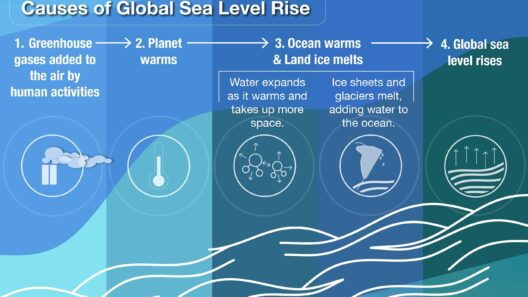
Global warming, a phenomenon increasingly scrutinized by scientists and the public alike, has led to significant alterations in our planet’s climate system. Among the most visible and alarming effects of this gradual rise in temperatures is the mass melting of glaciers. Though glaciers have always experienced cycles of advance and retreat, the current rate of melting is unprecedented and alarming. This transformation not only serves as an unequivocal indicator of climate change, but also raises critical questions about its implications for the Earth’s ecosystems, sea levels, and even human civilization.
The statistics regarding glacier retreat are staggering. The Danish Institute for Climate Science has reported that 82% of Greenland’s glaciers are retreating. Similarly, the vast ice sheets of Antarctica are losing mass at an accelerated pace, with losses tripling from 2007 to 2020. The visible shrinkage of these ice formations is not merely a natural occurrence; it is a harbinger of change that impacts communities, wildlife, and global weather patterns. The question then arises: What exactly is driving this rapid melting?
At the heart of glacier melting lies the concept of global warming, which is primarily driven by anthropogenic activities. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes have released disproportionate amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. CO2 levels have surged, tightly correlating with rising oceanic temperatures and altering the delicate balance of the Earth’s climate system. As temperatures increase, glaciers—massive reserves of freshwater—begin to melt at alarming rates. This melting contributes not only to rising sea levels but impacts local environments, causing nutrient runoff that can disrupt aquatic ecosystems.
The ecological ramifications of glacier retreat are profound. Glaciers serve as natural reservoirs, sustaining river flows during warmer months. Their melting can create a temporary increase in river water supply, misleadingly improving conditions for local agriculture. However, this transient boon masks a long-term devastation. As glaciers continue to disappear, the regions reliant on their meltwater face an existential crisis. Fisheries, agriculture, and potable water supplies are all directly threatened by this disruptive trend. There is a burgeoning concern among scientists that entire communities could face significant resource scarcity, prompting migration and potential conflict over diminishing supplies of fresh water.
Moreover, the melting of glaciers and complex ice formations has implications that extend far beyond local ecosystems. The release of fresh water into the oceans can disrupt oceanic currents, which are vital not only for maintaining global weather patterns but also for biodiversity. The alteration of these currents could lead to more severe weather events, including hurricanes and droughts, further exacerbating challenges for vulnerable populations. The increased stratification of the oceans due to the influx of freshwater leads to diminished mixing, which can negatively affect the global climate and marine life.
The cultural dimensions of this phenomenon cannot be overlooked either. For many indigenous communities, glaciers have long been part of their heritage, vital for their spiritual and cultural identities. The profound changes to these ancient ice formations represent not just a physical loss but a cultural erasure that is irreplaceable. The emotional weight of losing such a prominent part of their environment greatly compounds the environmental crises, turning a scientific issue into a deeply personal struggle for many communities.
Despite the sobering nature of these realities, there exists a promise of change driven by awareness and action. For years, the chorus of scientific voices warning about climate change has become louder and more urgent. Global agreements such as the Paris Accord reflect a collective commitment toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions and pursuing a more sustainable future. The shared responsibility of preserving glaciers and addressing global warming involves every sector of society—from policymakers and industry leaders to individual citizens.
Innovative research into renewable energy sources, carbon capture technologies, and sustainable agriculture practices offers pathways toward mitigating the adverse effects of global warming. Public consciousness around climate change has sparked movements, rallies, and educational initiatives, as people realize the profound importance of preserving our planet. Moreover, advancements in technology have allowed for better monitoring of glaciers, enabling scientists to predict future melting patterns and inform climate policies accordingly.
Actions must be taken urgently and decisively. Meeting ambitious carbon neutrality goals requires a concerted effort across the globe, with both individual and collective action. This necessitates not only government intervention but societal commitment towards more sustainable practices. Public transportation, community-based renewable energy projects, and conservation programs can play vital roles in decreasing our carbon footprint while preserving critical ecosystems.
As we reconcile the realities of climate change and its multifaceted impacts, the focus on public engagement and education becomes paramount. Encouraging curiosity and a shift in perspective will foster a deeper understanding of how closely humans are intertwined with their environments. Embracing stewardship of our planet is not optional; it is a necessity. The transformative journey towards a sustainable future hinges on our collective willingness to engage, adapt, and innovate. In preserving glaciers, we are preserving not only a physical landscape, but the very essence of life that depends upon the intricate mechanisms of our climate system.
The era of mass glacier meltdowns is upon us, and while the challenges are formidable, the opportunity for profound change lies within our grasp. By fostering a commitment to environmental stewardship, we can turn the tide on global warming and secure a sustainable future for generations to come.