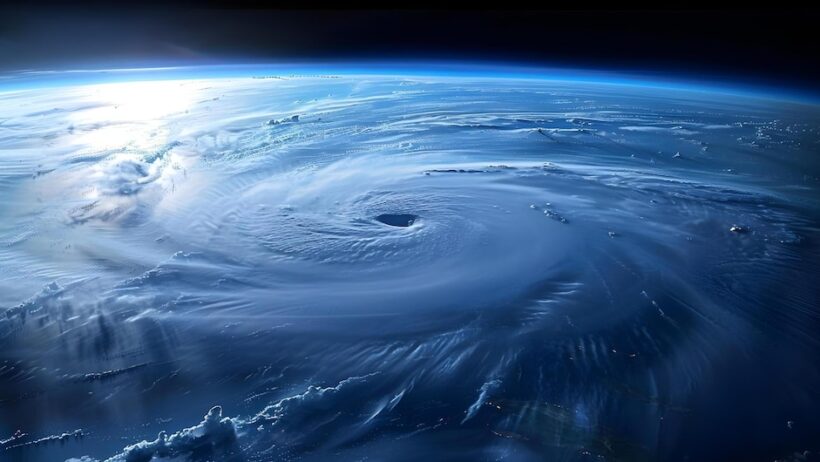
Global warming, an urgent and pressing issue of our time, has far-reaching consequences that reverberate through the natural world. As the planet’s temperature continues to rise, a pronounced shift in climatic patterns emerges, giving rise to extreme weather events. This phenomenon, often referred to as “when nature fights back,” unveils the interplay between anthropogenic activities and the environment, revealing the intricate balance that has been disrupted.
At the heart of the matter is the aggravation of natural systems due to increased greenhouse gas emissions. These gases, primarily carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat within the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to a cascade of environmental changes. The scientific consensus unequivocally links these changes to human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, exposing the integral relationship between our actions and the climatic fallout.
Extreme weather manifests in various forms: hurricanes, droughts, floods, heatwaves, and wildfires are just a few examples of how the Earth responds to the escalating temperatures. Understanding these phenomena requires an exploration of their characteristics, causes, and implications.
**Hurricanes** are perhaps the most ferocious manifestation of extreme weather. Proliferating over warm ocean waters, these storms become increasingly intense as temperatures rise. The Atlantic hurricane season has notably experienced a surge in both frequency and severity, a direct correlation observed with warmer sea surface temperatures. Elevated temperatures not only facilitate the formation of hurricanes but also enhance their destructive potential, enabling storms to sustain higher wind speeds and greater rainfall. Coastal regions, thus, bear the brunt of nature’s fury, suffering from storm surges and catastrophic flooding.
In stark contrast lies the phenomena of **drought**, characterized by extended periods of below-average precipitation. Global warming exacerbates drought conditions by increasing evaporation rates and altering weather patterns. Regions previously deemed fertile are now succumbing to aridity, jeopardizing agriculture and water supplies. The Great Plains of the United States and parts of sub-Saharan Africa serve as stark illustrations of this shift. The implications extend beyond agricultural losses, as drought can lead to economic hardship, food insecurity, and social unrest.
Meanwhile, **flooding** represents yet another facet of extreme weather, often interlinked with intensifying storms and rising sea levels. As precipitation becomes increasingly erratic, heavy downpours contribute to overwhelmed drainage systems and rising river levels. Cities like New Orleans and Miami are particularly vulnerable, grappling with the dual threats of storm surges and chronic flooding. Flooding not only inundates homes and infrastructure but also results in significant losses of life and displacement of populations. The aftermath often unveils broader socio-economic consequences, including strained emergency services and increased health risks due to waterborne diseases.
**Heatwaves**, defined as prolonged periods of excessively hot weather, pose another critical danger. With global temperatures on the rise, the frequency and intensity of heatwaves have surged. Regions historically unaccustomed to extreme heat are now experiencing unprecedented temperature spikes. This phenomenon is particularly perilous for vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with pre-existing health conditions. Heatwaves exacerbate existing health disparities, leading to increased hospitalizations and fatalities. Urban areas, with their heat-retaining infrastructure, often experience even more severe impacts, creating heat islands that can extend the duration of these extreme events.
Additionally, **wildfires** have become increasingly commonplace in areas dominated by forests and shrublands. Higher temperatures and prolonged drought conditions create the ideal environment for wildfires to thrive. Regions like California and Australia have witnessed devastating fire seasons that not only obliterate vast tracts of land but also contribute significantly to carbon emissions and air pollution. The vicious cycle of climate change feeds these fires, and in turn, the fires exacerbate climate change, releasing sequestered carbon back into the atmosphere.
As extreme weather events persist, the impacts on ecosystems cannot be overlooked. Biodiversity suffers acutely as habitats are altered or destroyed. Species face the threat of extinction as they struggle to adapt to rapidly changing conditions. Coral reefs, for instance, are particularly susceptible to temperature increases. Coral bleaching, caused by thermal stress, threatens marine ecosystems and the livelihoods of millions dependent on them for food and income.
Mitigating the multifaceted challenges posed by global warming necessitates a robust response that encompasses both environmental stewardship and sustainable practices. Transitioning to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy efficiency, and promoting sustainable agriculture are all crucial components of a holistic strategy. Policymakers must prioritize these initiatives, instituting regulatory frameworks that mandate reductions in greenhouse gas emissions while fostering resilience in communities vulnerable to climate impacts.
Furthermore, fostering public awareness and encouraging collective action could play pivotal roles in combating the dire consequences of climate change. By galvanizing communities toward sustainable practices, engaging in conservation efforts, and leveraging technology for climate resilience, the path toward mitigating extreme weather can be navigated effectively. Educational initiatives that underscore the link between individual choices and broader climate impacts are essential for cultivating a proactive citizenry.
In conclusion, the undeniable reality of global warming and its ensuing extreme weather phenomena warrants immediate action. As nature exhibits its formidable capacity to respond to anthropogenic insults, society must recognize its responsibility to mitigate this crisis. By half-heartedly addressing climate change, we risk entering a vicious cycle where nature’s wrath becomes increasingly severe and uncontrollable. The time for decisive action is now; our planet’s future hinges on the choices we make today.