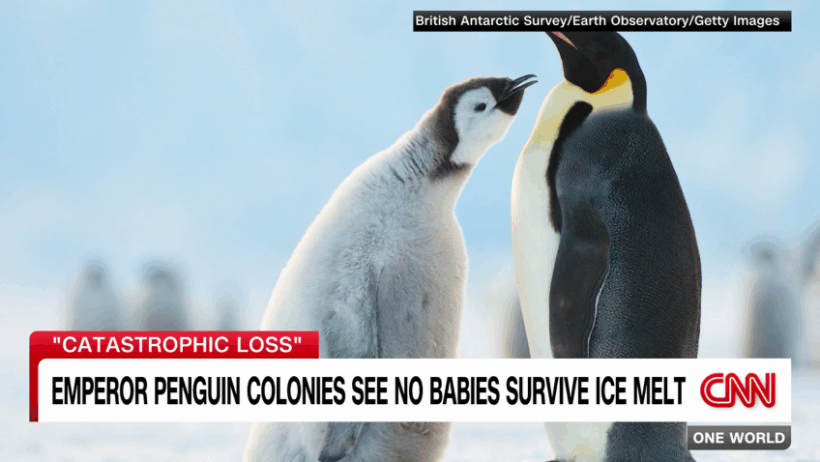
The plight of the emperor penguin captures the ecological crisis unfolding due to global warming. As the planet’s temperatures escalate at an alarming rate, the majestic life forms adapted to the frigid realms of Antarctica face unprecedented challenges. Are penguins, the iconic sentinels of the Southern Hemisphere, the next victims of climate change? The juxtaposition of their graceful movements on ice against the harsh realities of warming spells a narrative of vulnerability that demands attention.
Emperor penguins, the largest of all penguin species, have evolved uniquely over millennia. Their lifecycle is intricately intertwined with the seasonal dynamics of sea ice. During the brutal Antarctic winter, these birds endure frigid temperatures and fierce storms, relying heavily on the stability and expanse of sea ice for breeding and nurturing their young. However, as global temperatures ascend, the very landscape that sustains them morphs drastically, leading to a cascading ripple effect on their habitat.
Climate models project a dire forecast for the future of emperor penguins. By the end of the century, certain estimates suggest that more than half of the existing colonies could face extinction if current trends of global warming continue unmitigated. This statistic, stark and compelling, begs deeper exploration into the specific mechanisms through which climate change threatens their fate.
In the intricate ballet of life within the Antarctic ecosystem, sea ice plays a pivotal role. It provides not only a breeding ground for the emperor penguins but also a critical hunting platform. As climate change warms the oceans, this vital ice is diminishing, leaving foraging grounds compromised and too far away for the young chicks and their parent penguins. Without sufficient access to food sources, the survival rate of the chicks plummets. Increased temperatures also lead to unseasonable weather patterns that disrupt the delicate timing of breeding, further jeopardizing the future of these birds.
Furthermore, the warming climate invites an array of other ecological shifts that threaten emperor penguins. Altered ocean currents affect the marine food web upon which they depend. The decline of krill populations—tiny crustaceans that form the basis of the Antarctic food web—resulting from changing water temperatures and acidification directly impacts the diet of both adult and juvenile penguins. As their main food source dwindles, the ripple effect reverberates with debilitating consequences.
While the emperor penguin stands as a stark symbol of the fragility of polar ecosystems, it is not the only species feeling the impact of global warming. Other penguin species, such as the Adélie and Gentoo, are also experiencing stressors that threaten their survival. As temperatures rise, the historical territories of these species are shifting, resulting in competition for resources and habitat. The decline of sufficient nesting sites disrupts their breeding cycles and ultimately poses an existential threat to their populations.
In this era of unprecedented ecological change, the emperor penguin represents more than just a singular species facing extinction through global warming; it symbolizes a broader environmental crisis. The disappearance of these birds serves as a clarion call for urgent action. To stave off the encroaching threats of climate change, collective global commitments to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and protecting vital ecosystems must be prioritized. Efforts should focus on creating marine protected areas that minimize human interference, ensuring that penguins and other marine life can thrive and adapt.
Moreover, public awareness and education regarding climate change’s impact on these iconic species plays a crucial role in fostering a greater connection to environmental stewardship. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts can help mitigate the effects of climate change and encourage sustainable practices that respect the natural habitat of the emperor penguins and their ecosystem. Local challenges pose true opportunities for innovative strategies aimed at addressing the climate crisis holistically.
Collectively, as we reflect on the fate of the emperor penguin, it becomes evident that the trajectory toward their potential extinction mirrors a pivotal point for our entire planet. The mechanisms of climate change encompass a multifaceted array of challenges that extend far beyond the feathered inhabitants of frigid territories. The battle against global warming requires not only innovative scientific approaches but also a profound cultural shift towards more sustainable ways of living.
In conclusion, should we continue to turn a blind eye to the nuances of global warming, the emperor penguin may well become a poignant metaphor for the losses we suffer when we neglect the intricate tapestry of life on Earth. Addressing climate change is not merely about saving a species; it is about ensuring the survival of the rich biodiversity that sustains our planet. The global response to this crisis will define not just the future of diverse species like the emperor penguin but, more pressing, the fate of humanity itself.