The water cycle, a fundamental and intricate system, is vital for maintaining ecological balance on Earth. This hydrological cycle encompasses various processes including evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff. However, evolving climatic conditions induced by global warming are severely disrupting this equilibrium, leading to far-reaching repercussions on both the environment and human life.
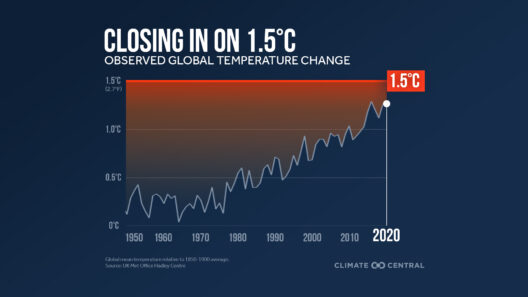
As global temperatures rise, the capacity of the atmosphere to retain moisture increases, which can lead to intense and sporadic precipitation events. This phenomenon is primarily due to a fundamental principle of physics: warmer air holds more water vapor. The ramifications of this alteration are profound. For example, regions that traditionally experience regular rainfall patterns may suddenly face severe storms and flooding, whereas other areas could fall victim to prolonged droughts as precipitation becomes more erratic. Such dichotomous weather patterns complicate agricultural practices, threatening food security across the globe.
Notably, the implications of these shifts extend beyond agricultural disruption. Ecosystems that depend on consistent water availability are destabilized, fostering conditions for species extinction. Freshwater systems, fragile by nature, become particularly vulnerable as altered precipitation patterns disturb their delicate balance. When intense rainfall leads to flooding, numerous contaminants are washed into nearby water bodies, harming aquatic organisms and degrading water quality. Consequently, this disruption not only affects biodiversity but also poses significant challenges for water supply and sanitation.
The melting of polar ice caps and glaciers represents another alarming consequence of global warming that exacerbates disruptions to the water cycle. As these ice masses diminishes, they contribute to rising sea levels, with profound implications for coastal communities worldwide. Moreover, the meltwater, rushing into oceans, alters salinity patterns which can in turn affect ocean currents, further complicating climatic systems. The ripple effect of such changes cannot be overstated; alterations in ocean currents can lead to shifts in weather patterns around the globe, set off cascading impacts on agricultural yields and biodiversity.
Drought conditions, exacerbated by climate change, also persist as a significant disturbance within the water cycle. Extended periods of low precipitation hinder not just agriculture but also the replenishment of groundwater aquifers. This depletion has dire consequences for populations reliant on well water for their daily sustenance. In many regions, particularly arid and semi-arid areas, groundwater serves as a crucial lifeline. The over-extraction compounded by diminished recharge exacerbates water scarcity, leading to socio-economic strife and potential conflicts over increasingly precious resources.
Furthermore, the processes of evaporation and transpiration are rampantly affected by increasing temperatures. Water evaporates more quickly from surfaces, including rivers, lakes, and reservoirs, while plants may also transpire at higher rates under warmer conditions. Consequently, this can lead to heightened water loss, affecting not only agriculture but also natural vegetation and habitats. As plant communities adjust to these new norms, many species may struggle to survive, further endangering ecosystems around the globe.
Additionally, the altered water cycle can influence the health of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems through increased temperatures. Warmer waters, combined with nutrient runoff from heavy rains, create ideal conditions for harmful algal blooms. These algal blooms can deplete oxygen levels in water, leading to hypoxic conditions that devastate aquatic life. Toxic blooms further pose risks to human health, complicating water treatment and supply solutions.
The socio-economic implications of these climatic changes and their effect on the water cycle extend into many facets of life. Communities that historically relied on traditional agricultural practices are challenged to adapt. The transformation of regional climates forces farmers to reconsider crop choices, operational practices, and water management strategies. In parts of the world afflicted by erratic weather patterns, resilience becomes a necessity, and investment in technology related to irrigation efficiency and crop variability offers potential pathways to adaptation.
In addition, the implications of a disrupted water cycle permeate social structures, particularly in under-resourced areas. Vulnerable populations tend to bear the brunt of these environmental injustices. Limited access to clean water exacerbates health disparities, particularly in regions already riddled with poverty. Water scarcity not only influences health and nutrition but can ignite tensions, prompting migration and displacement as communities search for more viable living conditions.
In conclusion, the disruption of the water cycle by global warming signifies a major threat to planetary balance. As precipitation becomes increasingly erratic, ecosystems collapse under the pressure of altered conditions, and human communities face unprecedented challenges. It is imperative that actions are taken to mitigate climate change, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable practices. Comprehensive strategies that encompass water management, conservation efforts, and adaptive agricultural practices are essential in confronting the multifaceted challenge posed by climate change. The health of our planet’s water systems is integrally linked to the stability of all life on Earth, underscoring the urgency of immediate and concerted action.