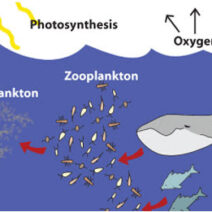
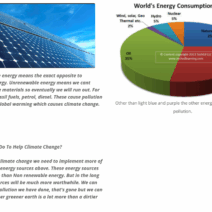
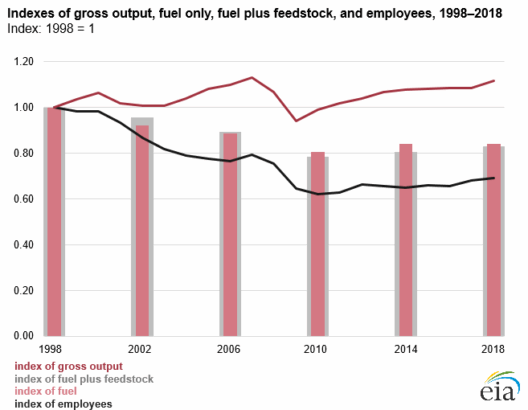
Earth’s climate is an intricate web of interdependent systems, constantly evolving, and increasingly impacted by anthropogenic activities. As global warming exacerbates the frequency and intensity of climate-related phenomena, visual representations of these changes provide crucial insights into the depth of our environmental predicament. This article aims to elucidate how visualizing our planet’s climate in flux helps us understand the urgency of the situation and compels us to take preventive measures.
Global warming is not an abstract concept confined to scientific papers or discussions among policy makers. Rather, it manifests in tangible changes across the globe. It is synonymous with shifting weather patterns, rising sea levels, melting glaciers, and unprecedented biodiversity loss. These alterations are palpable; they elicit both concern and fascination. Many people are captivated by the dramatic visuals of Earth’s transformations, which not only engage the mind but also spur significant emotional responses.
The depiction of climate change through evocative imagery serves as a call to action. For instance, images illustrating deforestation reveal stark transformations in once-vibrant landscapes, laying bare the fragility of ecosystems. Forests play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, and their destruction accelerates atmospheric carbon levels, contributing to global warming. The sickening sights of bare hillsides juxtaposed against the remnants of ancient woodlands exemplify humanity’s tendency towards ecological short-sightedness.
Likewise, the polar regions have become emblematic of climate change. The capricious melting of Arctic and Antarctic ice showcases the accelerated pace of climatic upheaval. Coastal cities and island nations face existential threats as rising sea levels devour land. Visualizations of these phenomena, such as side-by-side comparisons of historical and contemporary photographs of polar ice, underscore the alarming reality of a world in flux. This juxtaposition helps to frame the discussion on global responsibility and accountability; it raises questions about what future generations will inherit.
In urban settings, heatwaves have become more frequent, and their effects more apparent, as demonstrated by energetic visualizations of temperature anomalies across different cities. Heat maps reveal how urban centers, often referred to as heat islands, disproportionately absorb and retain heat due to impermeable surfaces. This results in dire health implications for residents, particularly vulnerable populations. Dynamic representations of these trends can effectively galvanize communities to prioritize sustainable urban planning and green infrastructure.
The effects of climate change are not merely environmental; they are economic and social as well. The cascading consequences of global warming disrupt agricultural patterns, leading to food insecurity in various parts of the world. Grappling with shifting precipitation patterns and extreme weather events, farmers are increasingly at risk of crop failures. Infographics and data visualizations that track these shifts can help amplify awareness of food systems’ vulnerabilities and foster a public dialogue about climate-resilient agriculture.
Climate migration also emerges as a harrowing consequence of a rapidly changing environment. Individuals are forced to leave their homes due to environmental degradation, flooding, and resource scarcity. Data visualizations that track migration patterns highlight the human cost of climate change. As populations relocate, the fabric of societies inevitably changes, leading to cultural frictions and tensions. Such realities paint a sobering portrait of global interconnectedness, underscoring that environmental degradation knows no borders.
Importantly, visual representations of climate change also bring to light the positive narratives of resilience and adaptation. Communities worldwide are innovating to combat the adverse impacts of climate change. For instance, visualizing the surge in renewable energy infrastructure illustrates proactive efforts toward sustainable energy transitions. Wind turbines and solar panels dominate the skyline in many regions, symbolizing a pivot towards cleaner energy and reduced carbon emissions. These images inspire hope and underlie a critical aspect of climate activism—the potential for transformation and innovation through collective action.
Moreover, the conservation of biodiversity emerges as a crucial but often overlooked facet of climate action. Illustrative data on endangered species and their habitats elucidates the inextricable link between a stable climate and ecological stability. Visuals that depict reforestation efforts juxtaposed against barren land exemplify the commitment needed to reverse the devastation wrought by habitat destruction. Herein lies the potential for communities and individuals to engage in restoration initiatives that rejuvenate ecosystems, ultimately benefiting both wildlife and human populations alike.
Engagement in climate activism may be propelled by the stark realities depicted through visual storytelling. Art, photography, and dynamic graphics have all become tools of advocacy, igniting public discourse around climate issues. They enkindle a sense of urgency that transcends mere numbers or statistics, engaging emotions and stimulating concern on a visceral level.
Finally, as climate change accelerates, visualizing its impacts becomes indispensable for education and policy formulation. Policymakers and citizens alike must grapple with myriad uncertainties regarding future climatic scenarios. In this context, projections powered by data visualizations that model potential pathways for reducing carbon emissions can guide decisions. This information plays an essential role in fostering informed public debate and elevating the collective understanding of our consequential choices.
In conclusion, the visualization of Earth’s climate in flux offers profound insight into the ongoing ramifications of global warming. It encapsulates the myriad challenges associated with environmental degradation while simultaneously emphasizing the potential for transformation and adaptation. Striking imagery serves to galvanize individuals and communities, manifesting the fierce interplay between humans and the natural world. As such, it remains imperative that we confront our climate reality with clarity, empathy, and resolve, allowing the visual narratives of our planet to guide us toward a more sustainable future.