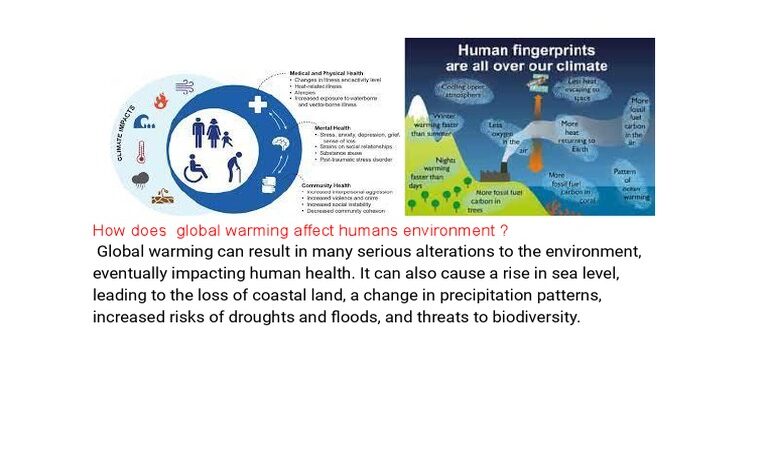
Global warming, an increasingly critical issue, poses severe ramifications for humans, animals, and ecosystems alike. As the planet’s temperature rises due to the accumulation of greenhouse gases, the effects are felt across various domains, leading to complex interconnections between climatic changes and biological systems. Understanding these impacts is essential for fostering a collective response to this global challenge.
One of the most direct ways global warming affects humans is through health concerns. Rising temperatures have been correlated with increased incidents of heat-related illnesses and exacerbated cardiovascular and respiratory conditions. The elderly, children, and individuals with preexisting health issues are particularly vulnerable. Additionally, shifting weather patterns can also facilitate the spread of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, as warmer climates expand the habitats of mosquitoes and other vectors, increasing the likelihood of outbreaks.
Moreover, food security is gravely compromised by the repercussions of climate change. Elevated temperatures can diminish crop yields due to heat stress. Droughts and irregular rainfall patterns further exacerbate the situation, leading to reduced agricultural productivity. This decline not only threatens the livelihoods of farmers but also contributes to rising food prices, which disproportionately affects low-income populations. As food scarcity escalates, the potential for malnutrition increases, further jeopardizing public health.
The economic implications of global warming are profound. Many industries, particularly agriculture, fisheries, and tourism, experience significant disruptions due to climatic fluctuations. The decline in fish stocks attributable to warmer oceans and altered marine ecosystems poses severe risks to food sources and economies reliant on fishing. In tourism, natural attractions such as coral reefs are degrading, deterring visitors and affecting local economies dependent on their beauty and ecological richness.
Global warming also manifests in extreme weather events. Hurricanes, wildfires, floods, and droughts are becoming more frequent and severe. These phenomena not only threaten human lives but also incur substantial economic costs through infrastructure damage and recovery expenses. Coastal communities suffer from rising sea levels, which encroach upon habitations, necessitating costly adaptations or relocations. This displacement can breed conflict over increasingly scarce resources and instigate climate refugees—people forced to leave their homes due to climate-related disasters.
The ramifications extend beyond human health and economics to encompass animal populations. Many species find their habitats drastically altered as temperatures rise. Species that cannot adapt swiftly enough to changes in their environment face extinction. Polar bears, for instance, are losing their ice platform in the Arctic, diminishing their ability to hunt and survive. Similarly, amphibians, which are highly sensitive to temperature changes, are experiencing population declines as their habitats become inhospitable.
Moreover, as ecosystems experience stress, interspecies interactions are disrupted. Predator-prey relationships can be altered, affecting food webs. For example, migratory patterns of certain birds may shift, leading them to miss optimal breeding grounds. Such mismatches disrupt ecosystems and can lead to declines in biodiversity. Biodiversity loss is critical, as it undermines ecosystem resilience, reducing nature’s ability to adapt to ongoing climatic changes.
Coral reefs, often referred to as the “rainforests of the sea,” are another poignant example of the impacts of global warming. As ocean temperatures rise and acidity increases due to higher carbon dioxide levels, coral bleaching occurs. This phenomenon weakens coral and leads to the loss of marine habitats that support myriad species. The degradation of these ecosystems not only affects marine biodiversity but also the millions of people who rely on these waters for their livelihoods, further highlighting the interconnectedness of human and animal welfare.
Furthermore, global warming impacts result in significant alterations to ecosystems, affecting their structure and function. Forests, which play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, are experiencing increased susceptibility to pests and diseases, driven by warmer temperatures. Such stressors can lead to forest dieback, releasing stored carbon back into the atmosphere, thereby exacerbating climate change. In turn, this leads to a feedback loop that continues to intensify global warming.
In response to these multifaceted impacts, advocacy and action become paramount. Individuals and communities can engage in climate-resilient practices, such as adopting sustainable agricultural techniques, reducing waste, and advocating for renewable energy solutions. Policy changes at local, national, and international levels are crucial to mitigate the effects of climate change, including adherence to environmental regulations and investing in green technology.
As awareness grows, so too does the urgency for cohesive action. It is imperative that humans recognize their role within the broader ecosystem and the direct consequences our actions have on the planet. A synergistic approach combining conservation, sustainable development, and climate adaptation strategies will ensure a more resilient future for every living organism on Earth.
In conclusion, the impacts of global warming are extensive and far-reaching. From health crises and economic disruptions to alterations in animal populations and ecosystem dynamics, the repercussions are profound. A forward-thinking approach that emphasizes education, advocacy, and sustainable practices is essential for mitigating these impacts and safeguarding the well-being of both humanity and the planet.