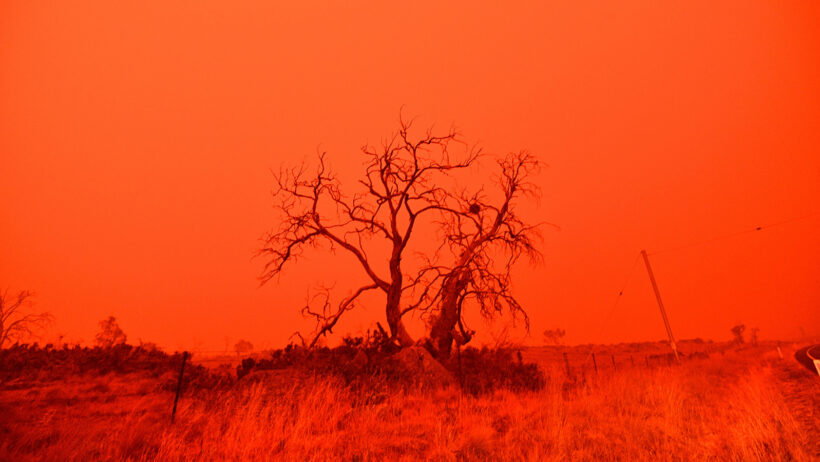
The recent bushfires ravaging Australia have thrust the issue of climate change into the global spotlight. The correlation between rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and the occurrence of wildfires has become increasingly evident. While wildfires are not a new phenomenon in Australia, their intensity, frequency, and devastation have escalated alarmingly in recent years. Hence, it beguiles one to ponder: are the Australian fires fueled by climate change?
To understand the intricate relationship between climate change and bushfires, one must delve into the fundamental elements of the ecosystem. Australia, with its unique flora and fauna, is inherently susceptible to fire. Native vegetation such as eucalyptus is highly flammable, creating a dangerous cocktail when paired with rising ambient temperatures and prolonged dry spells. Historical data reveals that the continent is no stranger to fire, but recent climatic shifts have altered the landscape of fire occurrence dramatically.
Climate change is primarily driven by anthropogenic factors, including excessive carbon emissions, deforestation, and land-use changes. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) warns that greenhouse gas emissions contribute significantly to global warming, resulting in hotter and drier conditions. For Australia, this culminates in a perilous state with extended droughts and increased fire risks. Statistical models predict that even a modest rise in global temperatures leads to an uptick in the frequency of extreme fire weather days.
One pivotal factor contributing to the surge in bushfire activity is the phenomenon of heatwaves. As climate change continues its relentless advance, the intensity and duration of heatwaves are increasing. This extreme weather not only creates ideal conditions for wildfires to ignite but also accelerates their propagation. Australia has witnessed record-breaking temperatures, transforming vast landscapes into tinderboxes.
Furthermore, a changing climate disrupts precipitation patterns, resulting in erratic rainfall and prolonged dry spells. This inconsistency leads to an accumulation of dry vegetation, providing ample fuel for wildfires. When conditions align—such as high winds and low humidity—the results can be catastrophic. A single spark can lead to infernos that engulf entire ecosystems, devastate wildlife, and obliterate human settlements.
While one can cite historical accounts of bushfires predating modern climate change, the current wave of fires cannot be disentangled from climate-driven realities. Analyses conducted in the aftermath of recent fires have indicated a troubling trend: areas that previously experienced lesser fire activity are now facing increasingly severe blazes. The new normal appears to be defined by an unprecedented severity that is undeniably linked to our changing climate.
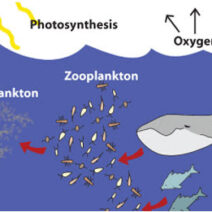
Consider the ecological ramifications of these fires. The destruction isn’t limited to just trees and habitats; the fires also significantly impact biodiversity. Charred remains of flora and fauna reveal a grim narrative of loss, with species unable to recover from the devastation or facing extinction. The intricate web of life, reliant on delicate ecosystems, is fraying, and the reverberations of these fires extend beyond Australia’s borders. They influence global carbon cycles and contribute to further climate change, creating a vicious feedback loop.
Moreover, the socio-economic implications are staggering. Communities are left in the wake of destruction, grappling with loss of property, livelihoods, and lives. The economic toll escalates as firefighting efforts intensify and recovery initiatives demand substantial resources. Moreover, the psychological burden on affected populations lingers long after the flames have been extinguished.
It’s crucial, then, to recognize that the fires are not isolated incidents but part of a larger, systemic issue. This realization beckons a shift in perspective—understanding wildfires through the lens of climate change compels action. It emphasizes the urgent need for robust policy changes and mitigation strategies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, enhancing forest management practices, and investing in renewable energy sources. Proactive measures can play a vital role in curbing the frequency and intensity of wildfires.
Public awareness and understanding of the link between climate change and bushfires are crucial components in this fight. Engaging dialogues within communities about sustainability, conservation, and climate resilience can foster a culture of responsibility. Collective action at local, national, and global levels can forge a path towards recovery and prevention, empowering individuals to become stewards of the environment.
As we examine the ramifications of the Australian fires, a stillness lingers—a solemn reminder of what is at stake. Engaging with this urgent narrative encourages us to evaluate our own contributions to climate change. Every action counts; reducing carbon footprints, supporting policies directing towards environmental preservation, and nurturing an ethical connection with nature can catalyze meaningful change.
In conclusion, the Australian fires serve as a poignant, clarion call for humanity. Climate change has emerged as a formidable adversary, profoundly exacerbating natural disasters. However, through informed discourse, strategic action, and unwavering commitment, it is possible to illuminate a path forward. A future where coexistence with nature is not only achievable but thrives amid the challenges. Addressing climate change will ultimately determine the fate of ecosystems and communities around the globe, and the fires of Australia stand as a testament to what is at stake.