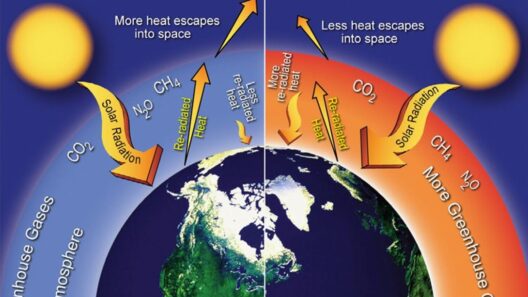
Global warming has emerged as one of the most pressing environmental concerns of our age, influencing various ecological systems and atmospheric phenomena. Among these is the behavior of the jet stream, a fast-flowing air current that significantly impacts weather patterns. As the planet continues to warm, researchers have been investigating how the changing climate may alter the characteristics and stability of the jet stream, which could lead to noteworthy ramifications for global weather. To comprehend the intricacies of this phenomenon, it is essential to delve into the dynamics of the jet stream and its relationship with climate change.
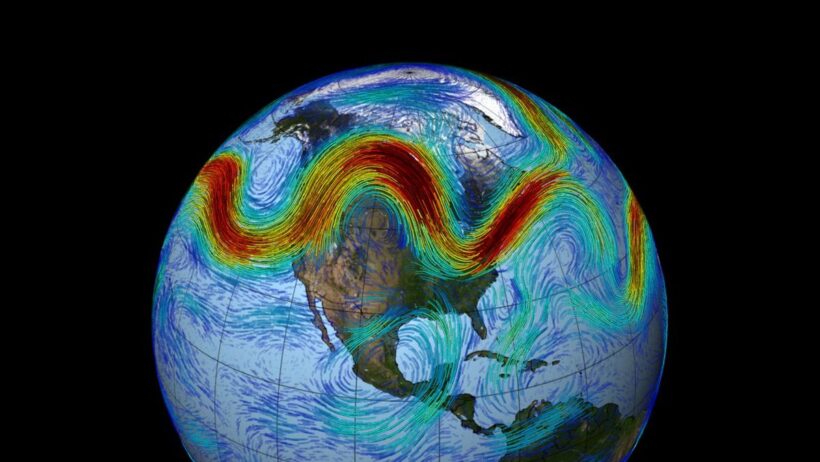
The jet stream is primarily formed by the temperature differential between the polar air masses and the warmer air from the tropics. It typically flows in a wavy pattern and plays a pivotal role in steering weather systems. As global temperatures increase due to greenhouse gas emissions, scientists propose that the standard behavior of the jet stream could be disrupted. The warming of the Arctic at a faster rate than mid-latitude regions has been observed, resulting in reduced temperature gradients. This diminishes the driving force behind the jet stream and potentially leads to a slowdown in its speed.
One of the most compelling implications of this alteration is the potential for prolonged weather patterns. While the jet stream’s normal oscillation helps to balance weather by allowing systems to move and change, a slower jet may cause certain conditions to linger longer than usual. This can lead to extended periods of extreme weather, such as heatwaves, cold spells, or heavy precipitation. For example, if the jet stream stalls over a region, it may result in extreme weather conditions lasting for days or even weeks, disrupting daily life, agriculture, and ecosystems.
The correlation between the jet stream and the frequency of extreme weather events is becoming increasingly evident. Intense storms, droughts, floods, and heatwaves are emerging more frequently due to this disrupted atmospheric pattern. A wavering jet stream allows for a greater influx of warm tropical air into higher latitudes, leading to more volatile weather conditions. The implications for agriculture, water supply management, and disaster preparedness are profound, as communities may face unpredictable and severe weather impacts.
Moreover, the disruption of the jet stream contributes to the intensification of tropical cyclones and hurricanes. With warmer ocean waters providing abundant energy, coupled with altered atmospheric conditions, storms can become more potent and destructive. The enhanced potential for cyclogenesis, or the development of new storms, poses a significant threat to coastal populations and environments. Ultimately, the economic and social consequences of these weather events can be staggering, creating a ripple effect through various sectors, including infrastructure, healthcare, and food security.
As scientists continue to investigate these relationships, they are utilizing sophisticated climate models to simulate future jet stream behavior under various global warming scenarios. These models suggest that the frequency and duration of extreme weather events could increase as global temperatures rise. Projections indicate that by 2060, we may witness a dramatic shift in the jet stream, leading to a more chaotic and unpredictable climate system. It highlights the need for sustained research and data collection to fully understand the extent of these changes and their global implications.
Addressing the pressing issue of jet stream alterations inevitable in a warming world requires a multifaceted approach. Governments, NGOs, and communities must work collaboratively to develop comprehensive adaptation strategies. These strategies should focus on building resilience within communities, enhancing early warning systems, and investing in infrastructure that can withstand increasingly extreme weather patterns. While mitigation efforts aiming to reduce carbon emissions are crucial, adapting to the impending changes will be equally imperative.
Public awareness and education about the consequences of global warming and its effect on the jet stream are also essential components in addressing this issue. A well-informed society can advocate for policies that prioritize sustainability and climate resilience. Engagement in local environmental initiatives and support for renewable energy sources are actions individuals can take to contribute positively toward combating climate change.
Another critical dimension to consider is the interaction between the jet stream and other climate-related phenomena. For instance, the El Niño Southern Oscillation and the North Atlantic Oscillation also influence jet stream behavior. These interactions can create complex feedback loops that either exacerbate or mitigate the effects of global warming on atmospheric currents. Understanding these relationships is vital in predicting future weather patterns and preparing for their consequences.
In conclusion, the interplay between global warming and the jet stream is a multidimensional challenge that encompasses various atmospheric science principles. The potential for altered weather patterns and increased frequency of extreme events underscores the urgency of climate action. Comprehensive research, effective policy, and public engagement form the backbone of a coordinated response to the challenges posed by changing jet stream dynamics. A concerted effort in understanding and addressing these atmospheric changes is necessary to protect our societies and ecosystems from the unforeseen impacts of a warming world.