The intricate relationship between carbon emissions and the greenhouse effect is pivotal in our understanding of climate change and global warming. At its core, carbon emissions, primarily in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2), play a significant role in altering the Earth’s natural atmospheric balance. This alteration leads to the greenhouse effect, a phenomenon that, while essential for sustaining life, has become more pronounced due to anthropogenic activities.
To embark on this exploration, it is crucial first to grasp the fundamental concept of the greenhouse effect. The Earth is enveloped by an atmosphere that comprises various gases, including nitrogen, oxygen, and greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. Without this atmospheric layer, the average temperature of our planet would plummet, rendering it inhospitable. These greenhouse gases function as a barrier, allowing sunlight to penetrate the atmosphere while simultaneously trapping some of the heat that the Earth radiates back into space.
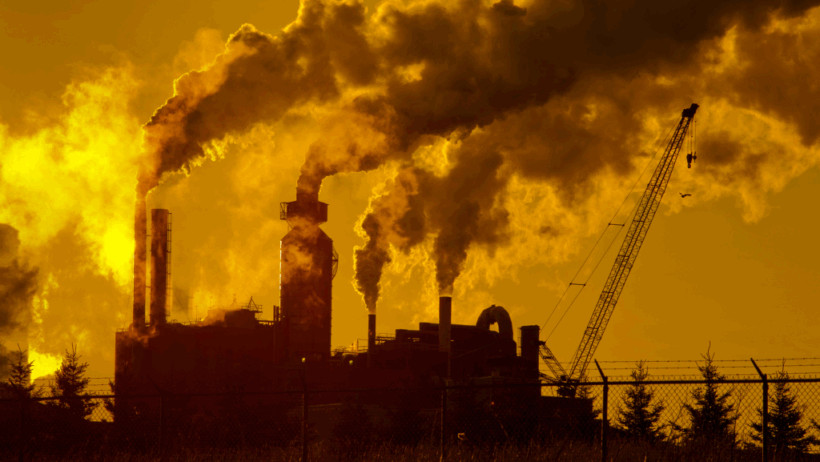
However, the equilibrium of this natural system is disrupted by the excessive release of carbon emissions, primarily from fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes. The significant increase in CO2 concentrations over the past century has led to a phenomenon known as enhanced greenhouse effect. This escalation exacerbates the natural greenhouse effect, causing global temperatures to rise to unprecedented levels.
The primary sources of carbon emissions can be broadly categorized into sectors: energy production, transportation, industrial processes, and agriculture. The energy sector, which heavily relies on coal, oil, and natural gas, represents the most substantial contributor to global carbon emissions. Each kilowatt-hour generated through fossil fuels releases significant amounts of CO2, contributing to the thickening of the atmospheric blanket.
Transportation also plays a vital role in carbon emissions. Vehicles powered by internal combustion engines—using gasoline or diesel fuel—are a major source of CO2 emissions. Personal vehicles, commercial trucks, airplanes, and ships collectively contribute to a staggering percentage of the world’s carbon footprint. The shift towards electric vehicles and renewable energy sources is critical in mitigating these emissions, but the pace of transition must accelerate.
Industrial processes, including cement production and chemical manufacturing, also generate substantial carbon emissions. These sectors are often overlooked in discussions about carbon neutrality. For instance, the cement industry is responsible for approximately 8% of global carbon emissions. Addressing industrial emissions requires innovative technologies and a substantial commitment to sustainability practices.
Agricultural practices, particularly livestock farming and rice cultivation, release greenhouse gases, including methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O). While these gases are more potent than CO2 in terms of heat-trapping abilities, they contribute to the same ultimate outcome: climate change. Sustainable agricultural practices, such as integrated crop-livestock systems and agroforestry, offer viable pathways to reduce such emissions.
As the levels of carbon emissions continue to escalate, the ramifications for global climates are profound. The rising concentrations of CO2 not only increase temperatures but also lead to a cascade of environmental impacts. Melting polar ice caps, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events are now part of the reality of modern life. The frequency and intensity of hurricanes, droughts, and floods are increasingly linked to climate change driven by carbon emissions.
Moreover, the very fabric of biodiversity is threatened as various ecosystems struggle to adapt to swiftly changing climates. Species unable to adapt to new conditions may face extinction, further destabilizing ecosystems. The loss of biodiversity has cascading effects, impacting food security, health, and economic stability.
Addressing carbon emissions and their role in global warming is not merely an environmental necessity; it is a moral imperative for humanity. The urgency of the climate crisis compels a collective response that transcends borders and ideologies. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, aim to unify efforts to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. This endeavor requires nations to commit to reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources.
Individuals too play a crucial role in this endeavor. From reducing energy consumption to choosing sustainable transportation options, each action contributes to the larger goal of carbon neutrality. The shift to renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and hydropower must be prioritized. These sources not only provide a viable alternative but also mitigate the adverse effects of carbon emissions on the climate.
This pivotal moment in history demands a reawakening of our collective consciousness toward the environment. The promise of a sustainable future lies in our willingness to rethink our current practices, embrace innovation, and foster a sense of stewardship for the planet. Climate education is vital, as it cultivates awareness and inspires action among individuals and communities. Understanding the intricate link between carbon emissions, the greenhouse effect, and global warming can spark change. The pursuit of sustainability is a journey, one that must be traveled together.
In conclusion, carbon emissions are not merely numbers on a chart; they represent a critical challenge that threatens the very fabric of life on Earth. The greenhouse effect, while a natural process, has been unnaturally amplified by human activity. The imperative to reduce carbon emissions and transition towards a sustainable future has never been clearer. Our actions today will dictate the climate we leave for future generations. By fostering innovation, championing sustainable practices, and embracing systemic change, we can mitigate the effects of climate change and preserve our planet for the generations to come.