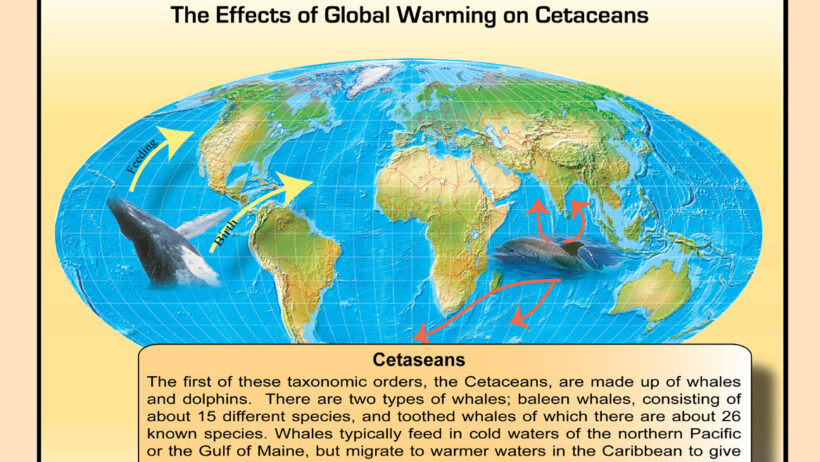
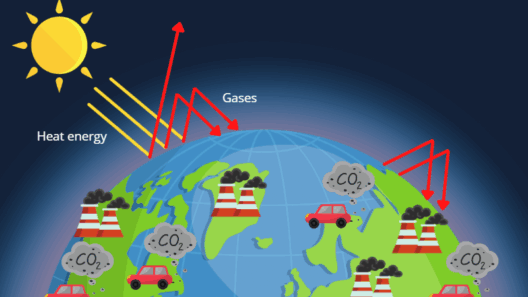
Global warming serves as a formidable orchestra conductor, modulating the climate’s natural rhythms and amplifying interannual variability, akin to a maestro elevating a symphony’s crescendos. Understanding this intricate interplay is crucial as it elucidates the profound implications for weather extremes. To appreciate the nuances, one must first grasp the essence of interannual climate variability, an energetic dance of climatic patterns that unfolds over the span of several years.
At its core, interannual climate variability refers to the fluctuations in weather patterns that occur from year to year, a capricious ebb and flow influenced by various atmospheric phenomena. The El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is one of the most recognized of these phenomena, manifesting in notable year-to-year climate changes. During an El Niño year, for example, the Pacific and global climate undergo significant shifts, leading to wetter conditions in some regions and droughts in others. While this variability has always existed within natural systems, global warming introduces a more chaotic undertone.
As greenhouse gas emissions climb steadily, the Earth’s surface temperatures rise, creating a perturbation in the delicate balance of the climate system. This rise in temperatures acts like a catalyzing agent, supercharging atmospheric moisture and augmenting the intensity and frequency of climate variability events. Wetter storms become wetter; dry spells become drier. The climate becomes increasingly prone to extremes, transforming the atmosphere into a high-stakes roulette wheel of unpredictable outcomes.
Moreover, the implications of this amplified variability extend far beyond mere weather forecasts. Agriculture, a delicate lifeline for billions, stands at the forefront of this eruption of unpredictability. Crops, which thrive within specific climatological parameters, are suddenly confronted with an onslaught of erratic precipitation patterns and temperature extremes. A single year of anomalous conditions can spell catastrophe, reaping havoc on harvests and precipitating food insecurity. The threat is exacerbated for regions reliant on rain-fed agriculture, vulnerable to both floods and droughts.
The economic ramifications tied to this climate variability are as staggering as they are far-reaching. Extreme weather oscillations, such as droughts, hurricanes, or flooding events, can yield sizable disruptions. The insurance costs skyrocket as phenomena like hurricanes descend upon coastal cities with terrifying ferocity, wreaking havoc on infrastructure and ecosystems alike. The societal costs of such events, intertwined with rising involuntary climate migrations, create a humanitarian tapestry woven from desperation.
In urban areas, the burgeoning intensity of climate variability fosters unique challenges. Cities embody heat islands, exacerbating the effects of climate change and creating environments where extreme heat events can become lethal. Urban planners must grapple with the intersection of increasing temperatures and moisture levels, as elevated temperatures fuel violent storms, creating a perfect storm for flash flooding. Innovative infrastructure adaptations, such as sustainable drainage systems and green roofs, emerge as crucial components of urban resiliency efforts.
The increased frequency of weather extremes as a consequence of global warming draws further attention to the intricacies of the hydrological cycle. Water vapor is a potent greenhouse gas; hence, as the atmosphere warms, it retains more moisture, potentially leading to heavier precipitation and more severe flooding events. In contrast, certain areas may experience prolonged dry spells due to atmospheric changes that reroute jet streams and influence weather patterns. This duality underscores a critical paradox: while some regions receive deluges, others may be thrust into parched desolation.
The interplay between warming temperatures and interannual variability also fosters a fertile ground for climate pitfall phenomena such as the Arctic Oscillation, which can influence mid-latitude weather patterns. Anomalous behavior in polar regions, including melting sea ice and shifting wind patterns, disrupts long-standing westerlies, fostering anomalous cold spells in some locales while unleashing balmy temperatures in others. The cascading effects of such phenomena ripple through ecosystems, impacting biodiversity and species distributions as flora and fauna scramble to adapt or face extinction.
As we delve deeper into the implications of global warming-induced variability, it is crucial to consider the role of human agency. The burgeoning realization that collective action can mitigate the most severe consequences emerges as a beacon of hope. Policy frameworks that prioritize sustainable practices, carbon neutrality, and renewable energy can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, ultimately stemming the tide of global warming. This confluence of science and policy thus emerges as a formidable ally against the specter of climate variability.
Education plays a vital role in this struggle, fostering a population equipped with the knowledge necessary to advocate and implement change. Developing an ecological consciousness encourages individuals to become active participants in combating climate impacts, ultimately coalescing into a more resilient society ready to withstand the shocks of climate variability. Through these concerted efforts, communities can harness their collective strength, creating a robust safety net against the tumultuous churning of an increasingly chaotic climate.
In summary, the complex tapestry woven from the threads of global warming and interannual climate variability evidences a harrowing reality: storms will intensify, droughts will deepen, and the very fabric of our existence will be challenged. Yet, amidst the challenges looms opportunity. By embracing innovative solutions and fostering resilience, society can navigate the tumult, ensuring that future generations inherit a world brimming with ecological and meteorological equilibrium.