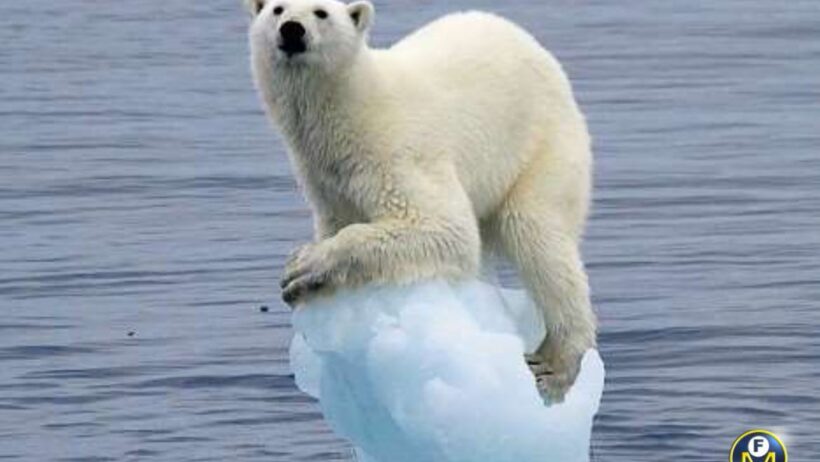
As the relentless march of global warming changes our planet, the polar bear stands as a poignant symbol of the Arctic’s plight, embodying the myriad ways climate change is intricately woven into its ecosystem’s fabric. These majestic creatures, reliant on sea ice for their survival, find themselves ensnared in a precarious predicament, akin to a ship adrift without a sail. With melting ice caps and warming waters, the Arctic landscape is transforming, steering these iconic bears toward an uncertain future.
The Arctic, often referred to as the “Earth’s refrigerator,” serves a critical role in regulating global temperatures. It is here that polar bears have evolved over millennia, developing adaptations that allow them to thrive in extreme cold. Their thick blubber and fur insulate them from frigid temperatures, while their powerful limbs and keen sense of smell enable them to hunt seals, their primary prey, with remarkable efficiency. However, as the climate warms and ice retreats, the very foundation of their existence is eroding.
With average temperatures in the Arctic rising at nearly twice the global rate, sea ice is rapidly diminishing. From the North Pole to the coastlines of Alaska and Canada, ice coverage during summer months has declined dramatically in recent decades. The reduction of sea ice not only limits hunting grounds but also alters the bears’ migration patterns, pushing them into unfamiliar territories in search of food. This phenomenon is reminiscent of a once-majestic ballet, now interrupted by dissonance, as these creatures struggle to adapt to an ever-volatile stage.
As the ice that supports their homes melts away, polar bears are faced with an alarming reality. They become increasingly reliant on land-based food sources, leading to dietary changes that could have cascading effects on their health and reproductive success. Instances of polar bears turning to scavenging—feeding on birds or human refuse—are becoming prevalent, a stark indication of desperation akin to a mighty warrior reduced to foraging for scraps. Nutritional deficiencies can lead to weakened immune systems and lower birth rates, precipitating a potential collapse of their populations.
Moreover, the loss of sea ice has a domino effect on the broader ecosystem. The melting ice exposes darker ocean waters, which absorb more sunlight and heat, further accelerating warming. This, in turn, affects fish populations and marine life that serve as vital links in the food chain. The displacement of these species not only threatens the bears but also disrupts the intricate balance of the Arctic marine ecosystem. It is a perilous spiral—each negative impact feeding into the next, forming a web of interlinked challenges that must be addressed to safeguard Arctic life.
Climate change has also exacerbated other environmental phenomena that directly impact polar bears. Increased human activity in the Arctic—whether from shipping routes opening up due to melting ice or resource extraction—introduces a host of challenges such as pollution, noise, and habitat destruction. Interactions between bears and humans have intensified, leading to conflicts that endanger both species. As bears wander into human settlements in search of food, their survival instincts clash with human interests, often resulting in tragic consequences.
It is imperative to understand that the plight of polar bears is not an isolated issue; it is a harbinger of broader ecological changes that affect all corners of the Earth. The fate of these bears serves as a poignant reminder of the interconnectedness of life. When the ice melts and polar bears struggle to survive, humanity faces a moment of reckoning. We become witnesses to a dramatic narrative unfolding—one that compels us to address the root causes of climate change rather than merely responding to its symptoms.
Efforts to reverse or mitigate the impacts of climate change are vital. Deliberate global initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions are essential not only for the Arctic’s future but for the planet as a whole. By transitioning to renewable energy sources, promoting sustainable practices, and investing in conservation efforts, humanity can help secure a more robust and resilient ecosystem for polar bears and countless other species threatened by environmental changes.
Education and awareness are equally crucial. By fostering a deeper understanding of the challenges faced by polar bears and the impacts of global warming, we can inspire collective action across communities and nations. The plight of the polar bear resonates on an emotional level; they represent both the fragility of life in a warming world and the potential for change. It is within our power to alter the course of the narrative, transforming a story of despair into one of hope.
As we navigate the turbulent waters of climate change, let us not forget the profound lessons imparted by the polar bear. They are not merely magnificent creatures of the Arctic but also emblematic of the delicate balance that sustains all life. By championing their cause, we advocate for the preservation of our planet’s integrity, ensuring that future generations inherit a world where polar bears continue to roam freely, and the Arctic remains a vibrant pillar of life and diversity. The time to act is now; the survival of the polar bear—and the planet—depends on it.