Global warming, a severe consequence of anthropogenic activities, has emerged as an urgent challenge facing humanity. As temperatures rise, ecosystems falter, weather patterns become erratic, and the livelihoods of communities are increasingly jeopardized. Thus, recognizing the strategies to mitigate and halt global warming is imperative. This discourse delineates the scientific understanding of global warming and elucidates various solutions that can be implemented at both individual and systemic levels.
First and foremost, it is crucial to comprehend the causative factors of global warming. The primary driver is the accumulation of greenhouse gases (GHGs), particularly carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat from the sun, thereby exacerbating the greenhouse effect. Carbon emissions predominantly emanate from burning fossil fuels in transportation, electricity generation, and industrial processes. Therefore, addressing these emissions is paramount to confronting the crisis.
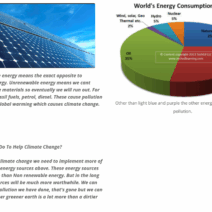
In the arena of energy production, transitioning to renewable sources stands as a beacon of hope. Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal energy present viable alternatives that possess the potential to substantially reduce GHG emissions. Solar panels and wind turbines harness natural forces without depleting finite resources or polluting the atmosphere. Diversifying our energy portfolio to include these sources can dramatically curtail reliance on fossil fuels. It is essential for governments to incentivize the adoption of renewables through tax credits, subsidies, and investments in infrastructure, making these technologies more accessible to the populace.
Moreover, enhancing energy efficiency measures is another pragmatic approach to mitigating global warming. The implementation of stricter building codes and standards can elevate energy performance in residential and commercial structures. Utilizing energy-efficient appliances, retrofitting buildings, and employing smart technologies can lead to significant reductions in energy consumption. Simple behavioral changes, such as turning off lights and unplugging devices when not in use, collectively contribute to energy conservation efforts.
Transportation, a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, requires innovative solutions. The advancement of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a substantial opportunity. EVs emit no tailpipe emissions, and when charged with renewable energy, they offer an environmentally friendly alternative to combustion engine vehicles. Additionally, expanding public transportation systems and promoting non-motorized transit options—such as biking and walking—can further diminish emissions, reduce traffic congestion, and improve air quality.
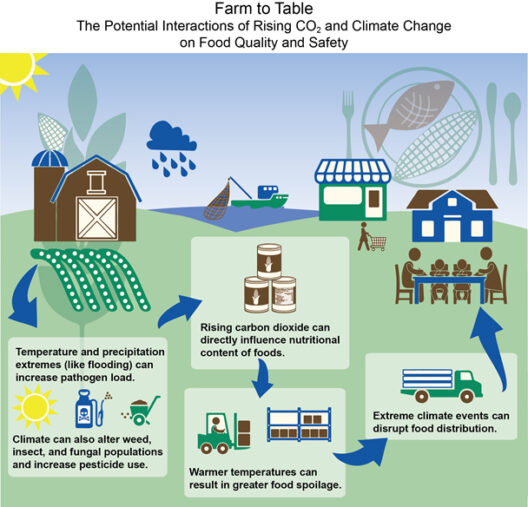
Agriculture, though vital for sustenance, also plays a contributory role in climate change. Practices such as deforestation for agricultural expansion release stored carbon into the atmosphere. Embracing sustainable agricultural practices, including crop rotation, agroforestry, and organic farming, can enhance soil health while reducing carbon footprints. Supporting local food systems decreases reliance on long-distance transportation, further minimizing emissions.
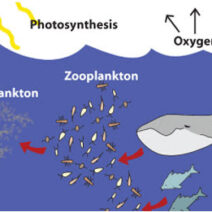
Forests act as essential carbon sinks, sequestering CO2 and regulating the climate. Consequently, the protection and restoration of forests are crucial in opposing global warming. Deforestation, driven by agriculture and logging, accelerates climate change. Emphasizing reforestation and afforestation initiatives can foster biodiversity and restore ecosystems that are essential for the planet’s health. Community-based forest management, which involves local stakeholders in conservation efforts, further enhances resilience against climate impacts.
Furthermore, global collaboration is indispensable to address climate change effectively. The implementation of international agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, seeks to unify countries in their commitment to reducing emissions and transitioning to sustainable practices. Countries must establish binding targets for emissions reductions and provide support for developing nations to adopt clean technologies. Knowledge sharing and financial aid are crucial for fostering global resilience and capacity in combating climate change.
On an individual level, the choices made daily can propagate significant environmental benefits. Embracing a plant-based diet, reducing meat consumption, and minimizing food waste can lower the carbon footprint associated with food production. Additionally, individuals should be encouraged to engage in sustainable practices, such as recycling and composting, to lessen landfill contributions and promote circular economies.
Climate education plays a vital role in empowering individuals to understand the issue and take informed action. Through educational initiatives and advocacy, awareness of climate change and its implications can inspire action within communities. Engaging in local environmental groups or participating in climate marches fosters a sense of community and shared purpose, which is essential in developing a collective response to global warming.
Ultimately, tackling global warming is a multifaceted endeavor that necessitates concerted efforts from individuals, communities, businesses, and governments alike. Recognizing the interconnectivity of economic, social, and environmental systems is essential to devise holistic strategies to combat climate change. By embracing renewable energy, enhancing efficiency, supporting sustainable practices, and fostering global cooperation, society can pave the way toward a sustainable future. As stewards of the planet, it is incumbent upon us to act decisively and implement actionable solutions to avert the looming crisis of global warming.