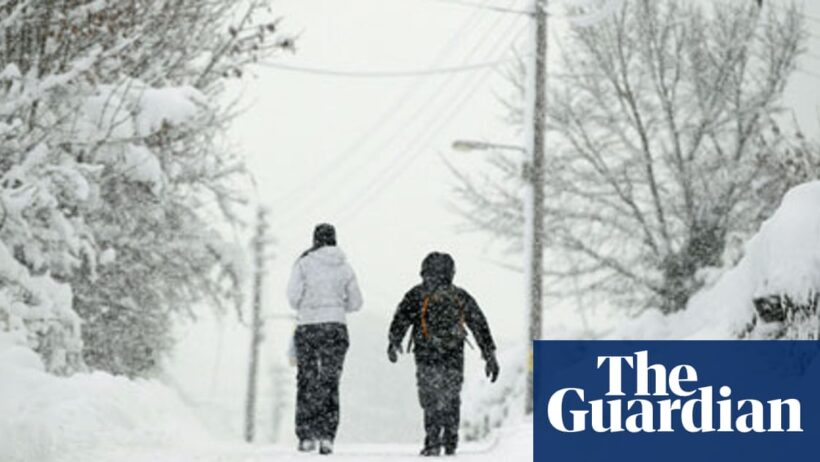
The intricate relationship between climate phenomena and global warming has become a focal point of discussion among scientists, policymakers, and the general populace. With an upsurge in severe weather events, many individuals find themselves pondering whether the fluctuations in temperature and the emergence of harsh winters can be directly correlated to the gradual warming of the planet. This inquiry reveals an interwoven tapestry of climate dynamics that necessitates careful examination and consideration.
Traditionally, winter has been characterized by its frigid temperatures and a certain predictability in weather patterns. However, recent years have witnessed a remarkable divergence from this norm, presenting increasingly erratic weather conditions. From unseasonably early snowfalls to abrupt temperature plunges, these phenomena have sparked curiosity and concern alike. It is essential to dissect these occurrences, as they may not merely be transient anomalies but rather indicators of deeper climatic shifts.
At the heart of this discussion lies the concept of atmospheric circulation. The behavior of the polar vortex—a large area of low pressure and cold air surrounding the Earth’s poles—plays a critical role in winter weather patterns. When the polar vortex is stable, it maintains cold air in polar regions. However, due to climate change, particularly the warming Arctic, this vortex has displayed increased instability. This instability can result in “waves” of cold air spilling southward, leading to severe winter weather in mid-latitude regions that historically would remain temperate.
Furthermore, oceanic currents—particularly, the Gulf Stream—act as a major regulator of climate. The intricate interactions between these currents and atmospheric patterns can significantly influence weather systems worldwide. Climate change has the potential to disrupt these currents, thereby engendering unusual weather events. As temperatures rise, the melting of polar ice caps alters salinity and density in ocean waters, which in turn affects global circulation patterns. This phenomenon must be recognized as a substantial player in the orchestration of more extreme and unpredictable winters.
Ironically, while global warming leads to an overall increase in average temperatures, it can also spawn paradoxical cold snaps. This duality is essential in understanding the complexities of climate systems. The increase in global temperatures does not negate the possibility of severe winters; rather, it recontextualizes them within a changing climate landscape. The notion that climate change yields exclusively warmer temperatures is a misconception that oversimplifies a multifaceted issue.
Data collected over the past few decades suggests an alarming trend: regions that once experienced temperate winters are now grappling with fluctuating temperature extremes. This disparity can be attributed to a myriad of factors, including changes in precipitation patterns, shifts in humidity, and alterations to the energy balance of the Earth. For instance, warmer air holds more moisture, which can lead to heavier snowfall during winter storms, creating conditions where snowfall may be more intense, albeit accompanied by milder temperatures in the aftermath.
The societal implications of these weather swings warrant attention. Communities that rely on consistent and predictable weather patterns for agriculture, transportation, and energy consumption face unprecedented challenges. Crop cycles are potentially disrupted. Energy demand peaks unpredictably, placing strain on infrastructure and resources. The economic ramifications of harsher winters and erratic weather manifest as increased costs for heating and necessary adaptations in urban planning and emergency management.
Equally significant are the psychological effects of experiencing extreme weather. The human penchant for stability can be disrupted by the sudden realization that the world is no longer as predictable as it once seemed. From grappling with cancellations of outdoor events to facing potential damage from unexpected snowfall or severe storms, individuals must navigate a new normal that is profoundly shaped by climate change. This recognition can foster a sense of urgency surrounding the issue, catalyzing individuals and communities to engage in climate action.
Public discourse must also contend with the misinformation that often clouds the narrative surrounding climate change and its consequences. The challenge is not merely to acknowledge the harsh winters and severe weather as immediate phenomena but to grasp their connection to global warming at a more profound level. Increasing public awareness and education about climate systems can empower citizens to advocate for policy changes aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainability.
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between severe winter weather and global warming transcends simplistic explanations. It calls for a nuanced understanding of atmospheric dynamics, oceanic currents, and the broader implications for society and ecosystems. As the Earth’s climate continues to evolve, so too must our responses—embracing proactive measures to combat climate change is imperative. Recognizing the ties between weather swings and warming trends enables a collective movement toward resilience and sustainability for future generations.
Ultimately, the discourse should evolve beyond mere observations of weather to encompass a comprehensive understanding of the underlying causes and interdependencies. This path leads not only to knowledge but also to informed action, championing stewardship of the environment amidst the complexities of a changing climate.