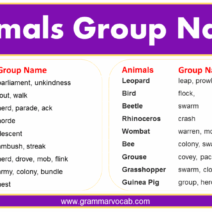
The intricate interplay between the greenhouse effect and global warming forms a fundamental aspect of contemporary climate science. These two phenomena, though distinct in their mechanisms, are inexorably linked in their implications for the environment, human activities, and future generations. Understanding their relationship is crucial for fostering effective climate action and motivating public engagement in environmental stewardship.
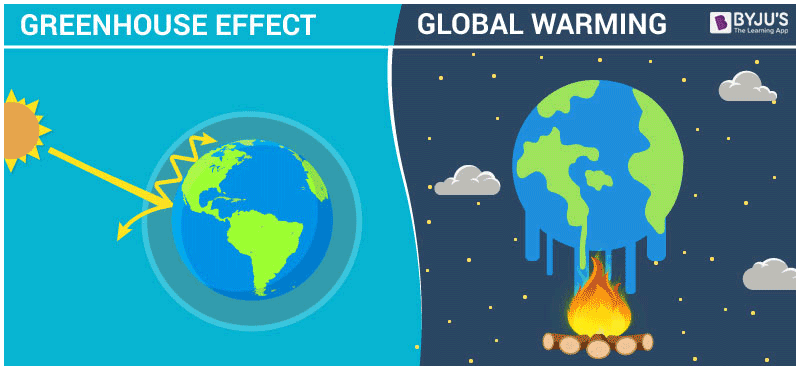
At the core of the greenhouse effect lies the presence of certain gases in the Earth’s atmosphere, commonly referred to as greenhouse gases (GHGs). These gases—including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O)—are capable of absorbing and re-emitting infrared radiation. As sunlight penetrates the atmosphere, some of it is reflected back into space while the remainder reaches the Earth’s surface, where it is converted into heat. The gases absorb some of this heat energy, trapping it within the atmosphere, which contributes to a warming effect that is critical for sustaining life.
This process, while natural, has been significantly amplified by human activities, particularly since the Industrial Revolution. The combustion of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes have propelled the concentrations of GHGs to unprecedented levels. According to the latest assessments, atmospheric CO2 levels have surged beyond 400 parts per million, a threshold not observed for millions of years. This rapid accumulation disrupts the delicate equilibrium of Earth’s energy balance, leading to enhanced greenhouse gas-induced warming.
The implications of an increasingly warmer planet are both multifaceted and profound. One of the most immediate consequences is the alteration of climatic patterns. We are witnessing an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, ranging from severe heatwaves to devastating floods. The concept of climate variability becomes paramount in understanding these shifts, as they are no longer mere anomalies but indicators of a systemic upheaval in climatic stability.
Furthermore, global warming has been linked to the ongoing loss of biodiversity. Ecosystems, which have evolved over millennia, face insurmountable challenges in adapting to rapid environmental changes. Habitats that once thrived are becoming inhospitable, leading to the extinction of numerous species. The phenomenon of shifting species ranges, where flora and fauna must migrate to cooler areas, is increasingly observable, yet many have no such refuge left. This not only threatens wildlife but also undermines the ecosystem services that underpin human societies, including pollination, water purification, and climate regulation.
Another critical dimension to consider is sea level rise, a direct consequence of the thermal expansion of water and the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers. Coastal communities face an existential threat as rising seas inundate their lands, displacing millions and diminishing arable land. The economic ramifications are staggering; cities that once flourished by the coast may become uninhabitable, leading to a cascade of societal issues including increased migration, economic instability, and geopolitical tensions over resources.
Food security is also jeopardized by global warming. Changes in rainfall patterns and increasing temperatures affect agricultural yields, leading to diminished crop productivity. Regions that depend on stable climates for farming are particularly vulnerable. The variability in weather not only affects crop growth but also exacerbates issues of water scarcity, making irrigation increasingly challenging in many parts of the world.
The symbiotic relationship between the greenhouse effect and global warming cannot be overlooked when considering solutions to mitigate climate change. Transitioning from fossil fuel dependency towards renewable energy sources is imperative. Solar, wind, and geothermal energy present viable alternatives that can significantly reduce GHG emissions. Moreover, enhancing energy efficiency in various sectors—from transportation to agriculture—can lead to substantial reductions in carbon footprints.
Moreover, reforestation and afforestation play pivotal roles in the carbon cycle, as trees absorb CO2 and provide habitats for countless species. Preserving existing forests is equally crucial, as they are vital carbon sinks. Conservation efforts, aligned with sustainable land management practices, foster resilience in ecosystems and enhance their quality of life.
Public policy must evolve to reflect the urgency of the situation. International agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, aim to unite nations in the battle against climate change. Such collaborative efforts underscore the need for collective action. However, policies must also recognize and address the socio-economic disparities that will influence a region’s adaptive capacity. Dedicated support for vulnerable populations becomes essential to ensure equitable transition pathways.
Educational initiatives can empower individuals to become informed decision-makers. Understanding the mechanics of the greenhouse effect, the implications of global warming, and the actionable steps available at the individual, community, and legislative levels can cultivate a culture of environmental mindfulness. Every small action contributes to a larger narrative of sustainability, whether it’s reducing energy consumption, advocating for change, or supporting eco-friendly practices.
The connection between the greenhouse effect and global warming is one that we must heed with urgency and resolve. As the Earth undergoes unprecedented changes, the stakes could not be higher. There lies an opportunity for innovation, collaboration, and leadership in the face of adversity. Building a sustainable future is not merely an environmental necessity, but a moral imperative for the health of our planet and the prosperity of generations to come. The intertwined fates of climate stability and biodiversity challenge us to reimagine our relationship with the environment, demanding a shared commitment to stewardship in this pivotal moment of our ecological history.