As 21st-century marvels of technology, self-driving cars promise a future where we can relinquish the strain of driving, allowing vehicles to transport us autonomously. The allure of this innovation is undeniable; however, lurking beneath this shiny facade lies a pressing question. Can self-driving cars contribute to global warming? To understand this potential consequence, one must delve into the mechanics of the autonomous vehicle industry and its intricate relationship with our environment.
Imagine a world where vehicles operate without human intervention, moving seamlessly from point A to point B. Autonomous vehicles, equipped with sophisticated algorithms and advanced sensors, are designed to enhance safety and efficiency. Yet, this romantic vision of a driverless utopia may come with unforeseen ecological ramifications. The aspirational image of a fleet of electric, self-driving cars distributing us like parcels may not be the panacea it appears. It resembles a mirage—inviting yet potentially disastrous for our climate.
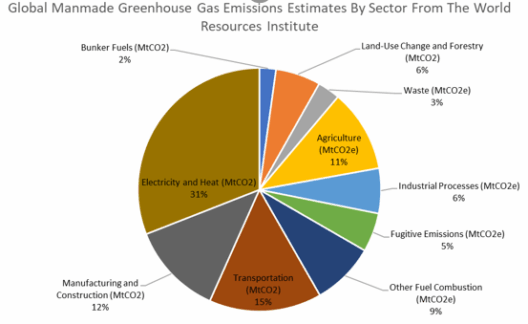
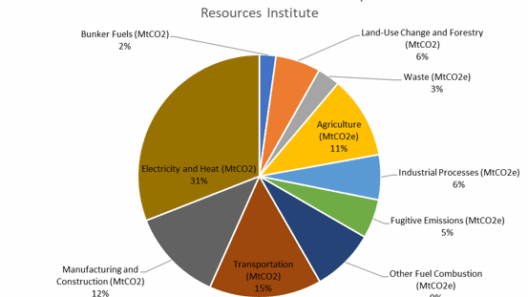
One critical aspect to consider is the energy consumption associated with self-driving technology. These vehicles require significant amounts of power to operate their onboard systems, which include cameras, radar, and complex processing units. While many of these vehicles are envisioned as electric, the reality of energy sourcing reveals a troubling picture. If the electricity that fuels these autonomous cars is derived from fossil fuels, the very act of driving, whether human-directed or autonomous, could perpetuate greenhouse gas emissions and exacerbate climate change.
Moreover, the implementation of self-driving cars could lead to a phenomenon known as induced demand. This economic principle suggests that as the supply of a good increases, demand often rises correspondingly. With the convenience of autonomous vehicles, individuals who previously relied on public transportation or other eco-friendly modes of transit may choose to opt for self-driving options instead. This shift can increase overall vehicle miles traveled (VMT), leading to higher emissions and further depletion of natural resources.
The allure of convenience may insidiously lure people back into the clutches of car dependence. Picture a cityscape where drivers once preferred walking or cycling, now transformed into a sprawling network of self-driving cars, generating congestion rather than alleviating it. As this wave of convenience washes over urban environments, the potential for increased traffic congestion rises like the tides, compounded by the omnipresent challenges of urban planning and sustainable infrastructure.
Furthermore, self-driving vehicles inherently possess a propensity for “robotaxi” programs—on-demand ride-sharing services, which could fundamentally alter transportation models in densely populated areas. While these services may appear to reduce the number of individual vehicles on the road, they also raise the specter of a rise in the number of trips taken. This paradox could exacerbate congestion and pollution levels due to the excessive number of short trips compared to fewer, consolidated journeys in conventional vehicles. An endless loop of short circuits contributes little to climate goals.
There is also the question of resource extraction associated with the production and disposal of advanced technology. The minerals required for electric vehicle batteries—such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel—are often procured through environmentally damaging mining practices. These operations frequently leave a devastating imprint on local ecosystems and communities, raising questions about the ecological footprint of the very technology we herald as the savior of our climate.
The importance of recycling and responsible disposal of self-driving vehicles cannot be overstated. As vehicles age and reach the end of their life cycles, improper disposal can lead to hazardous materials leaching into the soil and waterways. Imagine a landscape dotted with decommissioned autonomous vehicles—remnants of a technology that had the potential for a profound positive impact but ultimately fell prey to negligence.
Public perception plays a pivotal role as well. The notion that self-driving cars are a solution to climate change can lead to what experts term “moral licensing.” This phenomenon occurs when individuals feel absolved of responsibility after adopting one green practice; they may then engage in less sustainable behaviors without guilt. This attitude can pervade society, leading to a paradoxical increase in environmental impact through complacency.
So, how can we address these multifaceted challenges as we forge ahead? First, sustainable energy sourcing for the electricity that powers autonomous vehicles is paramount. Investing in renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and geothermal, can significantly mitigate the carbon footprint of self-driving technology. Additionally, fostering an integrated transportation system that encourages public transit and non-motorized transport is crucial. Emphasizing the importance of holistic urban planning can ensure that the adoption of autonomous vehicles does not spiral into a complete reliance on cars once more.
Education and awareness regarding the ecological impact of self-driving technology must be amplified. As society continues to embrace progress, it is vital that public discourse remains grounded in responsibility and sustainability, dissecting the pros and cons of emerging technologies.
In conclusion, self-driving cars are not unequivocal agents of salvation for our climate; they present a multifaceted quandary with the potential for both improvement and detriment to our environmental health. Visionaries must tread thoughtfully along the precipice of automotive innovation, ensuring that the allure of convenience does not eclipse the urgency of combating global warming. In acknowledging both the promise and peril of self-driving vehicles, we can pave the path to a more harmonious coexistence with our planet, preventing this technological revolution from spiraling into a climatic catastrophe.