fairs or sustainability workshops, participants gain a deeper appreciation for the essential role that conservation principles play in their daily lives.
Despite the scientific underpinnings of conservation of matter and energy, it is crucial to introduce an element of creativity and playfulness into the discussion. Curiosity drives innovation. Ask yourself: “How can I creatively utilize the existing resources without depleting them?” This challenge encourages out-of-the-box thinking and can lead to novel solutions that align with the principles of conservation.
In conclusion, the conservation of matter and energy serves as a vital framework that governs our understanding of the physical world. This principle informs everything from chemical reactions to large-scale ecological systems. By embracing these conservation laws, humanity can work towards a future that values sustainability and respects the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems. The challenge remains for each individual—to translate knowledge into action and creatively navigate the intricacies of energy conservation. The implications of this pursuit extend beyond scientific realms, coming to bear on future generations and the health of the biosphere. The quest for conservation is not merely a task; it’s a responsibility.