Greenhouse gases (GHGs) have become a ubiquitous topic in discussions surrounding climate change and global warming. These gases, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), are essential components of Earth’s atmosphere. They play a critical role in maintaining the planet’s temperature, yet their increasing concentrations are contributing to a significant rise in global temperatures. Understanding how greenhouse gases induce global warming necessitates an exploration of the greenhouse effect itself, as well as the anthropogenic activities that exacerbate these processes.
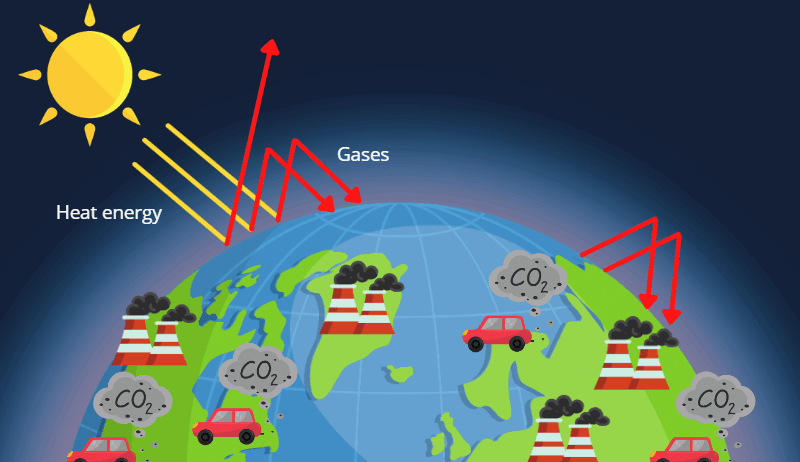
The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that occurs when certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere trap heat from the sun. This process is vital for sustaining life on Earth. Sunlight reaches the planet’s surface, where it is absorbed and subsequently re-radiated as infrared radiation or heat. Greenhouse gases absorb some of this infrared radiation, preventing it from escaping back into space. Instead, they re-radiate it in all directions, including back towards the Earth’s surface, which contributes to a warming effect. This delicate balance has existed for millennia, ensuring that Earth maintains a temperature conducive to life.
However, it is the amplification of this effect that raises alarm. Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, have led to unprecedented increases in the concentrations of greenhouse gases. Before the Industrial Revolution, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere was about 280 parts per million (ppm). As of 2021, it surpasses 410 ppm, a significant and worrying deviation from natural levels. This rise is primarily attributable to the combustion of fossil fuels for energy, which releases vast amounts of CO2. Other sources, such as agricultural practices and waste management, contribute additional greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide.
Methane, although present in much smaller quantities than CO2, is over 25 times more effective at trapping heat over a 100-year period. It is emitted during the production of oil and gas, as well as from agricultural practices, specifically from enteric fermentation in ruminants, landfills, and wetlands. The potency of methane as a greenhouse gas underscores the necessity of targeting multiple emission sources in climate change mitigation efforts.
The implications of rising global temperatures are profound. As the concentration of greenhouse gases escalates, the intensity of the greenhouse effect strengthens. This results in higher atmospheric temperatures, which consequently affect various climate systems, ocean temperatures, and ice caps. For instance, warmer temperatures lead to the melting of polar ice and glaciers, contributing to rising sea levels, which pose a significant threat to coastal communities worldwide.
Moreover, global warming manifests itself through increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. Droughts, floods, hurricanes, and heatwaves have become more prevalent and severe. As temperatures rise, the atmosphere can hold more moisture, leading to increased precipitation in some regions, while others experience prolonged dry periods. These extreme weather patterns disrupt ecosystems, leading to loss of biodiversity and challenges to food security.
Furthermore, the feedback mechanisms driven by climate change can exacerbate the situation. For example, as glaciers and polar ice caps melt, they expose darker ocean waters or land, which absorb more sunlight than reflective ice, thereby accelerating warming. Similarly, thawing permafrost releases trapped methane, creating a cycle that propels further warming. These feedback loops complicate predictive models, making the future landscape of climate change uncertain and challenging to navigate.
This phenomenon also has profound socioeconomic implications. Developing countries, which often lack the resources to adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change, are disproportionately affected. They may experience severe droughts that hinder agricultural output or flooding that displaces communities. The ripple effect of these changes can lead to political instability, increased migration, and heightened conflict over scarce resources, showcasing the interconnectedness of environmental health and human welfare.
In the quest for solutions, various strategies have emerged to combat the increasing levels of greenhouse gases. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, is a crucial step. These alternatives to fossil fuels can significantly reduce carbon emissions, fostering a sustainable and resilient energy future. Moreover, energy efficiency measures in transportation, buildings, and industry can lower overall demand and emissions, providing a dual benefit of cost savings and environmental protection.
Forestry plays an essential role in mitigating greenhouse gas concentrations. Trees absorb CO2 during photosynthesis, acting as vital carbon sinks. Reforestation and afforestation initiatives can help restore ecosystems and sequester carbon from the atmosphere. Furthermore, sustainable agricultural practices that minimize the use of synthetic fertilizers can reduce emissions of nitrous oxide, while improved manure management can decrease methane production.
Public engagement and awareness are also instrumental in combating global warming. Education on energy conservation, waste reduction, and sustainable practices can empower individuals to make informed decisions that collectively contribute to climate change mitigation. Advocacy for policy changes at local, national, and international levels is crucial to catalyze systemic shifts toward sustainability.
In summary, greenhouse gases are a crucial component of the Earth’s atmospheric balance, yet their excess leads to global warming with far-reaching consequences. The interplay between human activity, greenhouse gas concentrations, and climatic responses creates a complex challenge that necessitates urgent action. By understanding the mechanisms at play, we can formulate effective strategies to combat climate change and strive toward a sustainable future. The urgency of the situation demands that individuals, communities, and governments alike unite in this critical endeavor for current and future generations.