As we traverse the contours of climatic discourse, an intriguing predicament arises: how can a technology primarily designed to harness solar energy also mitigate the very existential threat of global warming? This entanglement of solar technology and climate change prompts a pivotal inquiry: can solar panels do more than simply convert sunlight into electricity? The answer, layered and multifaceted, lies at the intersection of engineering innovation, environmental stewardship, and systemic societal change.
Solar technology, at its core, is an exquisite amalgamation of physics and ecological consciousness. As the implications of fossil fuel dependency become increasingly catastrophic, the transition to renewable energy sources like solar power emerges as not just a feasible alternative, but an imperative. The mechanics of solar panels contribute to global warming mitigation through several dynamic mechanisms. First and foremost, utilizing solar energy diminishes our reliance on carbon-intensive fuels. By substituting traditional energy sources with solar power, we significantly curb greenhouse gas emissions. This shift is vital, as carbon emissions are a principal driver of climate change.
Yet, the engagement of solar technology does not stop at mere energy computation. The production and installation of solar panels themselves carry environmental consequences. It is vital to scrutinize the entire lifecycle of solar technology, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal. For instance, the mining of materials like silicon and rare earth elements can lead to habitat destruction and increased carbon footprints. This represents an ironic conundrum: in pursuit of a cleaner future, are we inadvertently causing environmental degradation today? In addressing this challenge, innovation in sustainable manufacturing processes and recycling techniques becomes paramount, paving the way for a net-positive impact on the planet.
Aside from direct emission reductions, solar panels also play a role in the broader ecosystem of energy systems. They facilitate energy decentralization, fostering localized energy production. This has profound implications for communities, especially in underdeveloped regions. By decentralizing energy resources, we not only enhance energy access but also fortify energy resilience. In locales where electrification is sporadic and unreliable, solar technology provides a stable alternative that diminishes dependency on fossil fuels and enhances self-sufficiency.
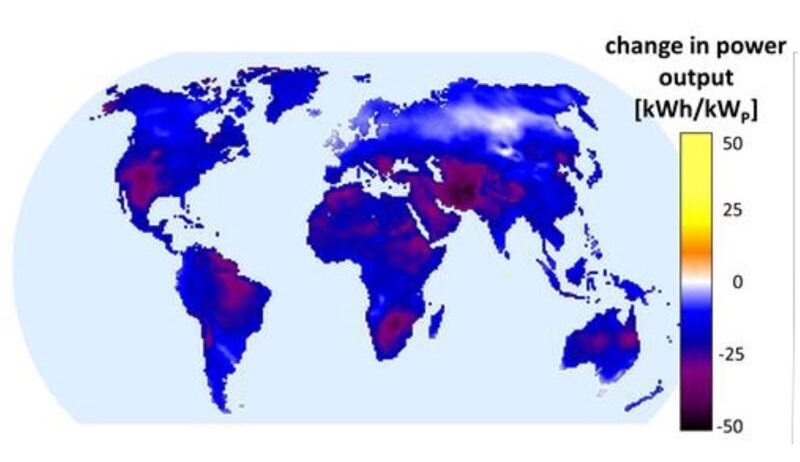
But what about the quite literal heat of the sun? At high concentrations, solar energy can exponentially increase the thermal energy around us, contributing to localized climate warming. This phenomenon, known as urban heat island effect, challenges the installation of solar panels in densely populated areas. How can we balance the imperative to utilize solar energy with its potential repercussions? Addressing these nuances necessitates vigilant site selection, urban planning, and the integration of greenery into our urban landscapes, thus creating an equilibrium between energy generation and environmental preservation.
Solar panels have also engendered a heightened sense of environmental awareness and activism. As communities adopt solar energy, they often become more attuned to various environmental issues, from biodiversity conservation to pollution reduction. This transformation of mindset is crucial; when individuals and communities recognize their agency in confronting climate change, collective action magnifies. It raises a playful question: if every household transitioned to solar energy, could our urban environments transform into thriving ecosystems rather than concrete jungles? Herein lies the challenge; the route toward a sustainable and eco-friendly society transcends technology alone—it demands a cultural shift toward sustainability.
To appreciate the profound potential of solar technology further, it is also prudent to consider its symbiotic relationship with complementary technologies. For example, the integration of solar energy with battery storage systems augments reliability, addressing the intermittent nature of solar power. Energy storage allows excess energy generated during peak sunlight hours to be harnessed during periods of high demand or low generation. This synergy not only secures energy availability but also supports grid stability, thereby facilitating a broader adoption of renewable technologies. Essentially, the greater the harmony attained between various energy systems, the more profound the impact we can achieve in combating global warming.
Moving forward, harnessing the innovations of solar technology requires a comprehensive approach that entails policy advocacy, community engagement, and continuous research and development. Policymakers must enact regulations that prioritize renewable energy adoption and incentivize sustainable practices. This could include tax rebates for solar installations or mandates on renewable energy sourcing for major corporates. Every legislative act plays a significant role in shaping the trajectory of solar energy utilization and application.
Moreover, public awareness and education must be amplified. Many people remain unaware of the ramifications of energy choices on climate change. By elucidating the benefits of solar energy and facilitating access to solar technologies, individuals can become informed consumers and active participants in the global climate conversation. Community workshops, informational campaigns, and educational programs can empower society as a collective entity capable of driving systemic change.
In conclusion, solar technology embodies a keystone in the arch of climate solutions. Beyond mere panels, it bridges the realms of energy efficiency, community empowerment, and environmental stewardship. While challenges remain—regarding production impacts, urban planning, and cultural shifts—each presents an opportunity for innovation and progress. The journey toward a sustainable future supported by solar energy requires steadfast resolve and collective action, making every step taken toward its widespread adoption a significant stride against the global warming that threatens our collective existence. What’s your collective step today?