The phenomenon of global warming has transcended the realm of scientific discussion and has burgeoned into an existential crisis threatening our planet’s ecosystems, human health, and economic stability. Recently, the United States has witnessed an escalating urgency concerning this issue, emphasizing the necessity to address global warming as a matter of paramount importance. It is a crisis that demands immediate and concerted action across all sectors of society.
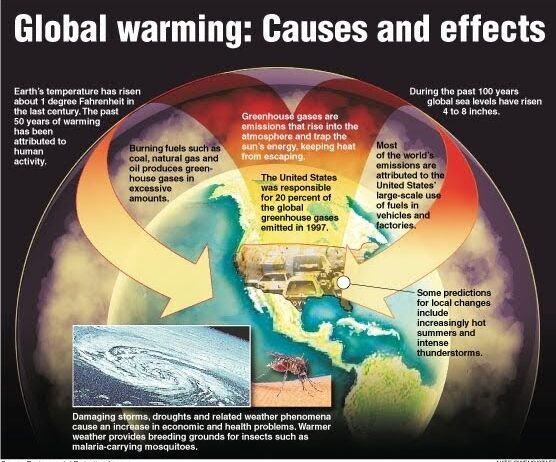
Understanding the underpinnings of global warming begins with its definition: an increase in Earth’s average surface temperature due to rising levels of greenhouse gases (GHGs), primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O). These gases trap heat in the atmosphere, resulting in a greenhouse effect that drives climate change. The consequences are far-reaching, affecting weather patterns, sea levels, and biodiversity.
Currently, the United States is facing alarming climatic manifestations, ranging from unprecedented heatwaves to severe droughts and monstrous hurricanes. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has reported an increase in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. These phenomena are not isolated instances; they are symptomatic of a broader trend meticulously documented in climate science. Global temperature increases have reached levels that are increasingly difficult to reverse, compelling policymakers and citizens alike to reevaluate their approach to environmental sustainability.
One significant aspect of this global warming crisis is its impact on biodiversity. As habitats transform due to shifting temperatures, many species find it challenging to adapt or migrate, leading to a dramatic decline in biodiversity. Ecosystems are interconnected, and the loss of a single species can have cascading effects throughout the food chain. In the United States, iconic species such as the polar bear and the bumblebee face existential threats as a result of shrinking habitats and altered ecosystems. Protecting these species is not merely an act of conservation; it is essential for maintaining ecological balance and public health.
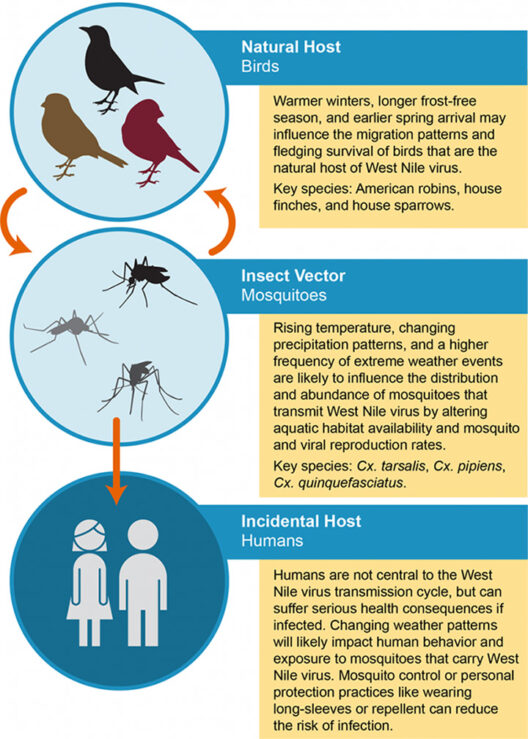
Furthermore, the implications of global warming extend to public health. The escalation of heat-related illnesses, respiratory ailments due to worsening air quality, and the proliferation of vector-borne diseases are pressing examples of how global warming impacts human health. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly and those with preexisting health conditions, are disproportionately affected. Addressing these health crises requires an integrated public health strategy that includes climate adaptation and mitigation efforts.
Turning our focus to economic repercussions, the financial toll of climate inaction is staggering. The U.S. economy is intricately tied to its natural resources, from agriculture to fisheries to tourism. Changing climate patterns disrupt agricultural yield, leading to food insecurity and increased prices for consumers. Additionally, extreme weather events lead to costly infrastructure repairs and disaster relief efforts. The financial burden of climate-related disasters in the U.S. alone runs into billions of dollars annually, a figure that is expected to swell as the impacts of climate change intensify.
Despite the daunting challenges posed by global warming, it is a crisis that offers opportunities for innovation and adaptation. The transition to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power is imperative in reducing our carbon footprint. In the U.S., there has been a marked increase in investments into clean energy technologies, driven by both environmental necessity and economic opportunity. Additionally, energy efficiency measures can help reduce emissions while promoting economic growth through job creation.
Policymaking is another crucial arena where action on global warming must take center stage. Legislative frameworks must evolve to reflect the urgency of the crisis. Emission reduction targets, carbon pricing, and incentives for sustainable practices require bipartisan support to materialize into meaningful action. The recent commitments made by states to achieve net-zero emissions by mid-century illustrate a growing recognition of the need for robust climate action. However, these initiatives must be complemented by global cooperation, as climate change knows no borders.
Community engagement and grassroots movements play a vital role in combating climate change. Local organizations are critical in fostering awareness, promoting sustainable practices, and advocating for policy reforms. Empowering individuals to make environmentally conscious choices, such as reducing waste and conserving energy, creates a ripple effect that can accelerate broader societal change. Education initiatives that spotlight the realities of climate change are necessary in cultivating an informed citizenry capable of demanding action from their leaders.
In addition, technological and scientific advancements hold promise for addressing the crisis. Innovations such as carbon capture and storage, advances in battery technology, and sustainable agricultural practices can mitigate the effects of climate change. The application of these technologies, combined with education and public policy, can accelerate the shift toward a more sustainable economy.
In conclusion, the phenomenon of global warming represents a multifaceted crisis that requires immediate action. The array of adverse effects on biodiversity, public health, and economic stability underscores the importance of addressing climate change as a collective priority. The United States stands at a crossroads: the decisions made today will reverberate for generations to come. By investing in renewable energy, fostering community engagement, and implementing informed policies, the country can forge a path towards sustainability and resilience in the face of climate change. The time for action is now, and it is imperative that we rise to this challenge with urgency and conviction.