The discourse surrounding climate change has become increasingly salient in contemporary society. Global warming, a manifestation of climate change, is characterized by the long-term rise in Earth’s average surface temperature due to human activities, primarily greenhouse gas emissions. This exposition endeavors to elucidate the intricacies of this phenomenon, shedding light on its accelerating trajectory and the multifaceted implications it holds for our planet.
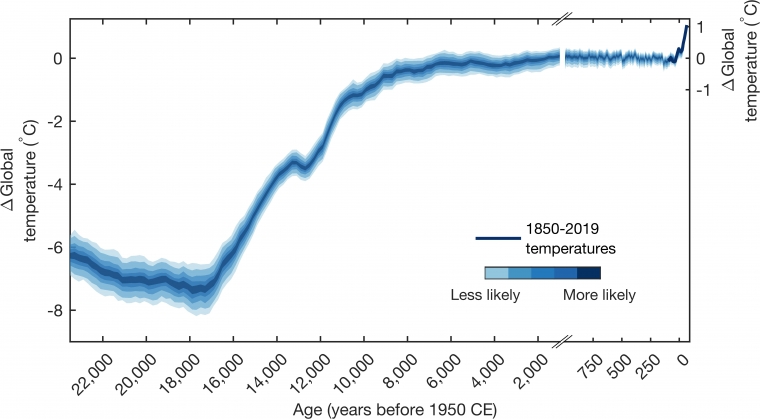
Beginning with a historical perspective, the Earth has experienced fluctuations in temperature over millennia. However, the recent trend observed over the last century signals a marked acceleration. In the depths of the last Ice Age, approximately 24,000 years ago, temperatures were significantly lower. The rise from these frigid conditions towards the current era has not been linear. Paleoclimatic data indicates that the rate of warming has exponentially increased since the onset of the Industrial Revolution in the late 18th century. The extensive use of fossil fuels and deforestation has led to a spike in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels, resulting in a greenhouse effect that ensnares heat in the atmosphere.
The period from 1880 to the present provides a stark illustration of this phenomenon. The average global temperature has increased by about 1.2 degrees Celsius since pre-industrial levels, with the last decade being the warmest on record. This rise, subtle at first glance, masks a cascade of dire consequences manifesting through extreme weather patterns, melting ice caps, and rising sea levels.
Delving deeper into the empirical data, it is essential to highlight the role of temperature anomalies in understanding global warming. Temperature anomalies are deviations from long-term average temperatures, serving as critical indicators. Recent studies illustrate that nearly all of the past decades have been warmer than the 20th-century average. Notably, each of the last four decades has been progressively warmer than the one preceding it, showcasing an alarming trend that emphasizes the need for immediate action.
One might ponder the implications of such a steady rise in global temperatures. The repercussions extend beyond mere discomfort. Ecosystems are being irrevocably altered. Biodiversity is under siege; species that once thrived within specific climatic conditions are now confronted with inhospitable environments. Coral reefs, often termed the “rainforests of the sea,” are experiencing widespread bleaching, a direct result of thermal stress coupled with ocean acidification, which further jeopardizes marine life. The loss of biodiversity compromises ecological balance, affecting food security and livelihoods across the globe.
Human health is another realm impacted by escalating temperatures. Higher temperatures correlate with a surge in heat-related illnesses, contributing to an uptick in mortality rates during heatwaves. Furthermore, the proliferation of vector-borne diseases, such as malaria and dengue fever, is exacerbated by the shifting habitats of insects and pests—species that thrive in warmer conditions. Air quality deteriorates due to increased pollutants, with countries heavily reliant on fossil fuels suffering disproportionately from respiratory ailments.
In addition to human health, economic ramifications are profound. The agricultural sector is particularly vulnerable, with crop yields fluctuating dramatically as a result of changing precipitation patterns and increased incidences of extreme weather events. Food production systems are strained, leading to disrupted supply chains and heightened prices. Developing nations, often less equipped to adapt, face existential threats due to their reliance on climate-sensitive resources.
Moreover, a pivotal aspect of the discussion on global warming is the concept of climate justice. Vulnerable communities, often marginalized economically and socially, bear the brunt of climate impacts despite contributing the least to greenhouse gas emissions. The disparity raises critical questions about equity and responsibility, emphasizing the urgency for a concerted global response to mitigate these impacts and foster resilience in the face of an ever-changing climate.
As one examines the interplay of scientific evidence and societal implications, it becomes evident that addressing global warming necessitates a multifaceted approach. Transitioning to renewable energy sources—such as wind, solar, and hydropower—is paramount to curtailing emissions. Investing in energy efficiency and promoting sustainable practices can contribute to significant reductions in our carbon footprint. Furthermore, reforestation and sustainable land management are critical in enhancing carbon sinks, thereby mitigating the effects of climate change.
Furthermore, public awareness and education are indispensable elements in combating climate change. Communities must be empowered with knowledge and resources to advocate for sustainable practices and engage in grassroots movements. Policies aimed at reducing emissions, incentivizing renewable energy adoption, and fostering climate resilience should be prioritized by governments globally. Collective action is not merely advisable; it is imperative.
In conclusion, the accelerating trend of global warming transcends mere environmental concerns, intertwining with social, economic, and ethical dimensions. Immediate and sustained action is requisite to curb its impacts and pave the way for a sustainable future. The urgency of now cannot be overstated; the fate of our planet hinges upon our response to this crisis. We must embrace our collective responsibility to protect and preserve the Earth, not only for ourselves but for future generations.