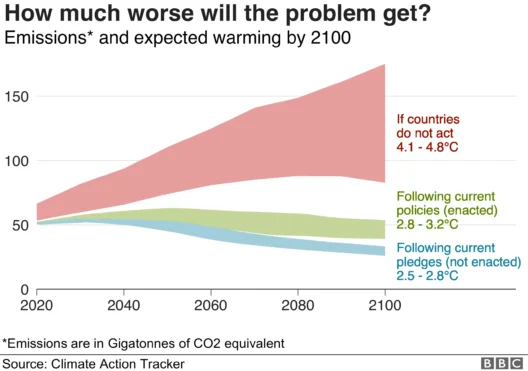
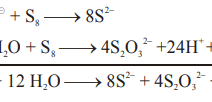Global warming, a pressing and ubiquitous issue, intertwines the destinies of humans, animals, and ecosystems. This phenomenon, driven chiefly by the relentless accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, alters climatic patterns and disrupts the delicate equilibrium that sustains life on Earth. A multifaceted concern, its ramifications extend far beyond rising temperatures. Understanding the web of life—encompassing various species, habitats, and human systems—illuminates the complexities of how global warming affects every aspect of our planet.
At the core of the global warming narrative lies the human dimension. Human health experiences significant repercussions from changes in the climate. Increased temperatures can exacerbate respiratory ailments, as diminished air quality leads to a rise in pollutants and allergens. Heatwaves not only threaten vulnerable populations—such as the elderly and those with preexisting health conditions—but also contribute to heat-related illnesses and fatalities. Furthermore, the distribution of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, is profoundly influenced by climatic shifts. Mosquitoes and other vectors thrive in warmer climates, expanding their reach and posing new threats to public health.
Yet, it is not merely the health of humans that is at stake; the plight of wildlife and natural ecosystems deserves equal attention. Various species find themselves on the frontlines of global warming. As their habitats change—be it through forest degradation, loss of polar ice, or altered migration patterns—many animals face unprecedented challenges. Polar bears, for instance, rely on sea ice as a platform for hunting seals. With diminishing ice cover, their ability to procure food diminishes, pushing them closer to the brink of extinction. Endangered species, such as the black rhino and the orangutan, encounter similar threats, emphasizing the urgent need for biodiversity preservation.
The disruption extends beyond individual species, cascading through entire ecosystems. The interconnectedness of these systems means that the loss of one species can cause a ripple effect, resulting in the decline of others. For instance, declining bee populations pose a significant threat to food security. These pollinators play a crucial role in the fertilization of numerous crops and plants. As climate change alters flowering times and habitats, the synchronization between plants and pollinators falters, jeopardizing both agricultural yields and natural food webs.
Marine ecosystems are not exempt from the insidious effects of global warming. Rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification threaten coral reefs—often described as the “rainforests of the sea.” Coral bleaching events, driven by elevated temperatures, result in the loss of vibrant marine biodiversity. With over a quarter of marine species relying on coral reefs for habitat, the degradation of these ecosystems represents a loss of invaluable biodiversity and a destabilization of marine food webs.
Beyond biodiversity and ecosystems, global warming presents critical challenges to agriculture and water resources. Shifts in weather patterns lead to erratic precipitation, droughts, and floods, directly impacting food production. Farmers face the daunting challenge of adapting to these changes while maintaining yields to support a growing global population. The strain on freshwater resources is equally alarming. Changing precipitation patterns and shrinking glaciers threaten the availability of clean water for millions, affecting both human consumption and agricultural irrigation.
As we delve deeper into the web of life, one begins to understand the profound psychological and cultural impacts of global warming. The infusion of anxiety related to climate change permeates contemporary society. Psychological research indicates that climate change can create feelings of helplessness, stress, and eco-anxiety among individuals. As communities witness extreme weather events and the visible detriment to their surroundings, a sense of loss and disconnection can envelop individuals, weakening traditional cultural ties to nature.
Furthermore, climate change exacerbates inequalities, further complicating the human experience. Vulnerable communities, often with the least resources, are disproportionately affected by environmental changes. They lack the adaptive capacity to effectively respond to the challenges presented by global warming. This inequitable distribution of impacts underscores the need for climate justice, which advocates for empowering marginalized communities to engage in climate action and decision-making processes.
In examining the intricate connections woven throughout the web of life, it becomes increasingly clear that addressing global warming requires a collective, multidisciplinary approach. Policymakers, scientists, businesses, and individuals must collaborate to implement innovative solutions to mitigate the effects of climate change. This might involve the transition to renewable energy sources, the development of sustainable agricultural practices, and the preservation of vital ecosystems through conservation efforts.
Education and awareness play pivotal roles in fostering proactive responses to climate challenges. By engaging communities and emphasizing the importance of ecological stewardship, society can cultivate a deeper appreciation for the natural world and its intrinsic value. This, in turn, motivates collective action and inspires individuals to become proactive agents of change in their respective spheres of influence.
As we navigate the uncertainties brought about by global warming, we must strive to appreciate the profound interconnectedness of all life forms. The web of life—home to humans, animals, and ecosystems alike—demands our care and commitment. Understanding the nuanced impacts of climate change illuminates our shared responsibilities. It compels us to act decisively and with empathy, ensuring a sustainable future for generations to come.